Transcriptomic-metabolomic reprogramming in EGFR-mutant NSCLC early adaptive drug escape linking TGFβ2-bioenergetics-mitochondrial priming
- PMID: 27852038
- PMCID: PMC5347670
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.13307
Transcriptomic-metabolomic reprogramming in EGFR-mutant NSCLC early adaptive drug escape linking TGFβ2-bioenergetics-mitochondrial priming
Abstract
The impact of EGFR-mutant NSCLC precision therapy is limited by acquired resistance despite initial excellent response. Classic studies of EGFR-mutant clinical resistance to precision therapy were based on tumor rebiopsies late during clinical tumor progression on therapy. Here, we characterized a novel non-mutational early adaptive drug-escape in EGFR-mutant lung tumor cells only days after therapy initiation, that is MET-independent. The drug-escape cell states were analyzed by integrated transcriptomic and metabolomics profiling uncovering a central role for autocrine TGFβ2 in mediating cellular plasticity through profound cellular adaptive Omics reprogramming, with common mechanistic link to prosurvival mitochondrial priming. Cells undergoing early adaptive drug escape are in proliferative-metabolic quiescent, with enhanced EMT-ness and stem cell signaling, exhibiting global bioenergetics suppression including reverse Warburg, and are susceptible to glutamine deprivation and TGFβ2 inhibition. Our study further supports a preemptive therapeutic targeting of bioenergetics and mitochondrial priming to impact early drug-escape emergence using EGFR precision inhibitor combined with broad BH3-mimetic to interrupt BCL-2/BCL-xL together, but not BCL-2 alone.
Keywords: EGFR; drug escape; inhibitor; lung cancer; resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
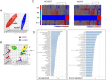
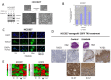
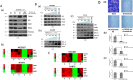



Comment in
-
Characterizing the last holdouts.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 21;8(8):12542-12543. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15090. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28177913 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Polyphyllin I Overcomes EMT-Associated Resistance to Erlotinib in Lung Cancer Cells via IL-6/STAT3 Pathway Inhibition.Biol Pharm Bull. 2017 Aug 1;40(8):1306-1313. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b17-00271. Epub 2017 May 18. Biol Pharm Bull. 2017. PMID: 28515374
-
Implication of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in IGF1R-induced resistance to EGFR-TKIs in advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 29;6(42):44332-45. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6293. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26554308 Free PMC article.
-
Intratumoral Heterogeneity in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Results in Divergent Resistance Mechanisms in Response to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition.Cancer Res. 2015 Oct 15;75(20):4372-83. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-0377. Epub 2015 Aug 17. Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26282169 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of acquired resistance to third-generation EGFR-TKIs in EGFR T790M-mutant lung cancer.Ann Oncol. 2018 Jan 1;29(suppl_1):i28-i37. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx705. Ann Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29462256 Review.
-
[Research Progress of the Role of EMT in EGFR-TKIs Resistance of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2018 Dec 20;21(12):907-911. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2018.12.08. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30591098 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Bax/Bcl-2 Cascade Is Regulated by the EGFR Pathway: Therapeutic Targeting of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 25;12:869672. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.869672. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35402265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysregulated Metabolism in EGFR-TKI Drug Resistant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review.Metabolites. 2022 Jul 14;12(7):644. doi: 10.3390/metabo12070644. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35888768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LCMD: Lung Cancer Metabolome Database.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Dec 7;20:65-78. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.12.002. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34976312 Free PMC article.
-
Autocrine TGF-β in Cancer: Review of the Literature and Caveats in Experimental Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 19;22(2):977. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020977. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33478130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TGFβ2-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and NF-κB pathway activation contribute to osimertinib resistance.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021 Mar;42(3):451-459. doi: 10.1038/s41401-020-0457-8. Epub 2020 Jul 16. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021. PMID: 32678313 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keedy VL, Temin S, Somerfield MR, Beasley MB, Johnson DH, McShane LM, Milton DT, Strawn JR, Wakelee HA, Giaccone G. American Society of Clinical Oncology provisional clinical opinion: epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) Mutation testing for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer considering first-line EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:2121–7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.31.8923. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, Feng J, Liu XQ, Wang C, Zhang S, Wang J, Zhou S, Ren S, Lu S, Zhang L, Hu C, et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:735–42. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70184-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tsao MS, Sakurada A, Cutz JC, Zhu CQ, Kamel-Reid S, Squire J, Lorimer I, Zhang T, Liu N, Daneshmand M, Marrano P, da Cunha Santos G, Lagarde A, et al. Erlotinib in lung cancer - molecular and clinical predictors of outcome. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:133–44. doi: 353/2/133 [pii] - PubMed
-
- Wang W, Li Q, Takeuchi S, Yamada T, Koizumi H, Nakamura T, Matsumoto K, Mukaida N, Nishioka Y, Sone S, Nakagawa T, Uenaka T, Yano S. Met kinase inhibitor E7050 reverses three different mechanisms of hepatocyte growth factor-induced tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in EGFR mutant lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:1663–71. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1171. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

