The Lutzomyia longipalpis complex: a brief natural history of aggregation-sex pheromone communication
- PMID: 27842601
- PMCID: PMC5109651
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-016-1866-x
The Lutzomyia longipalpis complex: a brief natural history of aggregation-sex pheromone communication
Abstract
In this paper we review the natural history of pheromone communication and the current diversity of aggregation-sex pheromones in the sand fly Lutzomyia longipalpis. This species complex is the main vector of Leishmania infantum, the agent of visceral leishmaniasis in the Americas. The identification of variation in pheromone chemotypes combined with molecular and sound analyses have all contributed to our understanding of the extent of divergence among cryptic members of this complex. The importance of chemical signals as pre-mating barriers and drivers of speciation is discussed. Moreover, the importance of aggregation-sex pheromones as sexually selected signals is highlighted with evidence from the literature suggesting their potential role in species and mate recognition as well as mate assessment. The distinct evolutionary forces possibly involved are briefly reviewed and discussed in the context of this intriguing insect.
Keywords: Aggregation pheromone; Evolution; Lutzomyia longipalpis; Sand flies; Sex pheromone; Species complex.
Figures
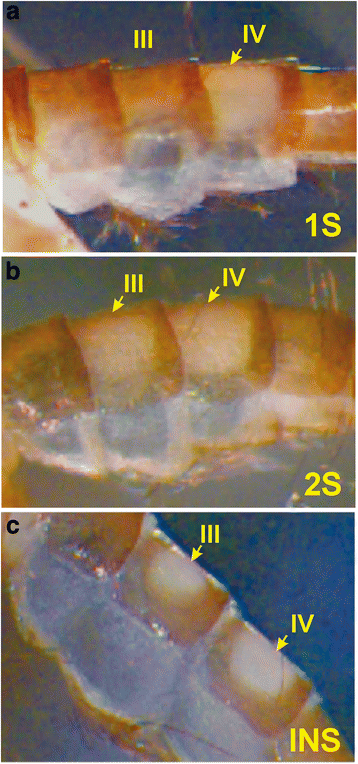

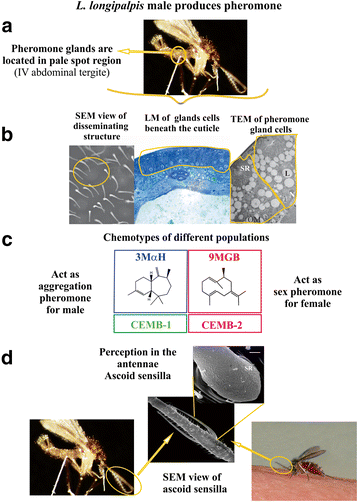
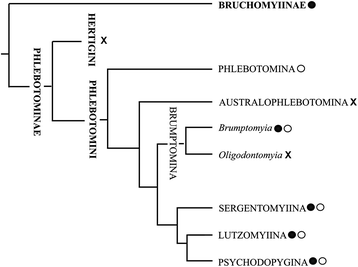
References
-
- Butenandt A, Beckman R, Stamm D, Hecker E. Uber den sexual lockstoff des seidenspinners Bombyx mori. Reindarstelling und konstitution. Z Naturforsch. 1959;14b:283–284.
-
- Karlson P, Butenandt A. Pheromones (ectohormones) in insects. Ann Rev Entomol. 1959;4:39–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.04.010159.000351. - DOI
-
- El-Sayed AM. The Pherobase: database of pheromones and semiochemicals. http://www.pherobase.com. Accessed 5 May 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

