An evidence based hypothesis on the existence of two pathways of mitochondrial crista formation
- PMID: 27849155
- PMCID: PMC5138035
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.18853
An evidence based hypothesis on the existence of two pathways of mitochondrial crista formation
Abstract
Metabolic function and architecture of mitochondria are intimately linked. More than 60 years ago, cristae were discovered as characteristic elements of mitochondria that harbor the protein complexes of oxidative phosphorylation, but how cristae are formed, remained an open question. Here we present experimental results obtained with yeast that support a novel hypothesis on the existence of two molecular pathways that lead to the generation of lamellar and tubular cristae. Formation of lamellar cristae depends on the mitochondrial fusion machinery through a pathway that is required also for homeostasis of mitochondria and mitochondrial DNA. Tubular cristae are formed via invaginations of the inner boundary membrane by a pathway independent of the fusion machinery. Dimerization of the F1FO-ATP synthase and the presence of the MICOS complex are necessary for both pathways. The proposed hypothesis is suggested to apply also to higher eukaryotes, since the key components are conserved in structure and function throughout evolution.
Keywords: F1FO-ATP synthase; MICOS; Mgm1/Opa1; S. cerevisiae; biochemistry; cell biology; crista formation; mitochondria; mitochondrial fusion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures



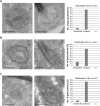
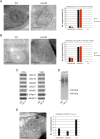
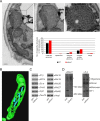
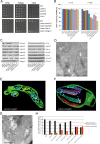
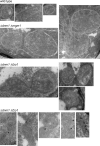
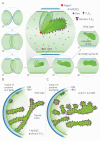
References
-
- Alkhaja AK, Jans DC, Nikolov M, Vukotic M, Lytovchenko O, Ludewig F, Schliebs W, Riedel D, Urlaub H, Jakobs S, Deckers M. MINOS1 is a conserved component of mitofilin complexes and required for mitochondrial function and cristae organization. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 2012;23:247–257. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-09-0774. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

