SRSF10 Connects DNA Damage to the Alternative Splicing of Transcripts Encoding Apoptosis, Cell-Cycle Control, and DNA Repair Factors
- PMID: 27851963
- PMCID: PMC5483951
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.10.071
SRSF10 Connects DNA Damage to the Alternative Splicing of Transcripts Encoding Apoptosis, Cell-Cycle Control, and DNA Repair Factors
Abstract
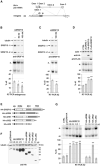
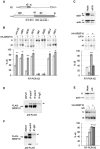
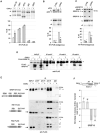
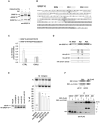
RNA binding proteins and signaling components control the production of pro-death and pro-survival splice variants of Bcl-x. DNA damage promoted by oxaliplatin increases the level of pro-apoptotic Bcl-xS in an ATM/CHK2-dependent manner, but how this shift is enforced is not known. Here, we show that in normally growing cells, when the 5' splice site of Bcl-xS is largely repressed, SRSF10 partially relieves repression and interacts with repressor hnRNP K and stimulatory hnRNP F/H proteins. Oxaliplatin abrogates the interaction of SRSF10 with hnRNP F/H and decreases the association of SRSF10 and hnRNP K with the Bcl-x pre-mRNA. Dephosphorylation of SRSF10 is linked with these changes. A broader analysis reveals that DNA damage co-opts SRSF10 to control splicing decisions in transcripts encoding components involved in DNA repair, cell-cycle control, and apoptosis. DNA damage therefore alters the interactions between splicing regulators to elicit a splicing response that determines cell fate.
Keywords: DNA damage response; DNA repair; RNA binding proteins; SR proteins; alternative splicing; apoptosis; cell cycle; cell fate; hnRNP proteins; oxaliplatin; phosphorylation; splicing.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Almeida LO, Garcia CB, Matos-Silva FA, Curti C, Leopoldino AM. Accumulated SET protein up-regulates and interacts with hnRNPK, increasing its binding to nucleic acids, the Bcl-xS repression, and cellular proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;445:196–202. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

