Epidemiology and Genetic Risk Factors of Drug Hepatotoxicity
- PMID: 27842775
- PMCID: PMC8290403
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2016.08.004
Epidemiology and Genetic Risk Factors of Drug Hepatotoxicity
Abstract
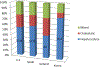
Idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury (DILI) from prescription medications and herbal and dietary supplements has an annual incidence rate of approximately 20 cases per 100,000 per year. However, the risk of DILI varies greatly according to the drug. In the United States and Europe, antimicrobials are the commonest implicated agents, with amoxicillin/clavulanate the most common, whereas in Asian countries, herbal and dietary supplements predominate. Genetic analysis of DILI is currently limited, but multiple polymorphisms of human leukocyte antigen genes and genes involved in drug metabolism and transport have been identified as risk factors for DILI.
Keywords: Drug-induced liver injury (DILI); Epidemiology; Genetics.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Zhang W, Roederer MW, Chen WQ, Fan L, Zhou HH. Pharmacogenetics of drugs withdrawn from the market. Pharmacogenomics 2012;13:223–31. - PubMed
-
- Björnsson ES, Bergmann OM, Björnsson HK, Kvaran RB, Olafsson S. Incidence, presentation, and outcomes in patients with drug-induced liver injury in the general population of Iceland. Gastroenterology 2013;144:1419–25. - PubMed
-
- Sgro C, Clinard F, Ouazir K, Chanay H, Allard C, Guilleminet C, Lenoir C, Lemoine A, Hillon P. Incidence of drug-induced hepatic injuries: a French population-based study. Hepatology 2002;36:451–5. - PubMed
-
- Suk KT, Kim DJ, Kim CH, Park SH, Yoon JH, Kim YS, Baik GH, Kim JB, Kweon YO, Kim BI, Kim SH, Kim IH, Kim JH, Nam SW, Paik YH, Suh JI, Sohn JH, Ahn BM, Um SH, Lee HJ, Cho M, Jang MK, Choi SK, Hwang SG, Sung HT, Choi JY, Han KH. A prospective nationwide study of drug-induced liver injury in Korea. Am J Gastroenterol 2012;107:1380–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

