Reduced Systolic Volume: Main Pathophysiological Mechanism in Patients with Orthostatic Intolerance?
- PMID: 27849259
- PMCID: PMC5102482
- DOI: 10.5935/abc.20160135
Reduced Systolic Volume: Main Pathophysiological Mechanism in Patients with Orthostatic Intolerance?
Abstract
Background: Orthostatic intolerance patients' pathophysiological mechanism is still obscure, contributing to the difficulty in their clinical management.
Objective: To investigate hemodynamic changes during tilt test in individuals with orthostatic intolerance symptoms, including syncope or near syncope.
Methods: Sixty-one patients who underwent tilt test at - 70° in the phase without vasodilators were divided into two groups. For data analysis, only the first 20 minutes of tilting were considered. Group I was made up of 33 patients who had an increase of total peripheral vascular resistance (TPVR) during orthostatic position; and Group II was made up of 28 patients with a decrease in TPVR (characterizing insufficient peripheral vascular resistance). The control group consisted of 24 healthy asymptomatic individuals. Hemodynamic parameters were obtained by a non-invasive hemodynamic monitor in three different moments (supine position, tilt 10' and tilt 20') adjusted for age.
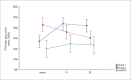
Results: In the supine position, systolic volume (SV) was significantly reduced in both Group II and I in comparison to the control group, respectively (66.4 ±14.9 ml vs. 81.8±14.8 ml vs. 101.5±24.2 ml; p<0.05). TPVR, however, was higher in Group II in comparison to Group I and controls, respectively (1750.5± 442 dyne.s/cm5 vs.1424±404 dyne.s/cm5 vs. 974.4±230 dyne.s/cm5; p<0.05). In the orthostatic position, at 10', there was repetition of findings, with lower absolute values of SV compared to controls (64.1±14.0 ml vs 65.5±11.3 ml vs 82.8±15.6 ml; p<0.05). TPVR, on the other hand, showed a relative drop in Group II, in comparison to Group I.
Conclusion: Reduced SV was consistently observed in the groups of patients with orthostatic intolerance in comparison to the control group. Two different responses to tilt test were observed: one group with elevated TPVR and another with a relative drop in TPVR, possibly suggesting a more severe failure of compensation mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential Conflict of Interest No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Orthostatic hypertension: An underestimated cause of orthostatic intolerance.Clin Neurophysiol. 2016 Apr;127(4):2102-7. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2015.12.017. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Clin Neurophysiol. 2016. PMID: 26806722
-
Autonomic activity and biomarker behavior in supine position and after passive postural stress in different orthostatic intolerance syndromes.Rev Port Cardiol. 2015 Sep;34(9):543-9. doi: 10.1016/j.repc.2015.03.009. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Rev Port Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 26320094
-
Tilt angles and positive response of head-up tilt test in children with orthostatic intolerance.Cardiol Young. 2015 Jan;25(1):76-80. doi: 10.1017/S1047951113001601. Epub 2013 Oct 15. Cardiol Young. 2015. PMID: 24124665
-
Neurological aspects of syncope and orthostatic intolerance.Med Clin North Am. 2009 Mar;93(2):427-49, ix. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2008.10.002. Med Clin North Am. 2009. PMID: 19272517 Review.
-
Increased Salt Intake for Orthostatic Intolerance Syndromes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Am J Med. 2020 Dec;133(12):1471-1478.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2020.05.028. Epub 2020 Jun 27. Am J Med. 2020. PMID: 32603788
Cited by
-
Efficacy of β-Blockers on Postural Tachycardia Syndrome in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Pediatr. 2019 Nov 7;7:460. doi: 10.3389/fped.2019.00460. eCollection 2019. Front Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31788462 Free PMC article.
-
Vasoactive Biomarkers in Patients With Vasovagal Syncope During Head-Up Tilt Test: A Case-Control Study.Clin Med Insights Cardiol. 2022 Aug 23;16:11795468221116848. doi: 10.1177/11795468221116848. eCollection 2022. Clin Med Insights Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 36046183 Free PMC article.
-
Dysautonomia: A Forgotten Condition - Part 1.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2021 Apr;116(4):814-835. doi: 10.36660/abc.20200420. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33886735 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese.
-
Differential hemodynamic adaptations to tilt test in patients with idiopathic atrial fibrillation.Physiol Rep. 2024 Jul;12(13):e16131. doi: 10.14814/phy2.16131. Physiol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38942728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kanjuwal K, Sheikh M, Karabin B, Kanjwal Y, Grubb BP. Neurocardiogenic syncope coexisting with postural orthostatic syndrome in patients suffering from orthostatic intolerance: a combined form of autonomic disfunction. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2011;34(5):549–554. - PubMed
-
- Medow MS, Stewart JM. The postural tachycardia syndrome. Cardiol Rev. 2007;15(2):67–75. - PubMed
-
- Fucà G, Dinelli M, Sazzani P, Scarfo S, Tossinari F, Alboni P. The venous system is the main determinant of Hypotension in patients with vasovagal syncope. Europace. 2006;8(10):839–845. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

