Sustained Morphine Administration Induces TRPM8-Dependent Cold Hyperalgesia
- PMID: 27845197
- PMCID: PMC5291755
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpain.2016.10.015
Sustained Morphine Administration Induces TRPM8-Dependent Cold Hyperalgesia
Abstract
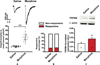
It is not uncommon for patients chronically treated with opioids to exhibit opioid-induced hyperalgesia, and this has been widely reported clinically and experimentally. The molecular substrate for this hyperalgesia is multifaceted, and associated with a complex neural reorganization even in the periphery. For instance, we have recently shown that chronic morphine-induced heat hyperalgesia is associated with an increased expression of GluN2B containing N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors, as well as of the neuronal excitatory amino acid transporter 3/excitatory amino acid carrier 1, in small-diameter primary sensory neurons only. Cold allodynia is also a common complaint of patients chronically treated with opioids, yet its molecular mechanisms remain to be understood. Here we present evidence that the cold sensor TRPM8 channel is involved in opioid-induced hyperalgesia. After 7 days of morphine administration, we observed an upregulation of TRPM8 channels using patch clamp recording on sensory neurons and Western blot analysis on dorsal root ganglia. The selective TRPM8 antagonist RQ-00203078 blocked cold hyperalgesia in morphine-treated rats. Also, TRPM8 knockout mice failed to develop cold hyperalgesia after chronic administration of morphine. Our results show that chronic morphine upregulates TRPM8 channels, which is in contrast with the previous finding that acute morphine triggers TRPM8 internalization.
Perspective: Patients receiving chronic opioid are sensitive to cold. We show in mice and rats that sustained morphine administration induces cold hyperalgesia and an upregulation of TRPM8. Knockout or selectively blocking TRPM8 reduces morphine-induced cold hyperalgesia suggesting TRPM8 is regulated by opioids.
Keywords: 5°C; Cold receptor; cold plate; menthol; paw lift; whole cell recording.
Copyright © 2016 American Pain Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Almaraz L, Manenschijn JA, de la Pena E, Viana F. Trpm8. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;222:547–579. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

