Metal-catalyzed reductive coupling of olefin-derived nucleophiles: Reinventing carbonyl addition
- PMID: 27846504
- PMCID: PMC5130112
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aah5133
Metal-catalyzed reductive coupling of olefin-derived nucleophiles: Reinventing carbonyl addition
Abstract
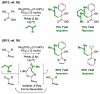
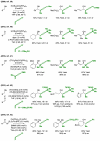
α-Olefins are the most abundant petrochemical feedstock beyond alkanes, yet their use in commodity chemical manufacture is largely focused on polymerization and hydroformylation. The development of byproduct-free catalytic C-C bond-forming reactions that convert olefins to value-added products remains an important objective. Here, we review catalytic intermolecular reductive couplings of unactivated and activated olefin-derived nucleophiles with carbonyl partners. These processes represent an alternative to the longstanding use of stoichiometric organometallic reagents in carbonyl addition.
Copyright © 2016, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures



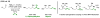

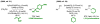
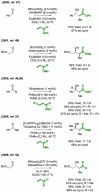
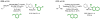
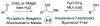
References
-
- Frohning CD, Kohlpaintner CW. In: Applied Homogeneous Catalysis with Organometallic Compounds. Cornils B, Herrmann WA, editors. Wiley-VCH; Weinheim: 1996. pp. 29–104.
-
- van Leeuwen PWNM. Homogeneous Catalysis: Understanding the Art. Kluwer; Dordrecht: 2004.
-
- Baier MC, Zuideveld MA, Mecking S. Post-Metallocenes in the Industrial Production of Polyolefins. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014;53:9722–9744. - PubMed
-
- Cornell CN, Sigman MS. Recent Progress in Wacker Oxidations: Moving toward Molecular Oxygen as the Sole Oxidant. Inorg. Chem. 2007;46:1903–1909. - PubMed
-
- Kablaoui NM, Buchwald SL. Reductive Cyclization of Enones by a Titanium Catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995;117:6785–6786.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

