Anti-tumor activity of high-dose EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor and sequential docetaxel in wild type EGFR non-small cell lung cancer cell nude mouse xenografts
- PMID: 27852073
- PMCID: PMC5354720
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.13327
Anti-tumor activity of high-dose EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor and sequential docetaxel in wild type EGFR non-small cell lung cancer cell nude mouse xenografts
Abstract
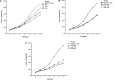
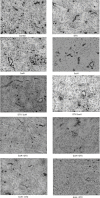
Treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with wild-type epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is still a challenge. This study explored antitumor activity of high-dose icotinib (an EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor) plus sequential docetaxel against wild-type EGFR NSCLC cells-generated nude mouse xenografts. Nude mice were subcutaneously injected with wild-type EGFR NSCLC A549 cells and divided into different groups for 3-week treatment. Tumor xenograft volumes were monitored and recorded, and at the end of experiments, tumor xenografts were removed for Western blot and immunohistochemical analyses. Compared to control groups (negative control, regular-dose icotinib [IcoR], high-dose icotinib [IcoH], and docetaxel [DTX]) and regular icotinib dose (60 mg/kg) with docetaxel, treatment of mice with a high-dose (1200 mg/kg) of icotinib plus sequential docetaxel for 3 weeks (IcoH-DTX) had an additive effect on suppression of tumor xenograft size and volume (P < 0.05). Icotinib-containing treatments markedly reduced phosphorylation of EGFR, mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK), and protein kinase B (Akt), but only the high-dose icotinib-containing treatments showed an additive effect on CD34 inhibition (P < 0.05), an indication of reduced microvessel density in tumor xenografts. Moreover, high-dose icotinib plus docetaxel had a similar effect on mouse weight loss (a common way to measure adverse reactions in mice), compared to the other treatment combinations. The study indicate that the high dose of icotinib plus sequential docetaxel (IcoH-DTX) have an additive effect on suppressing the growth of wild-type EGFR NSCLC cell nude mouse xenografts, possibly through microvessel density reduction. Future clinical trials are needed to confirm the findings of this study.
Keywords: docetaxel; epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR); icotinib; non-small cell lung cancer; nude mouse xenografts.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synergistic Inhibition of Thalidomide and Icotinib on Human Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinomas Through ERK and AKT Signaling.Med Sci Monit. 2018 May 15;24:3193-3203. doi: 10.12659/MSM.909977. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 29763936 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of combined icotinib and pemetrexed in EGFR mutant lung adenocarcinoma cell line xenografts.Thorac Cancer. 2018 Sep;9(9):1156-1165. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12818. Epub 2018 Jul 26. Thorac Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30047610 Free PMC article.
-
Lymecycline reverses acquired EGFR-TKI resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer by targeting GRB2.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Sep;159:105007. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105007. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32561477
-
Icotinib, a selective EGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer.Future Oncol. 2015;11(3):385-97. doi: 10.2217/fon.14.249. Future Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25675121 Review.
-
Clinical efficacy of icotinib in lung cancer patients with different EGFR mutation status: a meta-analysis.Oncotarget. 2017 May 16;8(20):33961-33971. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15475. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28430623 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Gefitinib Combined with Chemotherapy in Patients with Advanced NSCLC: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Jan 15;15:637-644. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S342917. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35068940 Free PMC article.
-
Vaping, Environmental Toxicants Exposure, and Lung Cancer Risk.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Sep 12;15(18):4525. doi: 10.3390/cancers15184525. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37760496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Self-Assembled Nanomicellar Formulation of Docetaxel as a Potential Breast Cancer Chemotherapeutic System.Life (Basel). 2022 Mar 27;12(4):485. doi: 10.3390/life12040485. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35454976 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Docetaxel Combined with Icotinib on Serum Tumor Markers and Quality of Life of Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Iran J Public Health. 2020 Oct;49(10):1885-1893. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v49i10.4691. Iran J Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33346209 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-218-5p/EGFR Signaling in Arsenic-Induced Carcinogenesis.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 14;15(4):1204. doi: 10.3390/cancers15041204. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831545 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Lam WK, White NW, Chan-Yeung MM. Lung cancer epidemiology and risk factors in Asia and Africa. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2004;8:1045–1057. - PubMed
-
- Youlden DR, Cramb SM, Baade PD. The International Epidemiology of Lung Cancer: geographical distribution and secular trends. J Thorac Oncol. 2008;3:819–831. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- National Cancer Institute Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment (PDQ®) http://www.cancer.gov/types/lung/hp/non-small-cell-lung-treatment-pdq#se..., Retrieved on May 18, 2016.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

