SPRTN is a mammalian DNA-binding metalloprotease that resolves DNA-protein crosslinks
- PMID: 27852435
- PMCID: PMC5127644
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.21491
SPRTN is a mammalian DNA-binding metalloprotease that resolves DNA-protein crosslinks
Abstract
Ruijs-Aalfs syndrome is a segmental progeroid syndrome resulting from mutations in the SPRTN gene. Cells derived from patients with SPRTN mutations elicit genomic instability and people afflicted with this syndrome developed hepatocellular carcinoma. Here we describe the molecular mechanism by which SPRTN contributes to genome stability and normal cellular homeostasis. We show that SPRTN is a DNA-dependent mammalian protease required for resolving cytotoxic DNA-protein crosslinks (DPCs)- a function that had only been attributed to the metalloprotease Wss1 in budding yeast. We provide genetic evidence that SPRTN and Wss1 function distinctly in vivo to resolve DPCs. Upon DNA and ubiquitin binding, SPRTN can elicit proteolytic activity; cleaving DPC substrates and itself. SPRTN null cells or cells derived from patients with Ruijs-Aalfs syndrome are impaired in the resolution of covalent DPCs in vivo. Collectively, SPRTN is a mammalian protease required for resolving DNA-protein crosslinks in vivo whose function is compromised in Ruijs-Aalfs syndrome patients.
Keywords: DNA replication; DNA-protein crosslinks; Dvc1; E. coli; Ruijs-Aalfs syndrome; S. cerevisiae; SPARTAN; SPRTN; Topoisomerase; aging; biochemistry; c1orf124; cell biology; human; metalloprotease; mouse; progeria; ubiquitination.
Conflict of interest statement
ID: Senior editor, eLife. The other authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
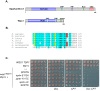
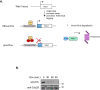
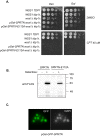










Similar articles
-
Metalloprotease SPRTN/DVC1 Orchestrates Replication-Coupled DNA-Protein Crosslink Repair.Mol Cell. 2016 Nov 17;64(4):704-719. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.09.032. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27871366 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism and Regulation of DNA-Protein Crosslink Repair by the DNA-Dependent Metalloprotease SPRTN.Mol Cell. 2016 Nov 17;64(4):688-703. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.09.031. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27871365 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms and Regulation of DNA-Protein Crosslink Repair During DNA Replication by SPRTN Protease.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Jun 15;9:916697. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.916697. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35782873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural Insight into DNA-Dependent Activation of Human Metalloprotease Spartan.Cell Rep. 2019 Mar 19;26(12):3336-3346.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.02.082. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 30893605
-
DNA-Protein Crosslinks and Their Resolution.Annu Rev Biochem. 2022 Jun 21;91:157-181. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-032620-105820. Epub 2022 Mar 18. Annu Rev Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35303790 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of damage tolerance and repair during DNA replication.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Apr 6;49(6):3033-3047. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab101. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33693881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maternal Haploid, a Metalloprotease Enriched at the Largest Satellite Repeat and Essential for Genome Integrity in Drosophila Embryos.Genetics. 2017 Aug;206(4):1829-1839. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.200949. Epub 2017 Jun 14. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28615282 Free PMC article.
-
Aldehyde-Associated Mutagenesis─Current State of Knowledge.Chem Res Toxicol. 2023 Jul 17;36(7):983-1001. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.3c00045. Epub 2023 Jun 26. Chem Res Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37363863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Excision repair of topoisomerase DNA-protein crosslinks (TOP-DPC).DNA Repair (Amst). 2020 May;89:102837. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2020.102837. Epub 2020 Mar 7. DNA Repair (Amst). 2020. PMID: 32200233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Replication-associated formation and repair of human topoisomerase IIIα cleavage complexes.Nat Commun. 2023 Apr 6;14(1):1925. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37498-6. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37024461 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

