Enrichment dynamics of Listeria monocytogenes and the associated microbiome from naturally contaminated ice cream linked to a listeriosis outbreak
- PMID: 27852235
- PMCID: PMC5112668
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-016-0894-1
Enrichment dynamics of Listeria monocytogenes and the associated microbiome from naturally contaminated ice cream linked to a listeriosis outbreak
Abstract
Background: Microbiota that co-enrich during efforts to recover pathogens from foodborne outbreaks interfere with efficient detection and recovery. Here, dynamics of co-enriching microbiota during recovery of Listeria monocytogenes from naturally contaminated ice cream samples linked to an outbreak are described for three different initial enrichment formulations used by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the International Organization of Standardization (ISO), and the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Enrichment cultures were analyzed using DNA extraction and sequencing from samples taken every 4 h throughout 48 h of enrichment. Resphera Insight and CosmosID analysis tools were employed for high-resolution profiling of 16S rRNA amplicons and whole genome shotgun data, respectively.
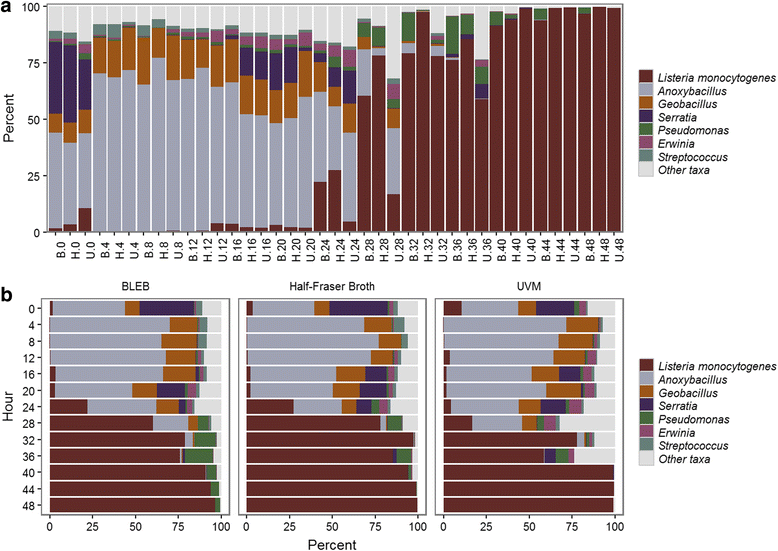
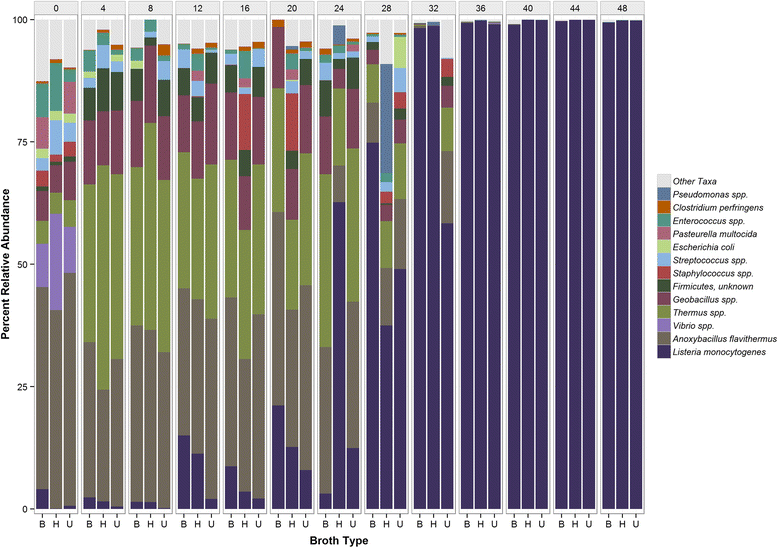
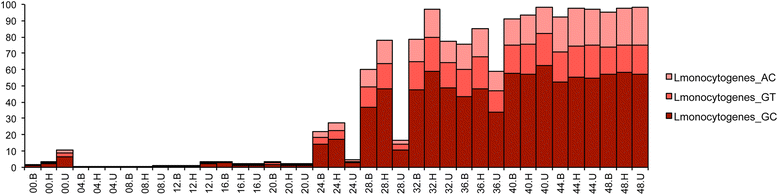
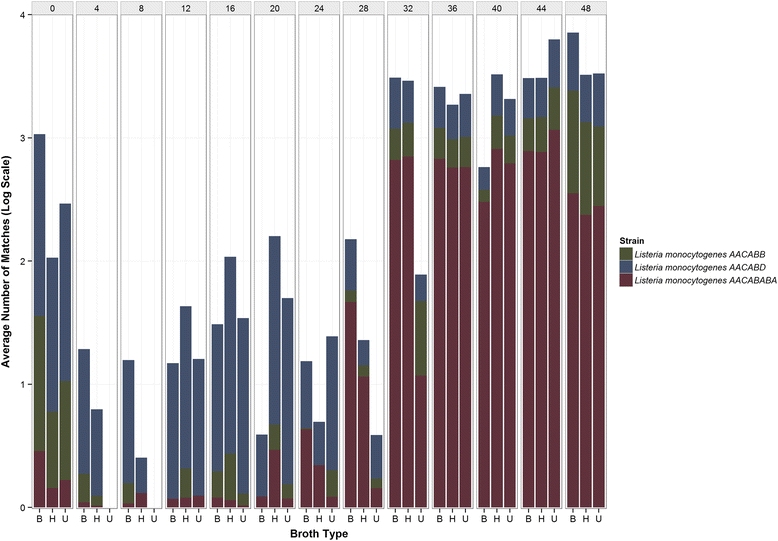
Results: During enrichment, other bacterial taxa were identified, including Anoxybacillus, Geobacillus, Serratia, Pseudomonas, Erwinia, and Streptococcus spp. Surprisingly, incidence of L. monocytogenes was proportionally greater at hour 0 than when tested 4, 8, and 12 h later with all three enrichment schemes. The corresponding increase in Anoxybacillus and Geobacillus spp.indicated these taxa co-enriched in competition with L. monocytogenes during early enrichment hours. L. monocytogenes became dominant after 24 h in all three enrichments. DNA sequences obtained from shotgun metagenomic data of Listeria monocytogenes at 48 h were assembled to produce a consensus draft genome which appeared to have a similar tracking utility to pure culture isolates of L. monocytogenes.
Conclusions: All three methods performed equally well for enrichment of Listeria monocytogenes. The observation of potential competitive exclusion of L. mono by Anoxybacillus and Geobacillus in early enrichment hours provided novel information that may be used to further optimize enrichment formulations. Application of Resphera Insight for high-resolution analysis of 16S amplicon sequences accurately identified L. monocytogenes. Both shotgun and 16S rRNA data supported the presence of three slightly variable genomes of L. monocytogenes. Moreover, the draft assembly of a consensus genome of L. monocytogenes from shotgun metagenomic data demonstrated the potential utility of this approach to expedite trace-back of outbreak-associated strains, although further validation will be needed to confirm this utility.
Keywords: 16S rRNA; Buffered Listeria enrichment broth (BLEB); Co-enriching bacteria; Enrichment; FDA; Fraser broth (FB); Half-Fraser broth (HFB); ISO; Ice cream; Listeria monocytogenes; Microbiota; NGS; Next-generation sequencing; Shotgun metagenomics; USDA; University of Vermont modified broth (UVM).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quasimetagenomic source tracking of Listeria monocytogenes from naturally contaminated ice cream.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Jan 29;20(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4747-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 31996135 Free PMC article.
-
Short communication: Long-term -20°C survival of Listeria monocytogenes in artificially and process-contaminated ice cream involved in an outbreak of listeriosis.J Dairy Sci. 2020 Jan;103(1):172-175. doi: 10.3168/jds.2019-16774. Epub 2019 Nov 6. J Dairy Sci. 2020. PMID: 31704018
-
Assessing the genome level diversity of Listeria monocytogenes from contaminated ice cream and environmental samples linked to a listeriosis outbreak in the United States.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 6;12(2):e0171389. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171389. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28166293 Free PMC article.
-
Listeria monocytogenes Illness and Deaths Associated With Ongoing Contamination of a Multiregional Brand of Ice Cream Products, United States, 2010-2015.Clin Infect Dis. 2023 Jan 6;76(1):89-95. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciac550. Clin Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 35797187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whole genome sequencing uses for foodborne contamination and compliance: Discovery of an emerging contamination event in an ice cream facility using whole genome sequencing.Infect Genet Evol. 2019 Sep;73:214-220. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2019.04.026. Epub 2019 Apr 27. Infect Genet Evol. 2019. PMID: 31039448 Review.
Cited by
-
Prior exposure to microcystin alters host gut resistome and is associated with dysregulated immune homeostasis in translatable mouse models.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 7;12(1):11516. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15708-3. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35799048 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiomes of commercially-available pine nuts and sesame seeds.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 21;16(6):e0252605. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252605. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34153055 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of a Standardized Oral Pomegranate Extract on the Gut Microbiome and Short-Chain Fatty Acids.Foods. 2023 Dec 19;13(1):15. doi: 10.3390/foods13010015. Foods. 2023. PMID: 38201042 Free PMC article.
-
Occurrence of Listeria spp. in Soft Cheese and Ice Cream: Effect of Probiotic Bifidobacterium spp. on Survival of Listeria monocytogenes in Soft Cheese.Foods. 2022 Oct 30;11(21):3443. doi: 10.3390/foods11213443. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36360056 Free PMC article.
-
Metagenomics of pasteurized and unpasteurized gouda cheese using targeted 16S rDNA sequencing.BMC Microbiol. 2018 Nov 19;18(1):189. doi: 10.1186/s12866-018-1323-4. BMC Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30453904 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murray EGD, Webb RA, Swann MBR. A disease of rabbits characterised by a large mononuclear leucocytosis, caused by a hitherto undescribed bacillus Bacterium monocytogenes (n.sp.) J Pathol Bacteriol. 1926;29(4):407–39. doi: 10.1002/path.1700290409. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

