Depression induces poor prognosis associates with the down-regulation brain derived neurotrophic factor of serum in advanced small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 27852063
- PMCID: PMC5349890
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.13291
Depression induces poor prognosis associates with the down-regulation brain derived neurotrophic factor of serum in advanced small cell lung cancer
Abstract
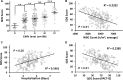
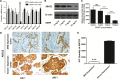
Patients with lung cancer often experience a state of depression, and these conditions may severely affect their quality of life (QoL) and prescription compliance. The current study was conducted to delineate the complex links between depression and the prognosis of patients with small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and the underlying mechanism was also explored.186 patients who received platinum-based chemotherapy for newly diagnosed stage III or stage IV SCLC were enrolled. The Self-Rating Depression Scale (SDS) questionnaire was completed the day before the start of chemotherapy to assess the depression status of the patients. Patients with stage IV SCLC or lower BMI have higher depression scores. In terms of the adverse effects of chemotherapy, depression severely decreases patient tolerance to chemotherapy and their QoL score (R2 = 0.2385) and is also associated with severe vomiting (P < 0.001), leukopenia (R2 = 0.2332), and prolonged hospital stay (R2 = 0.1961). More importantly, severe depression reduces the PFS (R2 = 0.1943) and OS (P < 0.01) of the patients. We found that patients with severe depression displayed a downregulated level of serum BDNF and that the level of serum BDNF was highly correlated with the OS of the patients (R2 = 0.2292). Using the MTT cell viability assay in vitro, we observed that cotreatment with BDNF clearly enhanced the chemosensitivity of NCI-H69 tumor cells to Cisplatin and induced the downregulation of ABCG2.Based on this evidence, it appears that a relationship does exist between depression and prognosis in SCLC and that the mechanism by which depression affects prognosis is achieved via the downregulation of BDNF expression.
Keywords: ABCG2; brain derived neurotrophic factor; chemotherapy; depression; small cell lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Outcomes of Platinum-Sensitive Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated With Platinum/Etoposide Rechallenge: A Multi-Institutional Retrospective Analysis.Clin Lung Cancer. 2015 Nov;16(6):e223-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2015.04.006. Epub 2015 Apr 24. Clin Lung Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25983005
-
Downregulation of HOXA1 gene affects small cell lung cancer cell survival and chemoresistance under the regulation of miR-100.Eur J Cancer. 2014 May;50(8):1541-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2014.01.024. Epub 2014 Feb 19. Eur J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24559685
-
Expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its receptor TrkB is associated with poor prognosis and a malignant phenotype in small cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2018 Jun;120:98-107. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.04.005. Epub 2018 Apr 5. Lung Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29748024
-
Cholesterol reduces the sensitivity to platinum-based chemotherapy via upregulating ABCG2 in lung adenocarcinoma.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Feb 20;457(4):614-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.01.035. Epub 2015 Jan 17. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 25603057
-
Role of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Small Cell Lung Cancer.Am J Ther. 2018 May/Jun;25(3):e349-e356. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0000000000000686. Am J Ther. 2018. PMID: 29722737 Review.
Cited by
-
High expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma is associated with intraneural invasion and unfavorable prognosis.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017 Oct 1;10(10):10399-10405. eCollection 2017. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017. PMID: 31966376 Free PMC article.
-
Growth of malignant extracranial tumors alters microRNAome in the prefrontal cortex of TumorGraft mice.Oncotarget. 2017 Aug 3;8(51):88276-88293. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19835. eCollection 2017 Oct 24. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29179434 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of BDNF/TrkB Signaling in Cardiovascular Diseases.Life (Basel). 2021 Jan 19;11(1):70. doi: 10.3390/life11010070. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33477900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of risk of depressive symptoms in menopausal women based on hot flash and sweating symptoms: a multicentre study.Clin Interv Aging. 2017 Nov 23;12:1993-2001. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S148688. eCollection 2017. Clin Interv Aging. 2017. PMID: 29200839 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Sympathovagal Imbalance with Increased Inflammation and Impaired Adaptive Immunity in Bladder Cancer Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 27;25(23):12765. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312765. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684475 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Faller H, Weis J, Koch U, Brahler E, Harter M, Keller M, Schulz H, Wegscheider K, Boehncke A, Hund B, Reuter K, Richard M, Sehner S, et al. Utilization of professional psychological care in a large German sample of cancer patients. Psychooncology. 2016 - PubMed
-
- Wu XN, Su D, Li HP, Wang WL, Wu WQ, Yang YJ, Yu FL, Zhang JP. Relationship between the depression status of patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer and their family members in China. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2013;17:668–672. - PubMed
-
- Kitagawa R, Yasui-Furukori N, Tsushima T, Kaneko S, Fukuda I. Depression increases the length of hospitalization for patients undergoing thoracic surgery: a preliminary study. Psychosomatics. 2011;52:428–432. - PubMed
-
- Buccheri R, Trygstad L, Buffum MD, Gerlock AA. Developing an evidence-based practice for psychiatric nursing. J Psychosoc Nurs Ment Health Serv. 2010;48:3–5. - PubMed
-
- Kaasa S, Mastekaasa A, Lund E. Prognostic factors for patients with inoperable non-small cell lung cancer, limited disease. The importance of patients’ subjective experience of disease and psychosocial well-being. Radiother Oncol. 1989;15:235–242. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

