The ratio of CD8+/FOXP3 T lymphocytes infiltrating breast tissues predicts the relapse of ductal carcinoma in situ
- PMID: 27853639
- PMCID: PMC5087306
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2016.1218106
The ratio of CD8+/FOXP3 T lymphocytes infiltrating breast tissues predicts the relapse of ductal carcinoma in situ
Abstract
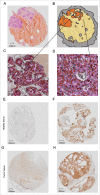
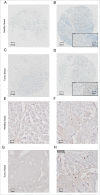
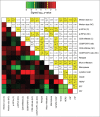
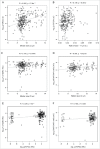
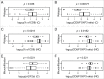
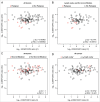
In a series of 248 tumor samples obtained from image-guided biopsies from patients diagnosed with ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast, we attempted to identify biomarkers that predict microinfiltration at definitive surgery or relapse during follow-up. For this, we used immunohistochemical methods, followed by automated image analyses, to measure the mean diameter of nuclei (which correlates with ploidy), the phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2α (eIF2α, which reflects endoplasmic reticulum stress) as well as the density and ratio of CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes and FOXP3+ regulatory T cells. The median nuclear diameter of malignant cells correlated with eIF2α phosphorylation (in cancerous tissue), which in turn correlated with the density of the CD8+ infiltrate and the CD8+/FOXP3 ratio (both in cancerous and the adjacent non-cancerous parenchyma). Neither microinfiltration nor lymph node involvement was associated with the probability of relapse. Both correlated positively with the CD8+/FOXP3 ratio in the malignant area. In contrast, relapse was associated with a paucity of the CD8+ infiltrate as well as an unfavorable CD8+/FOXP3 ratio, both in malignant and non-malignant parenchyma. The combined analysis of the CD8+/FOXP3 ratio in cancerous and non-cancerous tissues revealed a significant impact of their interaction on the probability of relapse, but not on the presence of microinfiltration or lymph node metastasis. Altogether, these results support the idea of an immunosurveillance system that determines the risk of relapse in ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast.
Keywords: Cytotoxic T cells; hyperploidy; immunogenic cell death; immunosuppressive regulatory T cells; intraductal carcinoma.
Figures
References
-
- Denkert C, Loibl S, Noske A, Roller M, Muller BM, Komor M, Budczies J, Darb-Esfahani S, Kronenwett R, Hanusch C et al.. Tumor-associated lymphocytes as an independent predictor of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28:105-13; PMID:19917869; http://dx.doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2009.23.7370 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Denkert C, von Minckwitz G, Brase JC, Sinn BV, Gade S, Kronenwett R, Pfitzner BM, Salat C, Loi S, Schmitt WD et al.. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with or without carboplatin in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive and triple-negative primary breast cancers. J Clin Oncol 2015; 33:983-91; PMID:25534375; http://dx.doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2014.58.1967 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dieci MV, Mathieu MC, Guarneri V, Conte P, Delaloge S, Andre F, Goubar A. Prognostic and predictive value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in two phase III randomized adjuvant breast cancer trials. Ann Oncol 2015; 26:1698-704; PMID:25995301; http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdv239 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dieci MV, Criscitiello C, Goubar A, Viale G, Conte P, Guarneri V, Ficarra G, Mathieu MC, Delaloge S, Curigliano G et al.. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes on residual disease after primary chemotherapy for triple-negative breast cancer: a retrospective multicenter study. Ann Oncol 2015; 26:1518; PMID:26109735; http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdv239 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kroemer G, Senovilla L, Galluzzi L, Andre F, Zitvogel L. Natural and therapy-induced immunosurveillance in breast cancer. Nat Med 2015; 21:1128-38; PMID:26444637; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nm.3944 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
