The Role of miRNAs in Common Inflammatory Arthropathies: Osteoarthritis and Gouty Arthritis
- PMID: 27845712
- PMCID: PMC5197954
- DOI: 10.3390/biom6040044
The Role of miRNAs in Common Inflammatory Arthropathies: Osteoarthritis and Gouty Arthritis
Abstract
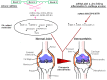
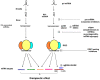
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, non-coding RNA species that are highly evolutionarily conserved, from higher invertebrates to man. Up to 1000 miRNAs have been identified in human cells thus far, where they are key regulators of the expression of numerous targets at the post-transcriptional level. They are implicated in various processes, including cell differentiation, metabolism, and inflammation. An expanding list of miRNAs is known to be involved in the pathogenesis of common, non-autoimmune inflammatory diseases. Interestingly, osteoarthritis (OA) is now being conceptualized as a metabolic disease, as there is a correlation among hyperuricemia and metabolic syndrome (MetS). Experimental evidence suggests that metabolic deregulation is a commonality between these different pathological entities, and that miRNAs are key players in the modulation of metabolic routes. In light of these findings, this review discusses the role of miRNAs in OA and gouty arthritis, as well as the possible therapeutic targetability of miRNAs in these diseases.
Keywords: arthropathy; cartilage erosion; hyperuricemia; metaflammation; monosodium urate crystals; overweight; post-transcriptional regulator.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Unraveling the impact of miRNAs on gouty arthritis: diagnostic significance and therapeutic opportunities.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr;398(4):3433-3450. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03603-9. Epub 2024 Nov 19. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39560752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of microRNA alternation in the pathogenesis of gouty arthritis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 11;13:967769. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.967769. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36034424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Could MicroRNAs be Regulators of Gout Pathogenesis?Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36(6):2085-92. doi: 10.1159/000430176. Epub 2015 Jul 21. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 26279417 Review.
-
Do MicroRNAs have a key epigenetic role in osteoarthritis and in mechanotransduction?Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2017 May-Jun;35(3):518-526. Epub 2017 Jan 4. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28079507 Review.
-
MicroRNAs: exploring new horizons in osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016 Apr;24(4):573-80. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2015.10.018. Epub 2015 Nov 11. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016. PMID: 26576510 Review.
Cited by
-
Research progress on microRNA in gout.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 20;13:981799. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.981799. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36339582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory Role of miRNAs and lncRNAs in Gout.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Jun 29;2022:6513565. doi: 10.1155/2022/6513565. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Jul 19;2023:9864323. doi: 10.1155/2023/9864323. PMID: 35813414 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
miR-335-5P contributes to human osteoarthritis by targeting HBP1.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Feb;21(2):109. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9541. Epub 2020 Nov 27. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33335572 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study revealed novel loci which aggravate asymptomatic hyperuricaemia into gout.Ann Rheum Dis. 2019 Oct;78(10):1430-1437. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215521. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019. PMID: 31289104 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of action and new developments in the study of curcumin in the treatment of osteoarthritis: a narrative review.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Mar;33(3):929-940. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01665-6. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40009345 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

