Infrared thermography: A potential noninvasive tool to monitor udder health status in dairy cows
- PMID: 27847416
- PMCID: PMC5104715
- DOI: 10.14202/vetworld.2016.1075-1081
Infrared thermography: A potential noninvasive tool to monitor udder health status in dairy cows
Abstract
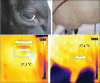
The animal husbandry and livestock sectors play a major role in the rural economy, especially for the small and marginal farmers. India has the largest livestock population in the world and ranks first in the milk production. Mastitis is the most common and expensive infectious disease in dairy cattle. The global economic losses per year due to mastitis amounts to USD 35 billion and for Indian dairy industry ₹6000 crores per year. Early detection of mastitis is very important to reduce the economic loss to the dairy farmers and dairy industry. Automated methods for early and reliable detection of mastitis are currently in focus under precision dairying. Skin surface temperature is an important indicator for the diagnosis of cow's illnesses and for the estimation of their physiological status. Infrared thermography (IRT) is a simple, effective, on-site, and noninvasive method that detects surface heat, which is emitted as infrared radiation and generates pictorial images without causing radiation exposure. In human and bovine medicine, IRT is used as a diagnostic tool for assessment of normal and physiological status.
Keywords: cows; infrared thermography; mastitis diagnosis; udder health; udder surface temperature.
Figures

References
-
- Anonymous. Cattle and Dairy Development, Government of India, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Department of Animal Husbandry, Dairying and Fisheries. [Accessed on 20-04-16]. Available from: http://www.dadf.gov.in .
-
- Srivastava A.K. Mastitis in Dairy Animal: Current Concepts and Future Concerns. Delhi, India: Satish Serial Publishing House; 2015. pp. 1–5.
-
- Culina M, Hahne J, Vorlop K.D. Design of an online sensor array for an early detection of udder affections in automatic milking systems. VDI Verlag GmbH, Bonn, Germany: World Congress of Agricultural Engineering for a Better World: Book of Abstracts; 2006. pp. 453–454.
-
- Poikalainen V, Praks J, Veermae I, Kokin E. Infrared temperature patterns of cow’s body as an indicator for health control at precision cattle farming. Agron. Res. Biosyst. Eng. 2012;1:187–194.
-
- Sykes D.J, Couvillion J.S, Cromiak A, Bowers S, Schenck E, Crenshaw M, Ryan P.L. The use of digital infrared thermal imaging to detect estrus in gilts. Theriogenology. 2012;78:147–152. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
