Akkermansia muciniphila mediates negative effects of IFNγ on glucose metabolism
- PMID: 27841267
- PMCID: PMC5114536
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms13329
Akkermansia muciniphila mediates negative effects of IFNγ on glucose metabolism
Abstract
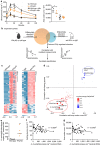
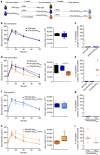
Cross-talk between the gut microbiota and the host immune system regulates host metabolism, and its dysregulation can cause metabolic disease. Here, we show that the gut microbe Akkermansia muciniphila can mediate negative effects of IFNγ on glucose tolerance. In IFNγ-deficient mice, A. muciniphila is significantly increased and restoration of IFNγ levels reduces A. muciniphila abundance. We further show that IFNγ-knockout mice whose microbiota does not contain A. muciniphila do not show improvement in glucose tolerance and adding back A. muciniphila promoted enhanced glucose tolerance. We go on to identify Irgm1 as an IFNγ-regulated gene in the mouse ileum that controls gut A. muciniphila levels. A. muciniphila is also linked to IFNγ-regulated gene expression in the intestine and glucose parameters in humans, suggesting that this trialogue between IFNγ, A. muciniphila and glucose tolerance might be an evolutionally conserved mechanism regulating metabolic health in mice and humans.
Figures



Comment in
-
Gut microbiota: Mucin-munching bacteria modulate glucose metabolism.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017 Feb;13(2):66. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2016.201. Epub 2016 Dec 2. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 27910881 No abstract available.
References
-
- Donath M. Y. & Shoelson S. E. Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 11, 98–107 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Nishimura S. et al. CD8+ effector T cells contribute to macrophage recruitment and adipose tissue inflammation in obesity. Nat. Med. 15, 914–920 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Duffaut C., Galitzky J., Lafontan M. & Bouloumie A. Unexpected trafficking of immune cells within the adipose tissue during the onset of obesity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 384, 482–485 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

