Neuroprotective effects of polydatin against mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in the rat cerebral cortex following ischemia/reperfusion injury
- PMID: 27840959
- PMCID: PMC5355690
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5936
Neuroprotective effects of polydatin against mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in the rat cerebral cortex following ischemia/reperfusion injury
Abstract
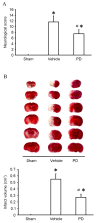
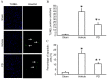
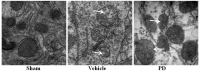
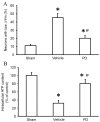
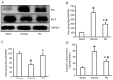
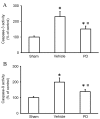
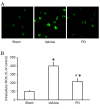
The neuroprotective effect of polydatin (PD) against hemorrhagic shock-induced mitochondrial injury has been described previously, and mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis were reportedly involved in ischemic stroke. In the present study the neuroprotective effect of PD in preventing apoptosis was evaluated following induction of focal cerebral ischemia by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) in rats. PD (30 mg/kg) was administered by caudal vein injection 10 min prior to ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. 24 h following I/R injury, ameliorated modified neurological severity scores (mNSS) and reduced infarct volume were observed in the PD treated group. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining and Annexin V/propidium iodide assays demonstrated the anti-apoptotic effect of PD in the ischemic cortex. In addition, PD improved I/R injury‑induced mitochondrial dysfunction, reflected by morphological observations and measurements of mitochondrial membrane potential and intracellular ATP measurement. Western blot analysis revealed an increase in B‑cell lymphoma 2 apoptosis regulator (Bcl-2) expression, and a decrease in Bcl‑2‑associated protein X apoptosis regulator expression in the PD group in comparison with the vehicle treated group. PD treatment also prevented the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria into the cytoplasm, and blunted the activities of caspase‑9 and caspase‑3. Furthermore, PD treatment decreased the levels of reactive oxygen species in neurons isolated from the ischemic cortex. The findings of this study, therefore, suggest that PD has a dual effect, ameliorating both oxidative stress and mitochondria‑dependent apoptosis, making it a promising new therapy for the treatment of ischemic stroke.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effects of leonurine on ischemia/reperfusion-induced mitochondrial dysfunctions in rat cerebral cortex.Biol Pharm Bull. 2010;33(12):1958-64. doi: 10.1248/bpb.33.1958. Biol Pharm Bull. 2010. PMID: 21139233
-
Acteoside Attenuates Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Apoptosis in Rats with Focal Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Biol Pharm Bull. 2018;41(11):1645-1651. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b18-00210. Biol Pharm Bull. 2018. PMID: 30381663
-
Mitochondrial calcium uniporter opener spermine attenuates the cerebral protection of diazoxide through apoptosis in rats.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2014 May-Jun;23(5):829-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2013.07.007. Epub 2013 Aug 15. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2014. PMID: 23954597
-
Neuroprotective effects of ischemic preconditioning in brain mitochondria following cerebral ischemia.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2004 Aug;36(4):323-7. doi: 10.1023/B:JOBB.0000041762.47544.ff. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2004. PMID: 15377866 Review.
-
Protection against ischemic brain injury by inhibition of mitochondrial oxidative stress.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2004 Aug;36(4):347-52. doi: 10.1023/B:JOBB.0000041766.71376.81. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2004. PMID: 15377870 Review.
Cited by
-
Narrative review of the mechanism of natural products and scar formation in wound repair.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Feb;10(4):236. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-7046. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35280378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The polyphenolic phytoalexin polydatin inhibits amyloid aggregation of recombinant human prion protein.RSC Adv. 2021 Jul 28;11(42):25901-25911. doi: 10.1039/d1ra01891d. eCollection 2021 Jul 27. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35479435 Free PMC article.
-
Polydatin inhibits mast cell-mediated allergic inflammation by targeting PI3K/Akt, MAPK, NF-κB and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 19;7(1):11895. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12252-3. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28928455 Free PMC article.
-
Arachis hypogaea resveratrol synthase 3 alters the expression pattern of UDP-glycosyltransferase genes in developing rice seeds.PLoS One. 2021 Jan 14;16(1):e0245446. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245446. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33444365 Free PMC article.
-
High-pressure carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum induces oxidative stress and mitochondria-associated apoptotic pathway in rabbit kidneys with severe hydronephrosis.Int J Mol Med. 2019 Jan;43(1):305-315. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3986. Epub 2018 Nov 8. Int J Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30431064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lin R, Lin Y, Tao J, Chen B, Yu K, Chen J, Li X, Chen LD. Electroacupuncture ameliorates learning and memory in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and promoting p-CREB expression in the hippocampus. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12:6807–6814. - PubMed
-
- Ljubisavljevic MR, Javid A, Oommen J, Parekh K, Nagelkerke N, Shehab S, Adrian TE. The Effects of different repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) protocols on cortical gene expression in a rat model of cerebral ischemic-reperfusion injury. PLoS One. 2015;10:e139892. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139892. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

