Activated Protein C Drives the Hyperfibrinolysis of Acute Traumatic Coagulopathy
- PMID: 27841821
- PMCID: PMC5257267
- DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000001428
Activated Protein C Drives the Hyperfibrinolysis of Acute Traumatic Coagulopathy
Abstract
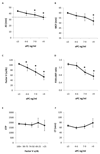
Background: Major trauma is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide with hemorrhage accounting for 40% of deaths. Acute traumatic coagulopathy exacerbates bleeding, but controversy remains over the degree to which inhibition of procoagulant pathways (anticoagulation), fibrinogen loss, and fibrinolysis drive the pathologic process. Through a combination of experimental study in a murine model of trauma hemorrhage and human observation, the authors' objective was to determine the predominant pathophysiology of acute traumatic coagulopathy.
Methods: First, a prospective cohort study of 300 trauma patients admitted to a single level 1 trauma center with blood samples collected on arrival was performed. Second, a murine model of acute traumatic coagulopathy with suppressed protein C activation via genetic mutation of thrombomodulin was used. In both studies, analysis for coagulation screen, activated protein C levels, and rotational thromboelastometry (ROTEM) was performed.
Results: In patients with acute traumatic coagulopathy, the authors have demonstrated elevated activated protein C levels with profound fibrinolytic activity and early depletion of fibrinogen. Procoagulant pathways were only minimally inhibited with preservation of capacity to generate thrombin. Compared to factors V and VIII, proteases that do not undergo activated protein C-mediated cleavage were reduced but maintained within normal levels. In transgenic mice with reduced capacity to activate protein C, both fibrinolysis and fibrinogen depletion were significantly attenuated. Other recognized drivers of coagulopathy were associated with less significant perturbations of coagulation.
Conclusions: Activated protein C-associated fibrinolysis and fibrinogenolysis, rather than inhibition of procoagulant pathways, predominate in acute traumatic coagulopathy. In combination, these findings suggest a central role for the protein C pathway in acute traumatic coagulopathy and provide new translational opportunities for management of major trauma hemorrhage.
Conflict of interest statement
of conflicts of interest The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
Acute Traumatic Coagulopathy: Thrombin Is the Driver!Anesthesiology. 2017 Sep;127(3):585. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000001760. Anesthesiology. 2017. PMID: 28816786 No abstract available.
-
In Reply.Anesthesiology. 2017 Sep;127(3):585-586. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000001761. Anesthesiology. 2017. PMID: 28816787 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bickell WH, Wall MJ, Jr, Pepe PE, Martin RR, Ginger VF, Allen MK, Mattox KL. Immediate versus delayed fluid resuscitation for hypotensive patients with penetrating torso injuries. N Engl J Med. 1994;331:1105–9. - PubMed
-
- Kauvar DS, Lefering R, Wade CE. Impact of hemorrhage on trauma outcome: an overview of epidemiology, clinical presentations, and therapeutic considerations. J Trauma. 2006;60:S3–11. - PubMed
-
- Brohi K, Singh J, Heron M, Coats T. Acute traumatic coagulopathy. J Trauma. 2003;54:1127–30. - PubMed
-
- MacLeod JB, Lynn M, McKenney MG, Cohn SM, Murtha M. Early coagulopathy predicts mortality in trauma. J Trauma. 2003;55:39–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

