Key clinical benefits of neuroimaging at 7T
- PMID: 27851995
- PMCID: PMC5832016
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.11.031
Key clinical benefits of neuroimaging at 7T
Abstract
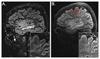
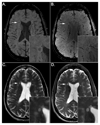
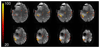
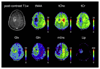
The growing interest in ultra-high field MRI, with more than 35.000 MR examinations already performed at 7T, is related to improved clinical results with regard to morphological as well as functional and metabolic capabilities. Since the signal-to-noise ratio increases with the field strength of the MR scanner, the most evident application at 7T is to gain higher spatial resolution in the brain compared to 3T. Of specific clinical interest for neuro applications is the cerebral cortex at 7T, for the detection of changes in cortical structure, like the visualization of cortical microinfarcts and cortical plaques in Multiple Sclerosis. In imaging of the hippocampus, even subfields of the internal hippocampal anatomy and pathology may be visualized with excellent spatial resolution. Using Susceptibility Weighted Imaging, the plaque-vessel relationship and iron accumulations in Multiple Sclerosis can be visualized, which may provide a prognostic factor of disease. Vascular imaging is a highly promising field for 7T which is dealt with in a separate dedicated article in this special issue. The static and dynamic blood oxygenation level-dependent contrast also increases with the field strength, which significantly improves the accuracy of pre-surgical evaluation of vital brain areas before tumor removal. Improvement in acquisition and hardware technology have also resulted in an increasing number of MR spectroscopic imaging studies in patients at 7T. More recent parallel imaging and short-TR acquisition approaches have overcome the limitations of scan time and spatial resolution, thereby allowing imaging matrix sizes of up to 128×128. The benefits of these acquisition approaches for investigation of brain tumors and Multiple Sclerosis have been shown recently. Together, these possibilities demonstrate the feasibility and advantages of conducting routine diagnostic imaging and clinical research at 7T.
Keywords: 7T; MRSI; clinical; fMRI; high resolution; neuroimaging.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

