Melioration Learning in Two-Person Games
- PMID: 27851815
- PMCID: PMC5112854
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166708
Melioration Learning in Two-Person Games
Abstract
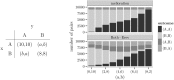
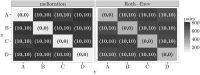
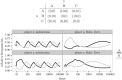
Melioration learning is an empirically well-grounded model of reinforcement learning. By means of computer simulations, this paper derives predictions for several repeatedly played two-person games from this model. The results indicate a likely convergence to a pure Nash equilibrium of the game. If no pure equilibrium exists, the relative frequencies of choice may approach the predictions of the mixed Nash equilibrium. Yet in some games, no stable state is reached.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
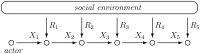

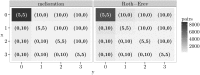

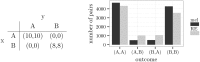
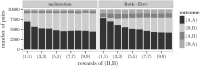


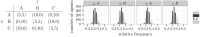


References
-
- Young HP. Strategic Learning and its Limits. New York: Oxford University Press; 2004. 10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199269181.001.0001 - DOI
-
- Hart S, Mas-Colell A. Uncoupled dynamics do not lead to Nash equilibrium. The American Economic Review. 2003;93(5):1830–1836. 10.1257/000282803322655581 - DOI
-
- Foster DP, Young HP. Regret testing: Learning to play Nash equilibrium without knowing you have an opponent. Theoretical Economics. 2006;1(3):341–367.
-
- Babichenko Y. Completely uncoupled dynamics and Nash equilibria. Games and Economic Behavior. 2012;76(1):1–14. 10.1016/j.geb.2012.06.004 - DOI
-
- Germano F, Lugosi G. Global Nash convergence of Foster and Young’s regret testing. Games and Economic Behavior. 2007;60(1):135–154.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

