Dural stimulation in rats causes brain-derived neurotrophic factor-dependent priming to subthreshold stimuli including a migraine trigger
- PMID: 27841839
- PMCID: PMC5315498
- DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000692
Dural stimulation in rats causes brain-derived neurotrophic factor-dependent priming to subthreshold stimuli including a migraine trigger
Abstract
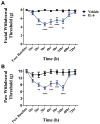
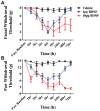
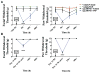
Migraine is one of the most common and most disabling disorders. Between attacks, migraine patients are otherwise normal but are sensitized to nonnoxious events known as triggers. The purpose of these studies was to investigate whether a headache-like event causes sensitization, or priming, to subsequent subthreshold events. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) was applied to the rat cranial dura mater which produced cutaneous facial and hind paw allodynia that lasted 24 hours. At 72 hours, IL-6-treated rats developed allodynia in response to dural stimulation with either a pH 6.8 or pH 7.0 solution and to a systemic nitric oxide (NO) donor, a well-known migraine trigger. Vehicle-treated rats did not respond to either pH stimulus or to the NO donor, demonstrating that IL-6 exposure primes rats to subthreshold stimuli. Inhibitors of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) signaling given either systemically or intracisternally 24 hours after IL-6 eliminated responses to dural pH stimulation at 72 hours. Additionally, intracisternal administration of BDNF without previous dural stimulation produced allodynia and once resolved, animals were primed to dural pH 6.8/pH 7.0 and a systemic NO donor. Finally, hind paw IL-6 produced paw allodynia but not priming to paw injection of pH 7.0 at 72 hours demonstrating differences in priming depending on location. These data indicate that afferent input from the meninges produces BDNF-dependent priming of the dural nociceptive system. This primed state mimics the interictal period of migraine where attacks can be triggered by normally nonnoxious events and suggests that BDNF-dependent plasticity may contribute to migraine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest
Figures






References
-
- Andress-Rothrock D, King W, Rothrock J. An analysis of migraine triggers in a clinic-based population. Headache. 2010;50(8):1366–1370. - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi A. Allodynia in cluster headache. Current pain and headache reports. 2010;14(2):140–144. - PubMed
-
- Bartsch T, Goadsby PJ. Increased responses in trigeminocervical nociceptive neurons to cervical input after stimulation of the dura mater. Brain. 2003;126(Pt 8):1801–1813. - PubMed
-
- Beggs S, Salter MW. The known knowns of microglia-neuronal signalling in neuropathic pain. Neurosci Lett. 2013;557(Pt A):37–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

