Efficacy and safety of tiotropium + olodaterol maintenance treatment in patients with COPD in the TONADO® and OTEMTO® studies: a subgroup analysis by age
- PMID: 27843306
- PMCID: PMC5098524
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S108758
Efficacy and safety of tiotropium + olodaterol maintenance treatment in patients with COPD in the TONADO® and OTEMTO® studies: a subgroup analysis by age
Abstract
Background: Increasing age is associated with poor prognosis in patients with COPD.
Objective: This analysis from the replicate Phase III OTEMTO® and TONADO® studies examined the efficacy and safety of tiotropium, a long-acting anticholinergic, combined with olodaterol, a long-acting β2-agonist, compared to monotherapies and placebo in patients with COPD aged 40 years to <65 years, 65 years to <75 years, 75 years to <85 years, and ≥85 years.
Methods: In these double-blind, parallel-group, active-controlled, multicenter, randomized studies, patients received tiotropium + olodaterol 2.5/5 μg or 5/5 μg, tiotropium 5 μg or 2.5 μg (TONADO only), olodaterol 5 μg (TONADO only), or placebo (OTEMTO only). This analysis used the approved doses of tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 μg, tiotropium 5 μg, and olodaterol 5 μg. Primary end points at 12 weeks (OTEMTO) or 24 weeks (TONADO) included St George's Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) total score, forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) area under the curve from 0 hour to 3 hours (AUC0-3) response, and trough FEV1 response.
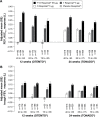
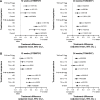
Results: A total of 1,621 patients were randomized (40 years to <65 years, n=749; 65 years to <75 years, n=674; 75 years to <85 years, n=186; ≥85 years, n=12) in OTEMTO and 5,162 patients (40 years to <65 years, n=2,654; 65 years to <75 years, n=1,967; 75 to <85 years, n=528; ≥85 years, n=13) in TONADO. FEV1 AUC0-3 and trough FEV1 responses improved with tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 μg at 12 weeks and 24 weeks compared to monotherapies or placebo for all age groups. SGRQ scores generally improved with tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 μg after 12 weeks in OTEMTO and improved after 24 weeks in all age groups in TONADO. In all age groups receiving tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 μg compared to monotherapies or placebo, transition dyspnea index scores generally improved, while rescue medication usage improved.
Conclusion: No differences were noted in relative responses to treatment or safety when using tiotropium + olodaterol 5/5 μg compared to monotherapies or placebo across all age groups.
Keywords: FEV1; SGRQ; TDI; lung function; rescue medication.
Conflict of interest statement
GTF has received consulting and advisory board fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Pearl Therapeutics, Novartis, Forest, Sunovion, and Verona, consulting fees from Receptos, speaker fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, AstraZeneca, Pearl Therapeutics, Forest, and Sunovion, and is in receipt of research grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Pearl Therapeutics, Sunovion, Novartis, Theravance, Sanofi, Forest, and GlaxoSmithKline. JPK discloses no conflicts of interest. ECB, LG, and FV are employees of Boehringer Ingelheim. RB reports grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, Roche, and the German Research Foundation. RB also reports consulting, Speaker Bureau, and advisory committee fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, GlaxoSmithKline, Grifols, Novartis, Roche, and Takeda. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of tiotropium + olodaterol versus tiotropium or placebo by COPD disease severity and previous treatment history in the OTEMTO® studies.Respir Res. 2016 Jun 18;17(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s12931-016-0387-7. Respir Res. 2016. PMID: 27316465 Free PMC article.
-
Benefits of Tiotropium/Olodaterol Compared with Tiotropium in Patients with COPD Receiving only LAMA at Baseline: Pooled Analysis of the TONADO® and OTEMTO® Studies.Adv Ther. 2020 Aug;37(8):3485-3499. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01373-3. Epub 2020 May 27. Adv Ther. 2020. PMID: 32462607 Free PMC article.
-
Lung function and long-term safety of tiotropium/olodaterol in East Asian patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2017 Nov 20;12:3329-3339. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S137719. eCollection 2017. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2017. PMID: 29200840 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of tiotropium-olodaterol fixed-dose combination in COPD.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016 Dec 13;11:3163-3177. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S92840. eCollection 2016. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016. PMID: 28008243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined bronchodilators (tiotropium plus olodaterol) for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015 Oct 30;10:2347-56. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S88246. eCollection 2015. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015. PMID: 26586940 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Once daily long-acting beta2-agonists and long-acting muscarinic antagonists in a combined inhaler versus placebo for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Mar 6;3(3):CD012930. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012930.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30839102 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of a novel, nebulized glycopyrrolate for the treatment of COPD: effect of baseline disease severity and age; pooled analysis of GOLDEN 3 and GOLDEN 4.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018 Dec 18;14:27-37. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S184808. eCollection 2019. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018. PMID: 30587959 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Success in Swiss COPD Patients Receiving Dual Bronchodilation Therapy as COPD Maintenance Treatment.Clin Pract. 2022 Jan 7;12(1):46-56. doi: 10.3390/clinpract12010006. Clin Pract. 2022. PMID: 35076494 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term safety of tiotropium/olodaterol Respimat® in patients with moderate-to-very severe COPD and renal impairment in the TONADO® studies.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018 Jun 1;13:1819-1831. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S161489. eCollection 2018. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018. PMID: 29910611 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of tiotropium/olodaterol on sedentary and active time in patients with COPD: post hoc analysis of the VESUTO® study.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019 Aug 7;14:1789-1801. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S208081. eCollection 2019. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019. PMID: 31496678 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease [homepage on the Internet] Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Updated 2016. [Accessed April 27, 2016]. Available from: http://www.goldcopd.org/
-
- Feenstra TL, van Genugten MLL, Hoogenveen RT, Wouters EF, Rutten-van Mölken MPH. The impact of aging and smoking on the future burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a model analysis in the Netherlands. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164(4):590–596. - PubMed
-
- Barnes PJ, Celli BR. Systemic manifestations and comorbidities of COPD. Eur Respir J. 2009;33(5):1165–1185. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

