Mitigation of radiation-induced hematopoietic injury by the polyphenolic acetate 7, 8-diacetoxy-4-methylthiocoumarin in mice
- PMID: 27849061
- PMCID: PMC5110976
- DOI: 10.1038/srep37305
Mitigation of radiation-induced hematopoietic injury by the polyphenolic acetate 7, 8-diacetoxy-4-methylthiocoumarin in mice
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Mitigation of radiation-induced hematopoietic injury by the polyphenolic acetate 7, 8-diacetoxy-4-methylthiocoumarin in mice.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 30;11(1):23482. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-02777-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34848814 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
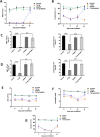
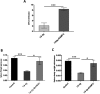
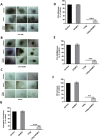
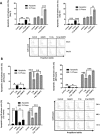
Protection of the hematopoietic system from radiation damage, and/or mitigation of hematopoietic injury are the two major strategies for developing medical countermeasure agents (MCM) to combat radiation-induced lethality. In the present study, we investigated the potential of 7, 8-diacetoxy-4-methylthiocoumarin (DAMTC) to ameliorate radiation-induced hematopoietic damage and the associated mortality following total body irradiation (TBI) in C57BL/6 mice. Administration of DAMTC 24 hours post TBI alleviated TBI-induced myelo-suppression and pancytopenia, by augmenting lymphocytes and WBCs in the peripheral blood of mice, while bone marrow (BM) cellularity was restored through enhanced proliferation of the stem cells. It stimulated multi-lineage expansion and differentiation of myeloid progenitors in the BM and induced proliferation of splenic progenitors thereby, facilitating hematopoietic re-population. DAMTC reduced the radiation-induced apoptotic and mitotic death in the hematopoietic compartment. Recruitment of pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages in spleen contributed to the immune-protection linked to the mitigation of hematopoietic injury. Recovery of the hematopoietic compartment correlated well with mitigation of mortality at a lethal dose of 9 Gy, leading to 80% animal survival. Present study establishes the potential of DAMTC to mitigate radiation-induced injury to the hematopoietic system by stimulating the re-population of stem cells from multiple lineages.
Figures




References
-
- Park E. et al. Dieckol rescues mice from lethal irradiation by accelerating hemopoiesis and curtailing immunosuppression. International Journal of Radiation Biology 86, 848–859 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Hall E. J. & Giaccia A. J. Radiobiology for the Radiobiologist. PA: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins 6th ed. Philadelphia (2006).
-
- Fliedner T. M. et al. Multi-organ involvement as a pathogenetic principle of the radiation syndromes: a study involving 110 case histories documented in SEARCH and classified as the bases of haematopoietic indicators of effect. British Journal of Radiology Supplement 27, 1–8 (2005).
-
- Hill R. P. Radiation effects on the respiratory system. Br. J. Radiol. Suppl. 27, 75–81 (2005).
-
- Moulder J. E. & Cohen E. P. Radiation-induced multi-organ involvement and failure: the contribution of radiation effects on the renal system. British Journal of Radiology Supplement 27, 82–88 (2005).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

