Significance of Exhaled Breath Test in Clinical Diagnosis: A Special Focus on the Detection of Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 27853412
- PMCID: PMC5083779
- DOI: 10.1007/s40846-016-0164-6
Significance of Exhaled Breath Test in Clinical Diagnosis: A Special Focus on the Detection of Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
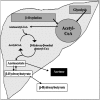
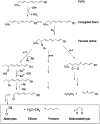
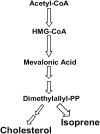
Analysis of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emanating from human exhaled breath can provide deep insight into the status of various biochemical processes in the human body. VOCs can serve as potential biomarkers of physiological and pathophysiological conditions related to several diseases. Breath VOC analysis, a noninvasive and quick biomonitoring approach, also has potential for the early detection and progress monitoring of several diseases. This paper gives an overview of the major VOCs present in human exhaled breath, possible biochemical pathways of breath VOC generation, diagnostic importance of their analysis, and analytical techniques used in the breath test. Breath analysis relating to diabetes mellitus and its characteristic breath biomarkers is focused on. Finally, some challenges and limitations of the breath test are discussed.
Keywords: Breath analysis; Breath biomarkers; Diabetes mellitus; Disease diagnosis; Noninvasive method; Volatile organic compound.
Figures
References
-
- Francesco FD, Fuoco R, Trivella MG, Ceccarini A. Breath analysis: Trends in techniques and clinical applications. Microchemical Journal. 2005;79:405–410. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2004.10.008. - DOI
-
- Kim KH, Jahan SA, Kabir E. A review of breath analysis for diagnosis of human health. Trends in Analytical Chemistry. 2012;33:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2011.09.013. - DOI
-
- Righettoni M, Amann A, Pratsinis SE. Breath analysis by nanostructured metal oxides as chemo-resistive gas sensors. Materials Today. 2015;18(3):163–171. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2014.08.017. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources