A Case of Complete Abscopal Response in High-Grade Pleiomorphic Sarcoma Treated with Radiotherapy Alone
- PMID: 27843739
- PMCID: PMC5101400
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.821
A Case of Complete Abscopal Response in High-Grade Pleiomorphic Sarcoma Treated with Radiotherapy Alone
Abstract
Background: "Abscopal response" refers to the spontaneous involution of untreated metastatic disease following local primary tumor-directed therapy. We report a case of an abscopal response of untreated lung metastasis in a man with pleomorphic sarcoma of the head and neck treated with hypofractionated radiotherapy.
Methods: An inoperable pleomorphic sarcoma of the postauricular soft tissue was treated with 40 Gy of radiation in eight fractions. Untreated disease in the lungs was followed with CT scans.
Results: At the two-month post-treatment follow-up, clinical exam and restaging CT demonstrated complete primary tumor involution. Additionally, CT chest images showed a dramatic disease response in the untreated pulmonary disease, which progressed to complete and persistent clinical response at one-year post-treatment follow-up.
Conclusions: We report the first described case of a complete abscopal resolution of untreated lung metastases in a patient with a primary pleomorphic sarcoma of the head and neck treated with hypofractionated radiotherapy.
Keywords: abscopal; head and neck cancer; radiotherapy; sarcoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

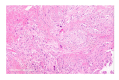


References
-
- Whole body irradiation; radiobiology or medicine? Mole RH. Br J Radiol. 1953;26:234–241. - PubMed
-
- Local radiotherapy and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor to generate abscopal responses in patients with metastatic solid tumours: a proof-of-principle trial. Golden EB, Chhabra A, Chachoua A, Adams S, Donach M, Fenton-Kerimian M, Friedman K, Ponzo F, Babb JS, Goldberg J, Demaria S, Formenti SC. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:795–803. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
