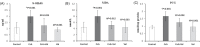The effects of valsartan on renal glutathione peroxidase expression in alleviation of cyclosporine nephrotoxicity in rats
- PMID: 27853675
- PMCID: PMC5108984
- DOI: 10.15171/bi.2016.18
The effects of valsartan on renal glutathione peroxidase expression in alleviation of cyclosporine nephrotoxicity in rats
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note: The effects of valsartan on renal glutathione peroxidase expression in alleviation of cyclosporine nephrotoxicity in rats.Bioimpacts. 2016;6(4):249. doi: 10.15171/bi.2016.31. Epub 2016 Dec 30. Bioimpacts. 2016. PMID: 28265540 Free PMC article.
Abstract
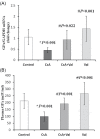
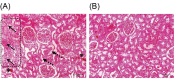
Introduction: Nephrotoxicity as a side effect caused by the immunosuppressive drug, cyclosporine-A (CsA), can be a major problem in transplant medicine. Oxidative stress may play an important role in the CsA-induced nephrotoxicity. It has been shown that the antihypertensive drug, valsartan (Val), has also renoprotective effects but, its molecular mechanism is largely unknown. In the present study, it was aimed to evaluate the Val effect in the alleviation of CsA nephrotoxicity via probable renal glutathione peroxidase (GPx) upregulation and oxidative stress decrease. Methods: Thirty-two Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into four groups based on CsA and/or Val administration: group A (Control, 1 mL/kg/day of olive oil as vehicle), group B (CsA, 30 mg/kg/day), group C (CsA+Val, 30+30 mg/kg/day), and group D (Val, 30 mg/kg/day). After the administration period (six weeks), renal GPx expression was evaluated by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Plasma levels of GPx and 8-Hydroxydeoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Malondialdehyde (MDA) and protein carbonyl groups (PCG) were measured by spectrophotometer. Plasma levels of urea and creatinine were measured by an autoanalyzer. Results: CsA treatment led to the decrease in renal expression and plasma levels of GPx in comparison to other study groups. Rats received CsA were detected to have significantly (p<0.05) higher plasma 8-OHdG, MDA, PCG, urea, and creatinine levels in comparison to other groups. Plasma urea and creatinine levels were negatively correlated with renal GPx expression and positively correlated with the oxidative stress markers. Conclusion: Administration of Val may result in attenuating the nephrotoxic side effect of CsA via probable renal GPx upregulation, and subsequently oxidative stress decrease.
Keywords: Cyclosporine-A; Glutathione peroxidase; Oxidative stress; Transplantation; Valsartan.
Similar articles
-
The Effects of Valsartan on Renal Klotho Expression and Oxidative Stress in Alleviation of Cyclosporine Nephrotoxicity.Transplantation. 2017 Jun 23. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000001350. Online ahead of print. Transplantation. 2017. Retraction in: Transplantation. 2017 Jul;101(7):e230. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000001788. PMID: 28650422 Retracted.
-
Effects of Angiotensin II Receptor Blockade on Soluble Klotho and Oxidative Stress in Calcineurin Inhibitor Nephrotoxicity in Rats.Iran J Kidney Dis. 2016 Nov;10(6):358-363. Iran J Kidney Dis. 2016. PMID: 27903993
-
Comparison of the effects of vitamin E and/or quercetin in attenuating chronic cyclosporine A-induced nephrotoxicity in male rats.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007 Aug;34(8):720-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2007.04623.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17600547
-
Attenuation of cyclosporine-induced renal dysfunction by catechin: possible antioxidant mechanism.Ren Fail. 2003 Sep;25(5):691-707. doi: 10.1081/jdi-120024285. Ren Fail. 2003. PMID: 14575278
-
Amelioration of cyclosporine nephrotoxicity by irbesartan, A selective AT1 receptor antagonist.Ren Fail. 2004 Sep;26(5):467-77. doi: 10.1081/jdi-200031731. Ren Fail. 2004. PMID: 15526904
Cited by
-
Therapeutic effect of valsartan against doxorubicin-induced renal toxicity in rats.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019 Mar;22(3):251-254. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2019.32871.7851. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31156784 Free PMC article.
-
Retraction Note: The effects of valsartan on renal glutathione peroxidase expression in alleviation of cyclosporine nephrotoxicity in rats.Bioimpacts. 2016;6(4):249. doi: 10.15171/bi.2016.31. Epub 2016 Dec 30. Bioimpacts. 2016. PMID: 28265540 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xiao Z, Li C, Shan J, Luo L, Feng L, Lu J. et al. Interventions to improve chronic cyclosporine A nephrotoxicity through inhibiting renal cell apoptosis: a systematic review. Chinese Med J. 2012;126:3767–74. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources