Microbiological efficacy of early MRSA treatment in cystic fibrosis in a randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 27852955
- PMCID: PMC5489741
- DOI: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2016-208949
Microbiological efficacy of early MRSA treatment in cystic fibrosis in a randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate microbiological effectiveness, that is, culture negativity of a non-blinded eradication protocol (Rx) compared with observation (Obs) in clinically stable cystic fibrosis participants with newly positive methicillin resistant Staphylococcusaureus (MRSA) cultures.
Design: This non-blinded trial randomised participants ages 4-45 years with first or early (≤2 positive cultures within 3 years) MRSA-positive culture without MRSA-active antibiotics within 4 weeks 1:1 to Rx or Obs. The Rx protocol was: oral trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or if sulfa-allergic, minocycline plus oral rifampin; chlorhexidine mouthwash for 2 weeks; nasal mupirocin and chlorhexidine body wipes for 5 days and environmental decontamination for 21 days. The primary end point was MRSA culture status at day 28.
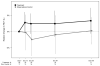
Results: Between 1 April 2011 to September 2014, 45 participants (44% female, mean age 11.5 years) were randomised (24 Rx, 21 Obs). At day 28, 82% (n=18/22) of participants in the Rx arm compared with 26% (n=5/19) in the Obs arm were MRSA-negative. Adjusted for interim monitoring, this difference was 52% (95% CI 23% to 80%, p<0.001). Limiting analyses to participants who were MRSA-positive at the screening visit, 67% (8/12) in the Rx arm and 13% (2/15) in the Obs arm were MRSA-negative at day 28, adjusted difference: 49% (95% CI 22% to 71%, p<0.001). Fifty-four per cent in the Rx arm compared with 10% participants in the Obs arm remained MRSA-negative through day 84. Mild gastrointestinal side effects were higher in the Rx arm.
Conclusions: This MRSA eradication protocol for newly acquired MRSA demonstrated microbiological efficacy with a large treatment effect.
Trial registration number: NCT01349192.
Keywords: Bacterial Infection; Cystic Fibrosis; Infection Control.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: None declared.
Figures



Comment in
-
Treatment decisions for MRSA in patients with cystic fibrosis (CF): when is enough, enough?Thorax. 2017 Apr;72(4):297-299. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2016-209605. Epub 2017 Jan 11. Thorax. 2017. PMID: 28077615 No abstract available.
References
-
- CDC. Active Bacterial Core Surveillance Report, Emerging INfections Program Network, MRSA. Secondary Active Bacterial Core Surveillance Report, Emerging INfections Program Network, MRSA. 2012 http://www.cdc.gov/abcs/reports-findings/survreports/mrsa12.pdf.
-
- Lee BY, Singh A, David MZ, et al. The economic burden of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) Clinical microbiology and infection : the official publication of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. 2013;19(6):528–36. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Knapp EA, Salsgiver E, Fink A, et al. Trends in respiratory microbiology of people with cystic fibrosis in the United States, 2006-2012. Ped Pulm. 2014;S38:282.
-
- CFF Registry CFF. Patient Registry Annual Report 2013. 2013 https://wwwcfforg/2013_CFF_Patient_Registry_Annual_Data_Reportpdf.
-
- Goss CH, Muhlebach MS. Review: Staphylococcus aureus and MRSA in cystic fibrosis. J Cyst Fibros. 2011;10(5):298–306. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000433/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001111/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK089507/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HL119073/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL113382/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI101307/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002319/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000077/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 FD003704/FD/FDA HHS/United States
- R01 HL103965/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025780/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002240/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001082/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001417/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000423/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
