A discrete event simulation model of clinical and operating room efficiency outcomes of sugammadex versus neostigmine for neuromuscular block reversal in Canada
- PMID: 27852231
- PMCID: PMC5112647
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-016-0281-3
A discrete event simulation model of clinical and operating room efficiency outcomes of sugammadex versus neostigmine for neuromuscular block reversal in Canada
Abstract
Background: The objective of this analysis is to explore potential impact on operating room (OR) efficiency and incidence of residual neuromuscular blockade (RNMB) with use of sugammadex (Bridion™, Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ USA) versus neostigmine for neuromuscular block reversal in Canada.
Methods: A discrete event simulation (DES) model was developed to compare ORs using either neostigmine or sugammadex for NMB reversal over one month. Selected inputs included OR procedure and turnover times, hospital policies for paid staff overtime and procedural cancellations due to OR time over-run, and reductions in RNMB and associated complications with sugammadex use. Trials show sugammadex's impact on OR time and RNMB varies by whether full neuromuscular recovery (train-of-four ratio ≥0.9) is verified prior to extubation in the OR. Scenarios were therefore evaluated reflecting varied assumptions for neuromuscular reversal practices.
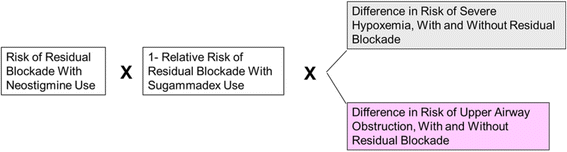
Results: With use of moderate neuromuscular block, when full neuromuscular recovery is verified prior to extubation (93 procedures performed with sugammadex, 91 with neostigmine), use of sugammadex versus neostigmine avoided 2.4 procedural cancellations due to OR time over-run and 33.5 h of paid staff overtime, while saving an average of 62 min per OR day. No difference was observed between comparators for these endpoints in the scenario when full neuromuscular recovery was not verified prior to extubation, however, per procedure risk of RNMB at extubation was reduced from 60% to 4% (reflecting 51 cases prevented), with associated reductions in risks of hypoxemia (12 cases avoided) and upper airway obstruction (23 cases avoided). Sugammadex impact in reversing deep neuromuscular block was evaluated in an exploratory analysis. When it was hypothetically assumed that 30 min of OR time were saved per procedure, the number of paid hours of staff over-time dropped from 84.1 to 32.0, with a 93% reduction in the per patient risk of residual blockade.
Conclusions: In clinical practice within Canada, for the majority of patients currently managed with moderate neuromuscular block, the principal impact of substituting sugammadex for neostigmine is likely to be a reduction in the risk of residual blockade and associated complications. For patients maintained at a deep level of block to the end of the procedure, sugammadex is likely to both enhance OR efficiency and reduce residual block complications.
Keywords: Efficiency; Neostigmine; Neuromuscular block; Operating room; Residual blockade; Reversal; Sugammadex.
Figures
References
-
- A randomized, safety-assessor blinded trial comparing 4.0 Mg.Kg-1 Sugammadex with placebo in adult subjects scheduled for surgery requiring profound neuromuscular blockade. Clinical Trial Report on Protocol 19.4.316. Merck & Co., Inc. 2010.
-
- Blobner M, Eriksson LI, Scholz J, Motsch J, Della RG, Prins ME. Reversal of rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade with sugammadex compared with neostigmine during sevoflurane anaesthesia: results of a randomised, controlled trial. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2010;27:874–81. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0b013e32833d56b7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources