Cargo Transport by Two Coupled Myosin Va Motors on Actin Filaments and Bundles
- PMID: 27851945
- PMCID: PMC5112936
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.09.046
Cargo Transport by Two Coupled Myosin Va Motors on Actin Filaments and Bundles
Abstract
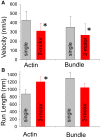
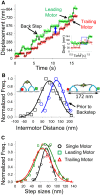
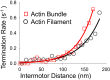
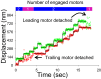
Myosin Va (myoVa) is a processive, actin-based molecular motor essential for intracellular cargo transport. When a cargo is transported by an ensemble of myoVa motors, each motor faces significant physical barriers and directional challenges created by the complex actin cytoskeleton, a network of actin filaments and actin bundles. The principles that govern the interaction of multiple motors attached to the same cargo are still poorly understood. To understand the mechanical interactions between multiple motors, we developed a simple in vitro model in which two individual myoVa motors labeled with different-colored Qdots are linked via a third Qdot that acts as a cargo. The velocity of this two-motor complex was reduced by 27% as compared to a single motor, whereas run length was increased by only 37%, much less than expected from multimotor transport models. Therefore, at low ATP, which allowed us to identify individual motor steps, we investigated the intermotor dynamics within the two-motor complex. The randomness of stepping leads to a buildup of tension in the linkage between motors-which in turn slows down the leading motor-and increases the frequency of backward steps and the detachment rate. We establish a direct relationship between the velocity reduction and the distribution of intermotor distances. The analysis of run lengths and dwell times for the two-motor complex, which has only one motor engaged with the actin track, reveals that half of the runs are terminated by almost simultaneous detachment of both motors. This finding challenges the assumptions of conventional multimotor models based on consecutive motor detachment. Similar, but even more drastic, results were observed with two-motor complexes on actin bundles, which showed a run length that was even shorter than that of a single motor.
Copyright © 2016 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Small teams of myosin Vc motors coordinate their stepping for efficient cargo transport on actin bundles.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jun 30;292(26):10998-11008. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.780791. Epub 2017 May 5. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28476885 Free PMC article.
-
More than just a cargo adapter, melanophilin prolongs and slows processive runs of myosin Va.J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 11;288(41):29313-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.476929. Epub 2013 Aug 26. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23979131 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin VI has a one track mind versus myosin Va when moving on actin bundles or at an intersection.Traffic. 2013 Jan;14(1):70-81. doi: 10.1111/tra.12017. Epub 2012 Oct 30. Traffic. 2013. PMID: 23046080 Free PMC article.
-
Vesicle transport: the role of actin filaments and myosin motors.Microsc Res Tech. 1999 Oct 15;47(2):93-106. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0029(19991015)47:2<93::AID-JEMT2>3.0.CO;2-P. Microsc Res Tech. 1999. PMID: 10523788 Review.
-
Cargo recognition and cargo-mediated regulation of unconventional myosins.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Oct 21;47(10):3061-70. doi: 10.1021/ar500216z. Epub 2014 Sep 17. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 25230296 Review.
Cited by
-
Active cargo positioning in antiparallel transport networks.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Jul 23;116(30):14835-14842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1900416116. Epub 2019 Jul 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31289230 Free PMC article.
-
Small teams of myosin Vc motors coordinate their stepping for efficient cargo transport on actin bundles.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jun 30;292(26):10998-11008. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.780791. Epub 2017 May 5. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28476885 Free PMC article.
-
Polarity sorting of actin filaments by motor-driven cargo transport.Biophys J. 2025 Feb 18;124(4):704-716. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2025.01.007. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Biophys J. 2025. PMID: 39827370
-
Cargo properties play a critical role in myosin Va-driven cargo transport along actin filaments.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021 Dec 31;29:101194. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.101194. eCollection 2022 Mar. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021. PMID: 35024461 Free PMC article.
-
Actin bundle architecture and mechanics regulate myosin II force generation.Biophys J. 2021 May 18;120(10):1957-1970. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2021.03.026. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Biophys J. 2021. PMID: 33798565 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu X.S., Rao K., Hammer J.A., 3rd Identification of an organelle receptor for myosin-Va. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002;4:271–278. - PubMed
-
- Hammer J.A., 3rd, Sellers J.R. Walking to work: roles for class V myosins as cargo transporters. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011;13:13–26. - PubMed
-
- Brozzi F., Diraison F., Váradi A. Molecular mechanism of myosin Va recruitment to dense core secretory granules. Traffic. 2012;13:54–69. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

