Videolaryngoscopy versus direct laryngoscopy for adult patients requiring tracheal intubation
- PMID: 27844477
- PMCID: PMC6472630
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011136.pub2
Videolaryngoscopy versus direct laryngoscopy for adult patients requiring tracheal intubation
Update in
-
Videolaryngoscopy versus direct laryngoscopy for adults undergoing tracheal intubation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Apr 4;4(4):CD011136. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011136.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35373840 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Successful tracheal intubation during general anaesthesia traditionally requires a line of sight to the larynx attained by positioning the head and neck and using a laryngoscope to retract the tongue and soft tissues of the floor of the mouth. Difficulties with intubation commonly arise, and alternative laryngoscopes that use digital and/or fibreoptic technology have been designed to improve visibility when airway difficulty is predicted or encountered. Among these devices, a rigid videolaryngoscope (VLS) uses a blade to retract the soft tissues and transmits a lighted video image to a screen.
Objectives: Our primary objective was to assess whether use of videolaryngoscopy for tracheal intubation in adults requiring general anaesthesia reduces risks of complications and failure compared with direct laryngoscopy. Our secondary aim was to assess the benefits and risks of these devices in selected population groups, such as adults with obesity and those with a known or predicted difficult airway.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE and Embase on 10 February 2015. Our search terms were relevant to the review question and were not limited by outcomes. We carried out clinical trials register searches and forward and backward citation tracking. We reran the search on 12 January 2016; we added potential new studies of interest from the 2016 search to a list of 'Studies awaiting classification', and we will incorporate these studies into the formal review during the review update.
Selection criteria: We considered all randomized controlled trials and quasi-randomized studies with adult patients undergoing laryngoscopy performed with a VLS or a Macintosh laryngoscope in a clinical, emergency or out-of-hospital setting. We included parallel and cross-over study designs.
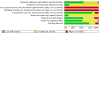
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed trial quality and extracted data, consulting a third review author to resolve disagreements. We used standard Cochrane methodological procedures, including assessment of risk of bias.
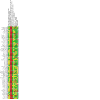
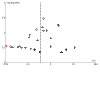
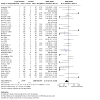
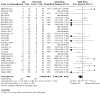
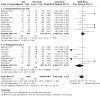
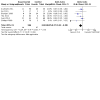
Main results: We included 64 studies identified during the 2015 search that enrolled 7044 adult participants and compared a VLS of one or more designs with a Macintosh laryngoscope. We identified 38 studies awaiting classification and seven ongoing studies. Of the 64 included studies, 61 included elective surgical patients, and three were conducted in an emergency setting. Among 48 studies that included participants without a predicted difficult airway, 15 used techniques to simulate a difficult airway. Seven recruited participants with a known or predicted difficult airway, and the remaining studies did not specify or included both predicted and not predicted difficult airways. Only two studies specifically recruited obese participants. It was not possible to blind the intubator to the device, and we noted a high level of inevitable heterogeneity, given the large number of studies.Statistically significantly fewer failed intubations were reported when a VLS was used (Mantel-Haenszel (M-H) odds ratio (OR), random-effects 0.35, 95% confidence Interval (CI) 0.19 to 0.65; 38 studies; 4127 participants), and fewer failed intubations occurred when a VLS was used in participants with an anticipated difficult airway (M-H OR, random-effects 0.28, 95% CI 0.15 to 0.55; six studies; 830 participants). We graded the quality of this evidence as moderate on the basis of the GRADE system. Failed intubations were fewer when a VLS was used in participants with a simulated difficult airway (M-H OR, random-effects 0.18, 95% CI 0.04 to 0.77; nine studies; 810 participants), but groups with no predicted difficult airway provided no significant results (M-H OR, random-effects 0.61, 95% CI 0.22 to 1.67; 19 studies; 1743 participants).Eight studies reported on hypoxia, and only three of these described any events; results showed no differences between devices for this outcome (M-H OR, random-effects 0.39, 95% CI 0.10 to 1.44; 1319 participants). Similarly, few studies reported on mortality, noting no differences between devices (M-H OR, fixed-effect 1.09, 95% CI 0.65 to 1.82; two studies; 663 participants), and only one study reporting on the occurrence of respiratory complications (78 participants); we graded these three outcomes as very low quality owing to lack of data. We found no statistically significant differences between devices in the proportion of successful first attempts (M-H OR, random-effects 1.27, 95% CI 0.77 to 2.09; 36 studies; 4731 participants) nor in those needing more than one attempt. We graded the quality of this evidence as moderate. Studies reported no statistically significant differences in the incidence of sore throat in the postanaesthesia care unit (PACU) (M-H OR, random-effects 1.00 (95% CI 0.73 to 1.38); 10 studies; 1548 participants) nor at 24 hours postoperatively (M-H OR random-effects 0.54, 95% CI 0.27 to 1.07; eight studies; 844 participants); we graded the quality of this evidence as moderate. Data combined to include studies of cross-over design revealed statistically significantly fewer laryngeal or airway traumas (M-H OR, random-effects 0.68, 95% CI 0.48 to 0.96; 29 studies; 3110 participants) and fewer incidences of postoperative hoarseness (M-H OR, fixed-effect 0.57, 95% CI 0.36 to 0.88; six studies; 527 participants) when a VLS was used. A greater number of laryngoscopies performed with a VLS achieved a view of most of the glottis (M-H OR, random-effects 6.77, 95% CI 4.17 to 10.98; 22 studies; 2240 participants), fewer laryngoscopies performed with a VLS achieved no view of the glottis (M-H OR, random-effects 0.18, 95% CI 0.13 to 0.27; 22 studies; 2240 participants) and the VLS was easier to use (M-H OR, random-effects 7.13, 95% CI 3.12 to 16.31; seven studies; 568 participants).Although a large number of studies reported time required for tracheal intubation (55 studies; 6249 participants), we did not present an effects estimate for this outcome owing to the extremely high level of statistical heterogeneity (I2 = 96%).
Authors' conclusions: Videolaryngoscopes may reduce the number of failed intubations, particularly among patients presenting with a difficult airway. They improve the glottic view and may reduce laryngeal/airway trauma. Currently, no evidence indicates that use of a VLS reduces the number of intubation attempts or the incidence of hypoxia or respiratory complications, and no evidence indicates that use of a VLS affects time required for intubation.
Conflict of interest statement
Sharon R Lewis: see Sources of support.
Andrew R Butler: see Sources of support.
Joshua Parker: none known.
Tim M Cook was paid for lecturing, several years ago (> 36 months), by Intavent Orthofix and the LMA Company. This company manufactures and distributes several supraglottic airway devices and one videolaryngoscope: AP Venner. Dr Cook's department has received free or at cost airway equipment from numerous 'airway' companies for evaluation or research. He and his family have no financial investments and no ownership of any such company of which he is aware. Dr Cook has reported no other conflicts of interest. He spoke at a Storz educational meeting in 2015, and the company paid the costs of travel to this meeting and accommodations. He received no financial benefit from the meeting and was not paid to speak.
Andrew Bulter: See Sources of support.
Andrew F Smith: See Sources of support.
Figures







References
References to studies included in this review
Abdallah 2011 {published data only}
-
- Abdallah R, Galway U, You J, Kurz A, Sessler DI, Doyle DJ.A randomized comparison between the Pentax AWS video laryngoscope and the Macintosh laryngoscope in morbidly obese patients. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2011;113(5):1082-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Ahmad 2013 {published data only}
Andersen 2011 {published data only}
-
- Andersen LH, Rovsing L, Olsen K.GlideScope videolaryngoscope vs. Macintosh direct laryngoscope for intubation of morbidly obese patients: a randomized trial. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 2011;55(9):1090-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Aoi 2010 {published data only}
-
- Aoi Y, Inagawa G, Nakamura K, Sato H, Kariya T, Goto T.Airway scope versus Macintosh laryngoscope in patients with simulated limitation of neck movements. Journal of Trauma-Injury Infection and Critical Care 2010;69(4):838-42. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Arici 2014 {published data only}
-
- Arici S, Karaman S, Dogru S, Karaman T, Tapar H, Ozsoy AZ, et al.The McGrath Series 5 video laryngoscope versus the Macintosh laryngoscope: a randomized trial in obstetric patients. Turkish Journal of Medical Sciences 2014;44(3):387-92. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Arima 2014 {published data only}
-
- Arima T, Nagata O, Miura T, Ikeda K, Mizushima T, Takahashi A.Comparative analysis of airway scope and Macintosh laryngoscope for intubation primarily for cardiac arrest in prehospital setting. American Journal of Emergency Medicine 2014;32(1):40-3. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Aziz 2012 {published data only}
-
- Aziz MF, Dillman D, Fu R, Ansgar MB.Comparative effectiveness of the C-MAC video laryngoscope versus direct laryngoscopy in the setting of the predicted difficult airway. Anesthesiology 2012;116(3):629-36. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Bensghir 2010 {published data only}
-
- Bensghir M, Alaoui H, Azendour H, Drissi M, Elwali A, Meziane M, et al.[Faster double-lumen tube intubation with the videolaryngoscope than with a standard laryngoscope]. Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia 2010;57(11):980-4. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Bensghir 2013 {published data only}
-
- Bensghir M, Chouikh C, Bouhabba N, Fjjouji S, Kasouati J, Azendour H.Comparison between the Airtraq, X-Lite, and direct laryngoscopes for thyroid surgery: a randomized clinical trial. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia-Journal Canadien D Anesthesie 2013;60(4):377-84. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Bilehjani 2009 {published data only}
-
- Bilehjani E, Fakhari S.Hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy in ischemic heart disease: Macintosh blade versus GlideScope videolaryngoscope. Rawal Medical Journal 2009;34(2):151-4.
Carassiti 2013 {published data only}
-
- Carassiti M, Biselli V, Cecchini S, Zanzonico R, Schena E, Silvestri S.Force and pressure distribution using Macintosh and GlideScope laryngoscopes in normal airway: an in vivo study. Minerva Anestesiologica 2013;79(5):515-24. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Cavus 2011 {published data only}
Choi 2011 {published data only}
Cordovani 2013 {published data only}
-
- Cordovani D, Russell T, Wee W, Suen A, Katznelson R, Cooper R.Measurement of forces applied using a Macintosh direct laryngoscope compared with the GlideScope video laryngoscope in patients with at least one difficult intubation risk. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia 2013;25(3):250-1.
Dashti 2014 {published data only}
Enomoto 2008 {published data only}
-
- Enomoto Y, Asai T, Arai T, Kamishima K, Okuda Y.Pentax-AWS, a new videolaryngoscope, is more effective than the Macintosh laryngoscope for tracheal intubation in patients with restricted neck movements: a randomized comparative study. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2008;100(4):544-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Frohlich 2011 {published data only}
-
- Frohlich S, Borovickova L, Foley E, O'Sullivan E.A comparison of tracheal intubation using the McGrath or the Macintosh laryngoscopes in routine airway management. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2011;28(6):465-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Griesdale 2012 {published data only}
-
- Griesdale DE, Chau A, Isac G, Ayas N, Foster D, Irwin C, et al.Video-laryngoscopy versus direct laryngoscopy in critically ill patients: a pilot randomized trial. Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia = Journal Canadien d'Anesthésie 2012;59(11):1032-9. - PubMed
Gupta 2013 {published data only}
-
- Gupta N, Rath GP, Prabhakar H.Clinical evaluation of C-MAC videolaryngoscope with or without use of stylet for endotracheal intubation in patients with cervical spine immobilization. Journal of Anesthesia 2013;27(5):663-70. - PubMed
Hindman 2014 {published data only}
Hirabayashi 2007a {published data only}
Hirabayashi 2009 {published data only}
-
- Hirabayashi Y, Seo N.Tracheal intubation by non-anesthesia residents using the Pentax-AWS airway scope and Macintosh laryngoscope. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia 2009;21(4):268-71. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Hsu 2012 {published data only}
-
- Hsu HT, Chou SH, Wu PJ, Tseng KY, Kuo YW, Chou CY, et al.Comparison of the GlideScope videolaryngoscope and the Macintosh laryngoscope for double-lumen tube intubation. Anaesthesia 2012;67(4):411-5. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Ilyas 2014 {published data only}
-
- Ilyas S, Symons J, Bradley WP, Segal R, Taylor H, Lee K, et al.A prospective randomised controlled trial comparing tracheal intubation plus manual in-line stabilisation of the cervical spine using the Macintosh laryngoscope vs the McGrath((R)) Series 5 videolaryngoscope. Anaesthesia 2014;69(12):1345-50. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Ithnin 2009 {published data only}
-
- Ithnin F, Lim Y, Shah M, Shen L, Sia AT.Tracheal intubating conditions using propofol and remifentanil target-controlled infusion: a comparison of remifentanil EC50 for Glidescope and Macintosh. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2009;26(3):223-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Jungbauer 2009 {published data only}
-
- Jungbauer A, Schumann M, Brunkhorst V, Borgers A, Groeben H.Expected difficult tracheal intubation: a prospective comparison of direct laryngoscopy and video laryngoscopy in 200 patients. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2009;102(4):546-50. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Kanchi 2011 {published data only}
Kill 2013 {published data only}
-
- Kill C, Risse J, Wallot P, Seidl P, Steinfeldt T, Wulf H.Videolaryngoscopy with glidescope reduces cervical spine movement in patients with unsecured cervical spine. Journal of Emergency Medicine 2013;44(4):750-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Kim 2013 {published data only}
-
- Kim MK, Park SW, Lee JW.Randomized comparison of the Pentax AirWay Scope and Macintosh laryngoscope for tracheal intubation in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2013;111(4):662-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Komatsu 2010 {published data only}
-
- Komatsu R, Kamata K, Sessler DI, Ozaki M.Airway scope and Macintosh laryngoscope for tracheal intubation in patients lying on the ground. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2010;111(2):427-31. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Lee 2009 {published data only}
-
- Lee RA, Van Zundert AAJ, Maassen RLJG, Willems RJ, Beeke LP, Schaaper JN, et al.Forces applied to the maxillary incisors during video-assisted intubation. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2009;108(1):187-91. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Lee 2012 {published data only}
-
- Lee RA, Zundert AAJ, Maassen RLJG, Wieringa PA.Forces applied to the maxillary incisors by video laryngoscopes and the Macintosh laryngoscope. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 2012;56(2):224-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Lee 2013 {published data only}
Lim 2005 {published data only}
-
- Lim Y, Yeo SW.Comparison of the GlideScope (R) with the Macintosh laryngoscope for tracheal intubation in patients with simulated difficult airway. Anaesthesia and Intensive Care 2005;33(2):243-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Lin 2012 {published data only}
-
- Lin W, Li H, Liu W, Cao L, Tan H, Zhong Z.A randomised trial comparing the CEL-100 videolaryngoscope(TM) with the Macintosh laryngoscope blade for insertion of double-lumen tubes. Anaesthesia 2012;67(7):771-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Maassen 2012 {published data only}
-
- Maassen R, Pieters BMA, Maathuis B, Serroyen J, Marcus MAE, Wouters P, et al.Endotracheal intubation using videolaryngoscopy causes less cardiovascular response compared to classic direct laryngoscopy, in cardiac patients according a standard hospital protocol. Acta Anaesthesiologica Belgica 2012;63(4):181-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Malik 2008 {published data only}
-
- Malik MA, Maharaj CH, Harte BH, Laffey JG.Comparison of Macintosh, Truview EVO2, Glidescope, and Airwayscope laryngoscope use in patients with cervical spine immobilization. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2008;101(5):723-30. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Malik 2009a {published data only}
-
- Malik MA, Subramaniam R, Churasia S, Maharaj CH, Harte BH, Laffey JG.Tracheal intubation in patients with cervical spine immobilization: a comparison of the Airwayscope, LMA CTrach, and the Macintosh laryngoscopes. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2009;102(5):654-61. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Malik 2009b {published data only}
-
- Malik MA, Subramaniam R, Maharaj CH, Harte BH, Laffey JG.Randomized controlled trial of the Pentax AWS, Glidescope, and Macintosh laryngoscopes in predicted difficult intubation. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2009;103(5):761-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Maruyama 2008a {published data only}
-
- Maruyama K, Yamada T, Kawakami R, Hara K.Randomized cross-over comparison of cervical-spine motion with the AirWay Scope or Macintosh laryngoscope with in-line stabilization: a video-fluoroscopic study. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2008;101(4):563-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Maruyama 2008b {published data only}
-
- Maruyama K, Yamada T, Kawakami R, Kamata T, Yokochi M, Hara K.Upper cervical spine movement during intubation: fluoroscopic comparison of the AirWay Scope, McCoy laryngoscope, and Macintosh laryngoscope. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2008;100(1):120-4. [PMID: ] - PubMed
McElwain 2011 {published data only}
-
- McElwain J, Laffey JG.Comparison of the C-MAC, Airtraq, and Macintosh laryngoscopes in patients undergoing tracheal intubation with cervical spine immobilization. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2011;107(2):258-64. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Najafi 2014 {published data only}
Nishikawa 2009 {published data only}
-
- Nishikawa K, Matsuoka H, Saito S.Tracheal intubation with the PENTAX-AWS (airway scope) reduces changes of hemodynamic responses and bispectral index scores compared with the Macintosh laryngoscope. Journal of Neurosurgical Anesthesiology 2009;21(4):292-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Peck 2009 {published data only}
-
- Peck MJ, Novikova O, Hung O, Launcelott S, Law JA, Macquarrie K, et al.Laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation using the McGrath laryngoscope in patients with cervical spine in-line immobilization. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia 2009;56:S85.
Pournajafian 2014 {published data only}
-
- Pournajafian AR, Ghodraty MR, Faiz SH, Rahimzadeh P, Goodarzynejad H, Dogmehchi E.Comparing GlideScope video laryngoscope and Macintosh laryngoscope regarding hemodynamic responses during orotracheal intubation: a randomized controlled trial. Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal 2014;16(4):e12334. [PMID: ] - PMC - PubMed
Robitaille 2008 {published data only}
-
- Robitaille A, Williams SR, Tremblay MH, Guilbert F, Theriault M, Drolet P.Cervical spine motion during tracheal intubation with manual in-line stabilization: direct laryngoscopy versus GlideScope videolaryngoscopy. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2008;106(3):935-41. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Russell 2012 {published data only}
-
- Russell T, Khan S, Elman J, Katznelson R, Cooper RM.Measurement of forces applied during Macintosh direct laryngoscopy compared with GlideScope videolaryngoscopy. Anaesthesia 2012;67(6):626-31. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Russell 2013 {published data only}
-
- Russell T, Slinger P, Roscoe A, McRae K, Rensburg A.A randomised controlled trial comparing the GlideScope and the Macintosh laryngoscope for double-lumen endobronchial intubation. Anaesthesia 2013;68(12):1253-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Sandhu 2014 {published data only}
-
- Sandhu H, Gombar S, Kapoor D.A comparative evaluation of glide scope and macintosh laryngoscope for endotracheal intubation. In: Indian Journal of Critical Care Medicine. Vol. 18. 2014:S9. [71398576]
Serocki 2010 {published data only}
-
- Serocki G, Bein B, Scholz J, Dorges V.Management of the predicted difficult airway: a comparison of conventional blade laryngoscopy with video-assisted blade laryngoscopy and the GlideScope. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2010;27(1):24-30. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Serocki 2013 {published data only}
-
- Serocki G, Neumann T, Scharf E, Dorges V, Cavus E.Indirect videolaryngoscopy with C-MAC D-Blade and GlideScope: a randomized, controlled comparison in patients with suspected difficult airways. Minerva Anestesiologica 2013;79(2):121-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Shippey 2013 {published data only}
-
- Shippey B, McGuire B, Dalton A.A comparison of the McGrath videolaryngoscope and the Macintosh laryngoscope in patients with cervical spine immobilisation. Anaesthesia 2013;68(8):883. - PubMed
Siddiqui 2009 {published data only}
-
- Siddiqui N, Katznelson R, Friedman Z.Heart rate/blood pressure response and airway morbidity following tracheal intubation with direct laryngoscopy, GlideScope and Trachlight: a randomized control trial. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2009;26(9):740-5. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Sun 2005 {published data only}
-
- Sun DA, Warriner CB, Parsons DG, Klein R, Umedaly HS, Moult M.The GlideScope Video Laryngoscope: randomized clinical trial in 200 patients. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2005;94(3):381-4. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Suzuki 2008 {published data only}
-
- Suzuki A, Toyama Y, Katsumi N, Kunisawa T, Henderson JJ, Iwasaki H.Cardiovascular responses to tracheal intubation with the Airway Scope (Pentax-AWS). Journal of Anesthesia 2008;22(1):100-1. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Takenaka 2011 {published data only}
-
- Takenaka I, Aoyama K, Iwagaki T, Kadoya T.Efficacy of the Airway Scope on tracheal intubation in the lateral position: comparison with the Macintosh laryngoscope. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2011;28(3):164-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Taylor 2013 {published data only}
-
- Taylor AM, Peck M, Launcelott S, Hung OR, Law JA, MacQuarrie K, et al.The McGrath (R) Series 5 videolaryngoscope vs the Macintosh laryngoscope: a randomised, controlled trial in patients with a simulated difficult airway. Anaesthesia 2013;68(2):142-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Teoh 2010 {published data only}
-
- Teoh WH, Saxena S, Shah MK, Sia AT.Comparison of three videolaryngoscopes: Pentax Airway Scope, C-MAC, GlideScope vs the Macintosh laryngoscope for tracheal intubation. Anaesthesia 2010;65(11):1126-32. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Turkstra 2005 {published data only}
-
- Turkstra 2005b.Erratum: Turkstra TP, Craen RA, Pelz DM, Gelb AW. Cervical spine motion: a fluoroscopic comparison during intubation with lighted stylet, GlideScope, and Macintosh laryngoscope. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2005;101(3):910-5. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2005;101(4):1011. - PubMed
-
- Turkstra TP, Craen RA, Pelz DM, Gelb AW.Cervical spine motion: a fluoroscopic comparison during intubation with lighted stylet, GlideScope, and Macintosh laryngoscope. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2005;101(3):910-5. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Walker 2009 {published data only}
-
- Walker L, Brampton W, Halai M, Hoy C, Lee E, Scott I, et al.Randomized controlled trial of intubation with the McGrath Series 5 videolaryngoscope by inexperienced anaesthetists. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2009;103(3):440-5. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Woo 2012 {published data only}
Xue 2007 {published data only}
-
- Xue Fu S, Zhang Guo H, Li Xuan Y, Sun Hai T, Li Ping, Li Cheng W, et al.Comparison of hemodynamic responses to orotracheal intubation with the GlideScope videolaryngoscope and the Macintosh direct laryngoscope. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia 2007;19(4):245-50. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Yeatts 2013 {published data only}
-
- Hemerka J.Effect of video laryngoscopy on trauma patient survival: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Emergency Medicine 2014;46(3):448.
-
- Yeatts DJ, Dutton RP, Hu PF, Chang YWW, Brown CH, Chen H, et al.Effect of video laryngoscopy on trauma patient survival: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery 2013;75(2):212-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
AhamdanechIdrissi 2011 {published data only}
-
- Ahamdanech Idrissi A, Paya Martinez E, Ribera C, Sanchez Garcia E, Perez Carbonell A, Company Teuler R.Intubation with Airtraq and bronchial blocker compared with conventional intubation with double-lumen tube in thoracic surgery: impact on the hemodynamic response. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2011;28:236.
Ali 2012 {published data only}
-
- Ali QE, Amir SH, Siddiqui OA, Mahopatra PS.A comparative evaluation of conventional Macintosh laryngoscope and the Airtraq in different intubation scenarios. Sri Lankan Journal of Anaesthesiology 2012;20(1):3-6.
Ali 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ali QE, Amir SH, Firdaus U, Siddiqui OA, Azhar AZ.A comparative study of the efficacy of Pediatric Airtraq with conventional laryngoscope in children. Minerva Anestesiologica 2013;79(12):1366-70. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Amor 2013 {published data only}
-
- Amor M, Nabil S, Bensghir M, Moussaoui A, Kabbaj S, Kamili ND, et al.[A comparison of Airtraq laryngoscope and standard direct laryngoscopy in adult patients with immobilized cervical spine]. Annales Francaises d Anesthesie et de Reanimation 2013;32(5):296-301. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Araki 2002 {published data only}
-
- Araki K, Nomura R, Tsuchiya N, Yoshikawa Y.Cardiovascular responses to endotracheal intubation with the Bullard and the Macintosh laryngoscopes. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia 2002;49(5):526. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Arenkiel 2013 {published data only}
-
- Arenkiel B, Smitt M, Eversbusch A, Olsen KS.Cricoid pressure prolongs the intubation time when using the GlideScope videolaryngoscope. A controlled randomized double blind trial. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica, Supplement 2013;57:19. - PubMed
Arora 2013 {published data only}
Barak 2007 {published data only}
-
- Barak M, Philipchuck P, Abecassis P, Katz Y.A comparison of the Truview blade with the Macintosh blade in adult patients. Anaesthesia 2007;62(8):827-31. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Burnett 2014 {published data only}
-
- Burnett AM, Frascone RJ, Wewerka SS, Kealey SE, Evens ZN, Griffith KR, et al.Comparison of success rates between two video laryngoscope systems used in a prehospital clinical trial. Prehospital Emergency Care 2014;18(2):231-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Byars 2011 {published data only}
-
- Byars D, Lo B, Haroutunian M, Deljoui K, Morris D.Comparison of airway management by physicians using the Glidescope video laryngoscope, the Storz C-MAC video laryngoscope, and direct laryngoscopy in simulated difficult adult airways. Academic Emergency Medicine 2011;1:S155.
Carlino 2009 {published data only}
-
- Carlino C, Pastore JC, Battistini GM, Cancellieri F, Caria D, Ruggieri N.Training resident anesthesiologists in adult challenging intubation comparing Truview EVO2 and Macintosh laryngoscope: a preliminary study. Minerva Anestesiologica 2009;10:563-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Chalkeidis 2010 {published data only}
-
- Chalkeidis O, Kotsovolis G, Kalakonas A, Filippidou M, Triantafyllou C, Vaikos D, et al.A comparison between the Airtraq and Macintosh laryngoscopes for routine airway management by experienced anesthesiologists: a randomized clinical trial. Acta Anaesthesiologica Taiwanica: Official Journal of the Taiwan Society of Anesthesiologists 2010;48(1):15-20. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Corso 2010 {published data only}
-
- Corso RM, Piraccini E, Terzitta M, Agnoletti V, Gambale G.The use of Airtraq videolaryngoscope for endotracheal intubation in intensive care unit. Minerva Anestesiologica 2010;76(12):1095-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
DiMarco 2011 {published data only}
-
- Di Marco P, Scattoni L, Spinoglio A, Luzi M, Canneti A, Pietropaoli P, et al.Learning curves of the Airtraq and the Macintosh laryngoscopes for tracheal intubation by novice laryngoscopists: a clinical study. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2011;112(1):122-5. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Enomoto 2008a {published data only}
-
- Enomoto Y, Shimizu K, Hashimoto Y, Kamishima K, Arai T, Inoue H, et al.Comparison of the Pentax-AWS and fine view video laryngoscopes in the ease of laryngoscopy in 50 patients. [Japanese]. Japanese Journal of Anesthesiology 2008;57(12):1498-501. - PubMed
Erden 2010 {published data only}
-
- Erden IA, Pamuk AG, Uzun S, Geyik S, Cekirge S, Aypar U.Cervical spine movement during intubation using the Airtraq(®) and direct laryngoscopy. Turkish Journal of Medical Sciences 2010;40(2):299-304.
Ferrando 2011 {published data only}
Gaszynski 2009 {published data only}
-
- Gaszynski T, Gaszynski W.[A comparison of the optical AirTraq and the standard Macintosh laryngoscope for endotracheal intubation in obese patients]. Anestezjologia Intensywna Terapia 2009;41(3):145-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Gupta 2012 {published data only}
-
- Gupta D, Rusin K.Videolaryngoscopic endotracheal intubation (GlideScope) of morbidly obese patients in semi-erect position: a comparison with rapid sequence induction in supine position. Middle East Journal of Anesthesiology 2012;21(6):843-50. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Hastings 1995 {published data only}
-
- Hastings RH, Vigil AC, Hanna R, Yang BY, Sartoris DJ.Cervical spine movement during laryngoscopy with the Bullard, Macintosh, and Miller laryngoscopes. Anesthesiology 1995;82(4):859-69. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Hayes 2011 {published data only}
-
- Hayes, Inc.Airtraq (Prodol Meditec S.A.) to aid difficult tracheal intubation in hospitalized adults (Structured abstract). Health Technology Assessment Database 2011;1.
Hayes 2012 {published data only}
-
- Hayes, Inc.Airtraq laryngoscope (Prodol Meditec S.A.) to aid difficult tracheal intubation in hospitalized adults (Structured abstract). Health Technology Assessment Database 2012;1.
He 2008 {published data only}
-
- He N, Xue FS, Xu YC, Liao X, Xu XZ.Awake orotracheal intubation under airway topical anesthesia using the Bonfils in patients with a predicted difficult airway. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia 2008;55(12):881-2. [PMID: 19050098 ] - PubMed
Hirabayashi 2006 {published data only}
-
- Hirabayashi Y.GlideScope videolaryngoscope facilitates nasotracheal intubation. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia 2006;53(11):1163-4. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Hirabayashi 2007b {published data only}
-
- Hirabayashi Y, Fujita A, Seo N, Sugimoto H.Cervical spine movement during laryngoscopy using the Airway Scope compared with the Macintosh laryngoscope. Anaesthesia 2007;62(10):1050-5. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Hirabayashi 2007c {published data only}
-
- Hirabayashi Y, Hakozaki T, Fujisawa K, Hiruta M, Niwa Y, Sata N, et al.Nasal endotracheal intubation using GlideScope. [Japanese]. Japanese Journal of Anesthesiology 2007;56(8):962-4. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Hirabayashi 2008a {published data only}
-
- Hirabayashi Y, Fujita A, Seo N, Sugimoto H.A comparison of cervical spine movement during laryngoscopy using the Airtraq (R) or Macintosh laryngoscopes. Anaesthesia 2008;63(6):635-40. - PubMed
Hirabayashi 2009a {published data only}
-
- Hirabayashi Y, Seo N.Airtraq laryngoscope has an advantage over Macintosh laryngoscope for nasotracheal intubation by novice laryngoscopists. Journal of Anesthesia 2009;23(1):172-3. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Hirabayashi 2010 {published data only}
-
- Hirabayashi Y, Fujita A, Seo N, Sugimoto H.Distortion of anterior airway anatomy during laryngoscopy with the GlideScope videolaryngoscope. Journal of Anesthesia 2010;24(3):366-72. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Hirabayashi 2013a {published data only}
-
- Hirabayashi Y, Hoshijima H, Kuratani N, Masaki E.Efficacy of videolaryngoscopes for nasotracheal intubation: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. [Japanese]. Japanese Journal of Anesthesiology 2013;62(11):1375-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Hirabayashi 2013b {published data only}
-
- Hirabayashi Y, Matoba A, Masaki E.Comparison of Pentax-AWS, GlideScope cobalt, and Macintosh laryngoscope in patients for nasotracheal intubation. [Japanese]. Japanese Journal of Anesthesiology 2013;62(8):952-5. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Jones 2008 {published data only}
-
- Jones PM, Armstrong KP, Armstrong PM, Cherry RA, Harle CC, Hoogstra J, et al.A comparison of glidescope videolaryngoscopy to direct laryngoscopy for nasotracheal intubation. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2008;107(1):144-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Jones 2010 {published data only}
-
- Jones PM, Turkstra TP, Armstrong KP, Armstrong PM, Harle CC.Comparison of a single-use GlideScope Cobalt videolaryngoscope with a conventional GlideScope for orotracheal intubation. Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia 2010;57(1):18-23. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Koh 2010 {published data only}
Lange 2009 {published data only}
-
- Lange M, Frommer M, Redel A, Trautner H, Hampel J, Kranke P, et al.Comparison of the Glidescope and Airtraq optical laryngoscopes in patients undergoing direct microlaryngoscopy. Anaesthesia 2009;64(3):323-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Li 2007 {published data only}
-
- Li XY, Xue FS, Sun L, Xu YC, Liu Y, Zhang GH, et al.Comparison of hemodynamic responses to nasotracheal intubations with Glide Scope videolaryngoscope, Macintosh direct laryngoscope, and fiberoptic bronchoscope. [Chinese]. Acta Academiae Medicinae Sinicae 2007;29(1):117-23. - PubMed
Maassen 2009 {published data only}
-
- Maassen R, Lee R, Hermans B, Marcus M, Zundert A.A comparison of three videolaryngoscopes: the Macintosh laryngoscope blade reduces, but does not replace, routine stylet use for intubation in morbidly obese patients. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2009;109(5):1560-5. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Maharaj 2006 {published data only}
-
- Maharaj CH, O'Croinin D, Curley G, Harte BH, Laffey JG.A comparison of tracheal intubation using the Airtraq or the Macintosh laryngoscope in routine airway management: a randomised, controlled clinical trial. Anaesthesia 2006;61(11):1093-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Maharaj 2007 {published data only}
-
- Maharaj CH, Buckley E, Harte BH, Laffey JG.Endotracheal intubation in patients with cervical spine immobilization - A comparison of Macintosh and Airtraq laryngoscopes. Anesthesiology 2007;107(1):53-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Maharaj 2008 {published data only}
-
- Maharaj CH, Costello JF, Harte BH, Laffey JG.Evaluation of the Airtraq and Macintosh laryngoscopes in patients at increased risk for difficult tracheal intubation. Anaesthesia 2008;63(2):182-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Mahjoubifar 2010 {published data only}
-
- Mahjoubifar M, Boroojeny SB.Hemodynamic changes during orotracheal intubation with the Glidescope and direct laryngoscope. Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal 2010;4:406-8.
Marco 2011 {published data only}
-
- Marco P, Scattoni L, Spinoglio A, Luzi M, Canneti A, Pietropaoli P, et al.Learning curves of the Airtraq and the Macintosh laryngoscopes for tracheal intubation by novice laryngoscopists: a clinical study. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2011;112(1):122-5. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Miner 2012 {published data only}
-
- Miner JR, Moore J, Rischall M, Beste R, Scott JN, McGill JW, et al.Randomized controlled trial of endotracheal intubation using the C-MAC videolaryngoscope versus standard laryngoscopy in patients undergoing emergent endotracheal intubation in the emergency department. Academic Emergency Medicine 2012;19:S229.
Moharari 2010 {published data only}
-
- Moharari RS, Fallah AH, Khajavi MR, Khashayar P, Lakeh M, Najafi A.The GlideScope facilitates nasogastric tube insertion: a randomized clinical trial. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2010;110(1):115-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Mont 2012 {published data only}
-
- Mont G, Biesler I, Pfortner R, Mohr C, Groeben H.Easy and difficult nasal intubation - A randomised comparison of Macintosh vs Airtraq laryngoscopes. Anaesthesia 2012;67(2):132-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Ndoko 2008a {published data only}
-
- Ndoko SK, Amathieu R, Tual L, Polliand C, Kamoun W, El Housseini L, et al.Tracheal intubation of morbidly obese patients: a randomized trial comparing performance of Macintosh and Airtraq (TM) laryngoscopes. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2008;100(2):263-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Ng 2011a {published data only}
-
- Ng I, Sim XLJ, Williams D, Segal R.A randomised controlled trial comparing the McGrath Videolaryngoscope with the straight blade laryngoscope when used in adult patients with potential difficult airways. Anaesthesia and Intensive Care 2011;39 (4):722-3. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Ng 2011b {published data only}
-
- Ng I, Sim XL, Williams D, Segal R.A randomised controlled trial comparing the McGrath(®) videolaryngoscope with the straight blade laryngoscope when used in adult patients with potential difficult airways. Anaesthesia 2011;66(8):709-14. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Ng 2012 {published data only}
-
- Ng I, Hill AL, Williams DL, Lee K, Segal R.Randomized controlled trial comparing the McGrath videolaryngoscope with the C-MAC videolaryngoscope in intubating adult patients with potential difficult airways. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2012;109(3):439-43. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Park 2010 {published data only}
Rai 2005 {published data only}
-
- Rai MR, Dering A, Verghese C.The Glidescope system: a clinical assessment of performance. Anaesthesia 2005;60(1):60-4. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Ranieri 2012 {published data only}
-
- Ranieri D Jr, Filho SM, Batista S, do Nascimento P Jr.Comparison of Macintosh and Airtraq laryngoscopes in obese patients placed in the ramped position. Anaesthesia 2012;67(9):980-5. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Ranieri 2014 {published data only}
-
- Ranieri D, Zinelli FR, Neubauer AG, Schneider AP, do Nascimento P.Preanesthetic assessment data do not influence the time for tracheal intubation with Airtraq (TM) video laryngoscope in obese patients. Revista Brasileira De Anestesiologia 2014;64(3):190-4. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Sahin 2004 {published data only}
-
- Sahin A, Salman MA, Erden IA, Aypar U.Upper cervical vertebrae movement during intubating laryngeal mask, fibreoptic and direct laryngoscopy: a video-fluoroscopic study. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2004;21(10):819-23. [15678738] - PubMed
Sansone 2012 {published data only}
-
- Sansone P, Stumbo R, D'Arienzo S, Passavanti MB, Pace MC, Aurilio C.Airtraq laryngoscopes in patients with facial trauma. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2012;29:229.
Saxena 2013 {published data only}
Smith 1999 {published data only}
-
- Smith CE, Pinchak AB, Sidhu TS, Radesic BP, Pinchak AC, Hagen JF.Evaluation of tracheal intubation difficulty in patients with cervical spine immobilization: fiberoptic (WuScope) versus conventional laryngoscopy. Anesthesiology 1999;91(5):1253-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Stumpner 2011 {published data only}
-
- Stumpner T, Hager H, Grubhofer G, Hamp T.Hemodynamic responses to tracheal intubation using double lumen tubes: a randomized trial comparing the Airtraq TM and the Macintosh laryngoscope. Intensive Care Medicine 2011;37:S88.
Suzuki 2008a {published data only}
-
- Suzuki A, Tampo A, Abe N, Otomo S, Minami S, Henderson JJ, et al.The Parker Flex-Tip tracheal tube makes endotracheal intubation with the Bullard laryngoscope easier and faster. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2008;25(1):43-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Teoh 2009 {published data only}
-
- Teoh WHL, Shah MK, Sia ATH.Randomised comparison of Pentax AirwayScope and Glidescope for tracheal intubation in patients with normal airway anatomy. Anaesthesia 2009;64(10):1125-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Terradillos 2009 {published data only}
-
- Terradillos E, Almaraz C, Penide L, Alonso A, De La Gala F.Airtraq and Macintosh laryngoscope in neurosurgery patients: hemodynamics changes. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2009;26:224.
Tolon 2012 {published data only}
-
- Tolon MA, Zanaty OM, Shafshak W, Arida EE.Comparative study between the use of Macintosh laryngoscope and Airtraq in patients with cervical spine immobilization. Alexandria Journal of Medicine 2012;48(2):179-85.
Trimmel 2011 {published data only}
-
- Trimmel H, Kreutziger J, Fertsak G, Fitzka R, Dittrich M, Voelckel WG.Use of the Airtraq laryngoscope for emergency intubation in the prehospital setting: a randomized control trial. Critical Care Medicine 2011;39(3):489-93. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Turkstra 2009a {published data only}
-
- Turkstra TP, Pelz DM, Jones PM.Cervical spine motion: a fluoroscopic comparison of the AirTraq laryngoscope versus the Macintosh laryngoscope. Anesthesiology 2009;111(1):97-101. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Turkstra 2009b {published data only}
-
- Turkstra TP, Pelz DM, Jones PM.Comparison of AirTraq laryngoscope to Macintosh laryngoscope for intubation of patients with potential cervical spine injury: a fluoroscopic randomized controlled trial. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia 2009;56:S112.
Vernick 2006 {published data only}
-
- Vernick C, Audu P, Mandato P, Heitz J, Bader S.Comparing the GlideScope (GL) with Macintosh laryngoscope (Mac) for intubating difficult airway. Anesthesiology 2006:A534.
Wang 2009 {published data only}
-
- Wang WH, Xing YF, Chen L, Wang ML.Hemodynamical comparison between Airtraq laryngoscope and Macintosh laryngoscope for orotracheal intubation. [Chinese]. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research 2009;13(39):7687-90.
Wasem 2013 {published data only}
-
- Wasem S, Lazarus M, Hain J, Festl J, Kranke P, Roewer N, et al.Comparison of the Airtraq and the Macintosh laryngoscope for double-lumen tube intubation: a randomised clinical trial. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2013;30(4):180-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Watts 1997 {published data only}
-
- Watts AD, Gelb AW, Bach DB, Pelz DM.Comparison of the Bullard and Macintosh laryngoscopes for endotracheal intubation of patients with a potential cervical spine injury. Anesthesiology 1997;87(6):1335-42. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Yang 2013 {published data only}
-
- Yang M, Kim JA, Ahn HJ, Choi JW, Kim DK, Cho EA.Double-lumen tube tracheal intubation using a rigid video-stylet: a randomized controlled comparison with the Macintosh laryngoscope. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2013;111(6):990-5. [PMID: ] - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Ahmad 2015 {published data only}
Ahmadi 2014 {published data only}
Ahmadi 2015 {published data only}
-
- Ahmadi K, Ebrahimi M, Hashemian AM, Sarshar S, Rahimi-Movaghar V.GlideScope video laryngoscope for difficult intubation in emergency patients: a quasi-randomized controlled trial. Acta Medica Iranica 2015;53(12):738-42. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Akbar 2015 {published data only}
-
- Akbar SH, Ooi JS.Comparison between C-MAC video-laryngoscope and Macintosh direct laryngoscope during cervical spine immobilization. Middle East Journal of Anaesthesiology 2015;23(1):43-50. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Amini 2015 {published data only}
Bakshi 2015 {published data only}
Bhandari 2013 {published data only}
Bhat 2015 {published data only}
Cattano 2013 {published data only}
-
- Cattano D, Ferrario L, Patel CB, Maddukuri V, Melnikov V, Gumbert SD, et al.Utilization of C-MAC videolaryngoscopy for direct and indirect assisted endotracheal intubation. Journal of Anesthesiology and Clinical Science 2013;10. [http://dx.doi.org/10.7243/2049-9752-2-10]
Colak 2015 {published data only}
Eto 2014 {published data only}
-
- Eto Y, Tampo A, Tanaka H, Kunisawa T, Suzuki A, Iwasaki H.Quick and reliable confirmation of tracheal tube placement by NEW type of Airway Scope. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2014;31:279. [71638668]
Gharehbaghi 2012 {published data only}
-
- Gharehbaghi M, Peirovifar A, Baghernia A.Comparing the efficacy of Glidescope video laryngoscopy and Macintosh direct laryngoscopy for intubation of obese patients. In: European Journal of Anaesthesiology. Vol. 29. 2012:229.
Hamp 2015 {published data only}
Ishida 2011 {published data only}
-
- Ishida Y, Aoyama T, Kondo U, Yamakawa S, Nakamura M, Nonogaki M.Hemodynamic responses to tracheal intubation with the Pentax-AWS video laryngoscope or Macintosh laryngoscope in patients scheduled for cardiovascular surgery. In: Anesthesia and Analgesia. Vol. 1. 2011:S189.
Janz 2015 {published data only}
Kido 2015 {published data only}
-
- Kido H, Komasawa N, Matsunami S, Kusaka Y, Minami T.Comparison of McGRATH MAC and Macintosh laryngoscopes for double-lumen endotracheal tube intubation by anesthesia residents: a prospective randomized clinical trial. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia 2015;27(6):476-80. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Kita 2014 {published data only}
-
- Kita S, Higashi K, Matsuo M, Iwagaki T, Sano H, Aoyama K, et al.Head extension during laryngoscopy for obtaining a best glottic view: comparison of the McGrath and MacIntosh laryngoscopes. [Japanese]. Japanese Journal of Anesthesiology 2014;63(12):1300-5. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Laosuwan 2015 {published data only}
-
- Laosuwan P, Earsakul A, Numkarunarunrote N, Khamjaisai J, Charuluxananan S.Randomized cinefluoroscopic comparison of cervical spine motion using McGrath Series 5 and Macintosh laryngoscope for intubation with manual in-line stabilization. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand 2015;98(Suppl 1):S63-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Liu 2010 {published data only}
-
- Liu H, Shi XY, Chen W, Pu J, Yuan HB, Liu G.Comparison between HPHJ-A video laryngoscope and Macintosh laryngoscope in clinical intubation. [Chinese]. Academic Journal of Second Military Medical University 2010;31(10):1073-5.
Morello 2009 {published data only}
-
- Morello G, Molino C, Sidoti MT, Parrinello L, Laudani A.GlideScope medium blade vs Macintosh blade: laryngoscopy and intubation in 300 patients. In: Anesthesiology. 2009:A475.
Nakayama 2010 {published data only}
-
- Nakayama Y, Yamauchi M, Yamakage M, Namiki A.An evaluation of double lumen tube placement using Airway scope, GlideScope or Macintosh laryngoscope. In: Anesthesia and Analgesia. Vol. 1. 2010:S258. [71788475]
NCT00178555 {published data only}
-
- NCT00178555.Comparison of the video and Macintosh laryngoscope in patients who may be difficult to intubate [A comparison of laryngoscopy techniques using the video laryngoscope and the traditional Macintosh laryngoscope in patients who may be difficult to intubate]. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=NCT00178555&Search=Search (first received 12 September 2005).
NCT00602979 {published data only}
-
- NCT00602979.Comparison study in adult surgical patients of 5 airway devices [Prospective, randomized comparison of intubating conditions with Airtraq optical, Storz DCI video, McGRATH video, GlideScope video, & Macintosh laryngoscope in randomly selected elective adult surgical patients]. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=NCT00602979&Search=Search (first received 15 January 2008).
NCT00664612 {published data only}
-
- NCT00664612.Comparison of AirTraq laryngoscope to Macintosh laryngoscope for intubation of patients with potential cervical spine injury. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=NCT00664612&Search=Search (first received 18 April 2008).
NCT01029756 {published data only}
-
- NCT01029756.Randomised controlled trial of intubation, comparing Pentax AWS against Macintosh laryngoscope (PAWS) [A randomised controlled trial of intubation by inexperienced anaesthetists, comparing the Pentax Airway Scope AWS-S100 rigid video laryngoscope (Pentax AWS) and the Macintosh laryngoscope]. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=NCT01029756&Search=Search (first received 9 December 2009).
NCT01114945 {published data only}
-
- NCT01114945.Comparative effectiveness of intubating devices in the morbidly obese [A prospective study comparing video laryngoscopy devices to direct laryngoscopy for tracheal intubation of patients undergoing bariatric surgery]. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=NCT01114945&Search=Search (first received 23 April 2010).
NCT01488695 {published data only}
-
- NCT01488695.GlideScope groove versus Macintosh blade for double-lumen endotracheal tube intubation [Comparison of GlideScope groove to Macintosh blade for orotracheal intubation with double-lumen endotracheal tube: a randomised controlled trial]. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=NCT01488695&Search=Search (first received 6 December 2011).
NCT01516164 {published data only}
-
- NCT01516164.A comparison of the ease of tracheal intubation using a McGrath MAC laryngoscope and a standard MacIntosh laryngoscope. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=NCT01516164&Search=Search (first received 19 January 2012).
NCT02190201 {published data only}
-
- NCT02190201.Comparison of McGrath and Macintosh laryngoscope for DLT intubation [A randomised controlled trial comparing McGrath Series 5 videolaryngoscope and Macintosh laryngoscope for double lumen tube intubation]. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=NCT02190201&Search=Search (first received 10 July 2014).
Pieters 2015 {published data only}
-
- Pieters B, Maassen R, Van E, Maathuis B, Dobbelsteen J, Zundert A.Indirect videolaryngoscopy using Macintosh blades in patients with non-anticipated difficult airways results in significantly lower forces exerted on teeth relative to classic direct laryngoscopy: a randomized crossover trial. Minerva Anestesiologica 2015;(8):846-54. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Postaci 2015 {published data only}
-
- Postaci A, Cakirca M, Sacan O, Aytac I, Sakizci Uyar B, Baskan S, et al.Comparison of the Mcgrath Series 5 videolaryngoscope to the standard Macintosh laryngoscope for the intubation of the obese patients. [Turkish]. Anestezi Dergisi 2015;23(3):126-30. [2015379595]
Rovsing 2010 {published data only}
-
- Rovsing L, Sylvestersen J, Skovgaard K, Joergensen D, Marding O, Andersen L.Intubation in morbidly obese patients. A randomised controlled study comparing the GlideScope videolaryngoscope and Macintosh direct laryngoscope. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2010;1:S254. [71788471]
Silverberg 2015 {published data only}
-
- Silverberg M, Li N, Kory P.Efficacy of video laryngoscopy vs. direct laryngoscopy during urgent endotracheal intubation: a randomized controlled trial. In: Chest. Vol. 144. 2013:580A. - PubMed
-
- Silverberg MJ, Li N, Acquah SO, Kory PD.Comparison of video laryngoscopy versus direct laryngoscopy during urgent endotracheal intubation: a randomized controlled trial. Critical Care Medicine 2015;43(3):336-41. - PubMed
Wallace 2015 {published data only}
-
- Wallace CD, Foulds LT, McLeod GA, Younger RA, McGuire BE.A comparison of the ease of tracheal intubation using a McGrath MAC laryngoscope and a standard Macintosh laryngoscope. Anaesthesia 2015;70(11):1281-5. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Wang 2008 {published data only}
-
- Wang XL, Li JB, Zhao XH.A comparison between Truview EVO2 optic laryngoscope and GlideScope video laryngoscope for laryngeal viewing. [Chinese]. Academic Journal of Second Military Medical University 2008;29(8):996-8.
Yao 2015 {published data only}
-
- Yao WL, Wan L, Xu H, Qian W, Wang XR, Tian YK, et al.A comparison of the McGrath Series 5 videolaryngoscope and Macintosh laryngoscope for double-lumen tracheal tube placement in patients with a good glottic view at direct laryngoscopy. Anaesthesia 2015;70(7):810-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Yousef 2012 {published data only}
References to ongoing studies
NCT01914523 {published data only}
-
- NCT01914523.Comparison of the Macintosh, King Vision®, Glidescope® and AirTraq® laryngoscopes in routine airway management. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT01914523?term=01914523&... (first received 28 July 2013).
NCT01914601 {published data only}
-
- NCT01914601.King Vision and cervical spines movement [Does King Vision® videolaryngoscope reduce cervical spine motion during endotracheal intubation? A cross-over study]. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT01914601?term=01914601&... (first received 28 July 2013).
NCT02088801 {published data only}
-
- NCT02088801.Evaluation of videolaryngoscopes in difficult airway (SWIVITII) [Phase 2 study of evaluation of videolaryngoscopes in difficult airway (SWIVITII)]. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT02088801?term=02088801&... (first received 11 March 2014).
NCT02167477 {published data only}
-
- NCT02167477.Comparison of indirect and direct laryngoscopy in obese patients [Comparison of the C-MAC video laryngoscope with conventional direct laryngoscopy in morbidly obese patients using a photographic overlay technique]. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT02167477?term=02167477&... (first received 17 July 2014).
NCT02292901 {published data only}
-
- NCT02292901.McGrath Mac videolaryngoscope vs the Macintosh laryngoscope [Randomised controlled trial of intubation with the McGrath Mac videolaryngoscope vs the Macintosh laryngoscope]. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT02292901?term=02292901&... (first received 12 November 2014).
NCT02297113 {published data only}
-
- NCT02297113.Rapid sequence intubation at the emergency department [The C-MAC videolaryngoscope compared with conventional laryngoscopy for rapid sequence intubation at the emergency department]. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT02297113?term=02297113&... (first received 13 November 2014).
NCT02305667 {published data only}
-
- NCT02305667.Videolaryngoscopes for double lumen tube intubations [A comparison of three videolaryngoscopes for double-lumen tubes intubation in humans. A randomized controlled study]. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT02305667?term=02305667&... (first received 27 November 2014).
Additional references
Abdelgadir 2014
Adams 2000
-
- Adams JP, Murphy PG.Obesity in anaesthesia and intensive care. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2000;85(1):91-108. - PubMed
Caplan 1990
-
- Caplan RA, Posner KL, Ward RJ, Cheney FW.Adverse respiratory events in anesthesia: a closed claims analysis. Anesthesiology 1990;72(5):828-33. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Cook 2000
-
- Cook TM.A new practical classification of laryngeal view. Anaesthesia 2000;55(3):274-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Cook 2011
-
- Cook TM, Woodall N, Frerk C.Major complications of airway management in the UK: results of the Fourth National Audit Project of the Royal College of Anaesthetists and the Difficult Airway Society. Part 1: anaesthesia. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2011;106(5):617-31. - PubMed
Cook 2012
-
- Cook TM, MacDougall-Davis SR.Complications and failure of airway management. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2012;109(Suppl 1):68-85. - PubMed
Cormack 1984
-
- Cormack RS, Lehane J.Difficult tracheal intubation in obstetrics. Anaesthesia 1984;39(11):1105-11. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Covidence [Computer program]
-
- www.covidence.org.Covidence, 2015.
Crosby 1998
-
- Crosby ET, Cooper RM, Douglas MJ, Doyle DJ, Hung OR, Labrecque P, et al.The unanticipated difficult airway with recommendations for management. Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia 1998;45(8):757-76. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Griesdale 2012b
Guyatt 2008
Healy 2012
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. www.cochrane-handbook.org.
Hoshijima 2014
-
- Hoshijima H, Kuratani N, Hirabayashi Y, Takeuchi R, Shiga T, Masaki E.Pentax Airway Scope(R) vs Macintosh laryngoscope for tracheal intubation in adult patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Anaesthesia 2014;69(8):911-8. [24820205] - PubMed
Juvin 2003
-
- Juvin P, Lavaut E, Dupont H, Lefevre P, Demetriou M, Dumoulin JL, et al.Difficult tracheal intubation is more common in obese than in lean patients. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2003;97(2):595-600. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Kaplan 2006
-
- Kaplan MB, Hagberg CA, Ward DS, Brambrink A, Chhibber AK, Heidegger T, et al.Comparison of direct and video-assisted views of the larynx during routine intubation. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia 2006;18(5):357-62. [PMID: ] - PubMed
King 1990
-
- King TA, Adams AP.Failed tracheal intubation. British Journal of Anaesthesia 1990;65(3):400-14. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Levitan 1998
-
- Levitan RM, Ochroch EA, Kush S, Shofer FS, Hollander JE.Assessment of airway visualization: validation of the percentage of glottic opening (POGO) scale. Academic Emergency Medicine 1998;5(9):919-23. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Lundstrom 2009
-
- Lundstrom LH, Moller AM, Rosenstock C, Astrup G, Wetterslev J.High body mass index is a weak predictor for difficult and failed tracheal intubation: a cohort study of 91,332 consecutive patients scheduled for direct laryngoscopy registered in the Danish Anesthesia Database. Anesthesiology 2009;110(2):266-74. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Malhotra 2008
Mallampati 1985
-
- Mallampati SR, Gatt SP, Gugino LD, Desai SP, Waraksa B, Freiberger D, et al.A clinical sign to predict difficult tracheal intubation: a prospective study. Canadian Anaesthetists' Society Journal 1985;32(4):429-34. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Marley 2005
-
- Marley RA, Hoyle B, Ries C.Perianesthesia respiratory care of the bariatric patient. Journal of Perianesthesia Nursing 2005;20(6):404-31; quiz 432-4. - PubMed
Mihai 2008
-
- Mihai R, Blair E, Kay H, Cook TM.A quantitative review and meta-analysis of performance of non-standard laryngoscopes and rigid fibreoptic intubation aids. Anaesthesia 2008;63(7):745-60. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Nicholson 2013a
-
- Nicholson A, Cook TM, Smith AF, Lewis SR, Reed SS.Supraglottic airway devices versus tracheal intubation for airway management during general anaesthesia in obese patients. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013, Issue 9. Art. No: CD010105. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010105] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Nicholson 2013b
-
- Nicholson A, Smith AF, Lewis SR, Cook TM.Tracheal intubation with a flexible intubation scope versus other intubation techniques for obese patients requiring general anaesthesia. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2014, Issue 1. Art. No: CD010320. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010320.pub2] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Niforopoulou 2010
-
- Niforopoulou P, Pantazopoulos I, Demestiha T, Koudouna E, Xanthos T.Video-laryngoscopes in the adult airway management: a topical review of the literature. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 2010;54(9):1050-61. [PMID: ] - PubMed
RevMan 5.3 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration Review Manager (RevMan).Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2012.
Rose 1994
-
- Rose DK, Cohen MM.The airway: problems and predictions in 18,500 patients. Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia 1994;41(5 Pt 1):372-83. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Shiga 2005
-
- Shiga T, Wajima Z, Inoue T, Sakamoto A.Predicting difficult intubation in apparently normal patients: a meta-analysis of bedside screening test performance. Anesthesiology 2005;103(2):429-37. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Su 2011
-
- Su YC, Chen CC, Lee YK, Lee JY, Lin KJ.Comparison of video laryngoscopes with direct laryngoscopy for tracheal intubation: a meta-analysis of randomised trials. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2011;28(11):788-95. [21897263] - PubMed
Van Rensburg 2013a
-
- Van Rensburg A, Roscoe A, Slinger P, Russel T.Randomised control trial comparing the GlideScope and Macintosh laryngoscope for double lumen endotracheal tube intubation. Applied Cardiopulmonary Pathophysiology. In: Conference: 28th Annual Meeting of the European Association of Cardiothoracic Anaesthesiologists (EACTA). Vol. 17. 2013:229.
Van Rensburg 2013b
-
- Van Rensburg AE, Roscoe A, Slinger P, Russell T.Randomized control trial comparing the Glydescope and Macintosh laryngoscope for left sided double lumen endotracheal tube intubation. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2013;116:6. - PubMed
Wilson 1988
-
- Wilson ME, Spiegelhalter D, Robertson JA, Lesser P.Predicting difficult intubation. British Journal of Anaesthesia 1988;61(2):211-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Woodall 2011
-
- Woodall NM, Cook TM.National census of airway management techniques used for anaesthesia in the UK: first phase of the Fourth National Audit Project at the Royal College of Anaesthetists. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2011;106(2):266-71. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Lewis 2014
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

