GSTF1 Gene Expression Analysis in Cultivated Wheat Plants under Salinity and ABA Treatments
- PMID: 27843973
- PMCID: PMC5019217
GSTF1 Gene Expression Analysis in Cultivated Wheat Plants under Salinity and ABA Treatments
Abstract
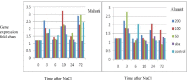
Most plants encounter stress such as drought and salinity that adversely affect growth, development and crop productivity. The expression of the gene glutathione-s-transferases (GST) extends throughout various protective mechanisms in plants and allows them to adapt to unfavorable environmental conditions. GSTF1 (the first phi GSTFs class) gene expression patterns in the wheat cultivars Mahuti and Alamut were studied under salt and ABA treatments using a qRT-PCR technique. Results showed that gene expression patterns were significantly different in these two cultivars. Data showed that in Mahuti, there was an increase of transcript accumulation under salt and ABA treatments at 3h, 10h and 72h respectively. In Alamut, however, the pattern of transcript accumulation was different; the maximum was at 3h. In contrast, there were no significant differences observed between the cultivars for GSTF1 gene expression profiles at three levels of NaCl concentration (50, 100, and 200 mM) or in ABA (Abscisic Acid) treatment. It is likely that difference of gene expression patterns between the cultivars (Mahuti as a salt tolerant cultivar and Alamut as a salt sensitive cultivar) is due to distinct signaling pathways which activate GSTF1 expression. Lack of a significant difference between the GSTF1 gene expression profile under salt and ABA treatments suggests that the GSTF1 gene is not induced by stress stimuli. Of course it is possible that other levels of NaCl and ABA treatments cause a change in the GSTF1 gene.
Keywords: ABA; GSTF1; qRT-PCR; salinity; wheat.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Up-regulation of plasma membrane H+-ATPase under salt stress may enable Aeluropus littoralis to cope with stress.Mol Biol Res Commun. 2014 Mar;3(1):67-75. Mol Biol Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 27843977 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative expression analysis of TaSOS1 and TaSOS4 genes in cultivated and wild wheat plants under salt stress.Mol Biotechnol. 2013 Feb;53(2):189-97. doi: 10.1007/s12033-012-9513-z. Mol Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 22367644
-
Interplay between GST and nitric oxide in the early response of soybean (Glycine max L.) plants to salinity stress.J Plant Physiol. 2014 Nov 15;171(18):1740-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2014.07.026. Epub 2014 Sep 6. J Plant Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25238654
-
A putative pyruvate transporter TaBASS2 positively regulates salinity tolerance in wheat via modulation of ABI4 expression.BMC Plant Biol. 2016 May 10;16(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s12870-016-0795-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2016. PMID: 27160076 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Factors Interact with ABA through Gene Expression and Signaling Pathways to Mitigate Drought and Salinity Stress.Biomolecules. 2021 Aug 5;11(8):1159. doi: 10.3390/biom11081159. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34439825 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zamani Babgohari M, Niazi A, Moghadam AA, Deihimi T, Ebrahimie E. Genome-wide analysis of key salinity-tolerance transporter (HKT1;5) in wheat and wild wheat relatives (A and D genomes) In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant. 2013;49:97–106.
-
- Boyer JS. Plant Productivity and Environment. Science. 1982;218:443–448. - PubMed
-
- Wang WX, Vinocur B, Altman A. Plant responses to drought, salinity and extreme temperatures: towards genetic engineering for stress tolerance. Planta. 2003;218:1–14. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials