A machine learning approach to identify functional biomarkers in human prefrontal cortex for individuals with traumatic brain injury using functional near-infrared spectroscopy
- PMID: 27843695
- PMCID: PMC5102640
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.541
A machine learning approach to identify functional biomarkers in human prefrontal cortex for individuals with traumatic brain injury using functional near-infrared spectroscopy
Abstract
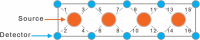
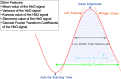
Background: We have explored the potential prefrontal hemodynamic biomarkers to characterize subjects with Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) by employing the multivariate machine learning approach and introducing a novel task-related hemodynamic response detection followed by a heuristic search for optimum set of hemodynamic features. To achieve this goal, the hemodynamic response from a group of 31 healthy controls and 30 chronic TBI subjects were recorded as they performed a complexity task.
Methods: To determine the optimum hemodynamic features, we considered 11 features and their combinations in characterizing TBI subjects. We investigated the significance of the features by utilizing a machine learning classification algorithm to score all the possible combinations of features according to their predictive power.
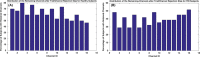
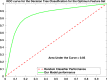
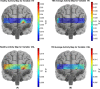
Results and conclusions: The identified optimum feature elements resulted in classification accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of 85%, 85%, and 84%, respectively. Classification improvement was achieved for TBI subject classification through feature combination. It signified the major advantage of the multivariate analysis over the commonly used univariate analysis suggesting that the features that are individually irrelevant in characterizing the data may become relevant when used in combination. We also conducted a spatio-temporal classification to identify regions within the prefrontal cortex (PFC) that contribute in distinguishing between TBI and healthy subjects. As expected, Brodmann areas (BA) 10 within the PFC were isolated as the region that healthy subjects (unlike subjects with TBI), showed major hemodynamic activity in response to the High Complexity task. Overall, our results indicate that identified temporal and spatio-temporal features from PFC's hemodynamic activity are promising biomarkers in classifying subjects with TBI.
Keywords: classification; feature selection; machine learning; near‐infrared spectroscopy; time series feature extraction; traumatic brain injury; wrapper method.
Figures
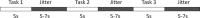
References
-
- Ahmadlou, M. , Adeli, H. , & Adeli, A. (2010). New diagnostic EEG markers of the Alzheimer's disease using visibility graph. Journal of Neural Transmission, 117, 1099–1109. - PubMed
-
- Bhambhani, Y. , Maikala, R. , Farag, M. , & Rowland, G. (2006). Reliability of near‐infrared spectroscopy measures of cerebral oxygenation and blood volume during handgrip exercise in nondisabled and traumatic brain‐injured subjects. Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development, 43, 845. - PubMed
-
- Bishop, C. M. (2006) Pattern recognition and machine learning. New York, NY: Springer‐Verlag.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

