Systemic cisplatin exposure during infancy and adolescence causes impaired cognitive function in adulthood
- PMID: 27851909
- PMCID: PMC5332150
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.11.013
Systemic cisplatin exposure during infancy and adolescence causes impaired cognitive function in adulthood
Abstract
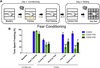
Cancer survivors diagnosed during infancy and adolescence may be at risk for chemotherapy-related cognitive impairments (CRCI), however the effects of pediatric chemotherapy treatment on adulthood cognitive function are not well understood. Impairments in memory, attention and executive function affect 15-50% of childhood leukemia survivors related to methotrexate exposure. Systemic cisplatin is used to treat a variety of childhood and adult cancers, yet the risk and extent of cognitive impairment due to platinum-based chemotherapy in pediatric patients is unknown. Systemic cisplatin penetrates the CNS, induces hippocampal synaptic damage, and leads to neuronal and neural stem/progenitor cell (NSC) loss. Survivors of non-leukemic cancers may be at risk for significant cognitive impairment related to cisplatin-driven neurotoxicity. We sought to examine the long-term effects of systemic cisplatin administration on cognitive function when administered during infancy and adolescence in a rat model. We performed cognitive testing in adult rats exposed to systemic cisplatin during either infancy or adolescence. Rats treated as adolescents showed significantly poor retrieval of a novel object as compared to controls. Further, cisplatin-treated infants and adolescents showed poor contextual discrimination as compared to controls, and an impaired response to cued fear conditioning. Ultimately, systemic cisplatin exposure resulted in more profound impairments in cognitive function in rats treated during adolescence than in those treated during infancy. Further, exposure to cisplatin during adolescence affected both hippocampus and amygdala dependent cognitive function, suggesting a more global cognitive dysfunction at this age.
Keywords: Chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment (CRCI); Cisplatin (CDDP); Memory; Pediatric.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
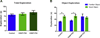
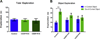
References
-
- Hodgson KD, Hutchinson AD, Wilson CJ, Nettelbeck T. A meta-analysis of the effects of chemotherapy on cognition in patients with cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2013;39:297–304. - PubMed
-
- Myers JS. Chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment: the breast cancer experience. Oncol. Nurs. Forum. 2012;39:E31–E40. - PubMed
-
- Dietrich J, Monje M, Wefel J, Meyers C. Clinical patterns and biological correlates of cognitive dysfunction associated with cancer therapy. Oncologist. 2008;13:1285–1295. - PubMed
-
- Anderson FS, Kunin-Batson AS. Neurocognitive late effects of chemotherapyin children: the past 10 years of research on brain structure and function. Pediatr. Blood Cancer. 2009;52:159–164. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

