Photoperiod Affects the Phenotype of Mitochondrial Complex I Mutants
- PMID: 27852950
- PMCID: PMC5210746
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.16.01484
Photoperiod Affects the Phenotype of Mitochondrial Complex I Mutants
Abstract
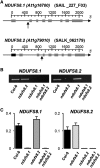
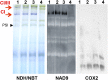
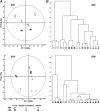
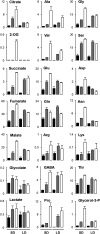
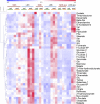
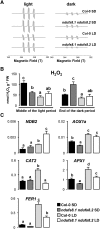
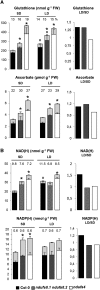
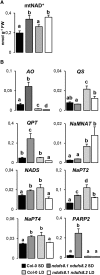
Plant mutants for genes encoding subunits of mitochondrial complex I (CI; NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase), the first enzyme of the respiratory chain, display various phenotypes depending on growth conditions. Here, we examined the impact of photoperiod, a major environmental factor controlling plant development, on two Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) CI mutants: a new insertion mutant interrupted in both ndufs8.1 and ndufs8.2 genes encoding the NDUFS8 subunit and the previously characterized ndufs4 CI mutant. In the long day (LD) condition, both ndufs8.1 and ndufs8.2 single mutants were indistinguishable from Columbia-0 at phenotypic and biochemical levels, whereas the ndufs8.1 ndufs8.2 double mutant was devoid of detectable holo-CI assembly/activity, showed higher alternative oxidase content/activity, and displayed a growth retardation phenotype similar to that of the ndufs4 mutant. Although growth was more affected in ndufs4 than in ndufs8.1 ndufs8.2 under the short day (SD) condition, both mutants displayed a similar impairment of growth acceleration after transfer to LD compared with the wild type. Untargeted and targeted metabolomics showed that overall metabolism was less responsive to the SD-to-LD transition in mutants than in the wild type. The typical LD acclimation of carbon and nitrogen assimilation as well as redox-related parameters was not observed in ndufs8.1 ndufs8 Similarly, NAD(H) content, which was higher in the SD condition in both mutants than in Columbia-0, did not adjust under LD We propose that altered redox homeostasis and NAD(H) content/redox state control the phenotype of CI mutants and photoperiod acclimation in Arabidopsis.
© 2017 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Ahmad M, Lin C, Cashmore AR (1995) Mutations throughout an Arabidopsis blue-light photoreceptor impair blue-light-responsive anthocyanin accumulation and inhibition of hypocotyl elongation. Plant J 8: 653–658 - PubMed
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, et al. (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301: 653–657 - PubMed
-
- Araújo WL, Nunes-Nesi A, Nikoloski Z, Sweetlove LJ, Fernie AR (2012) Metabolic control and regulation of the tricarboxylic acid cycle in photosynthetic and heterotrophic plant tissues. Plant Cell Environ 35: 1–21 - PubMed
-
- Becker B, Holtgrefe S, Jung S, Wunrau C, Kandlbinder A, Baier M, Dietz KJ, Backhausen JE, Scheibe R (2006) Influence of the photoperiod on redox regulation and stress responses in Arabidopsis thaliana L. (Heynh.) plants under long- and short-day conditions. Planta 224: 380–393 - PubMed
-
- Brangeon J, Sabar M, Gutierres S, Combettes B, Bove J, Gendy C, Chétrit P, Des Francs-Small CC, Pla M, Vedel F, et al. (2000) Defective splicing of the first nad4 intron is associated with lack of several complex I subunits in the Nicotiana sylvestris NMS1 nuclear mutant. Plant J 21: 269–280 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

