Implementing medical teaching policy in university hospitals
- PMID: 27853908
- PMCID: PMC5579150
- DOI: 10.1007/s10459-016-9737-y
Implementing medical teaching policy in university hospitals
Abstract
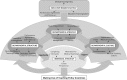
Within the unique and complex settings of university hospitals, it is difficult to implement policy initiatives aimed at developing careers in and improving the quality of academic medical teaching because of the competing domains of medical research and patient care. Factors that influence faculty in making use of teaching policy incentives have remained underexplored. Knowledge of these factors is needed to develop theory on the successful implementation of medical teaching policy in university hospitals. To explore factors that influence faculty in making use of teaching policy incentives and to develop a conceptual model for implementation of medical teaching policy in university hospitals. We used the grounded theory methodology. We applied constant comparative analysis to qualitative data obtained from 12 semi-structured interviews conducted at the Radboud University Medical Center. We used a constructivist approach, in which data and theories are co-created through interaction between the researcher and the field and its participants. We constructed a model for the implementation of medical teaching policy in university hospitals, including five factors that were perceived to promote or inhibit faculty in a university hospital to make use of teaching policy incentives: Executive Board Strategy, Departmental Strategy, Departmental Structure, Departmental Culture, and Individual Strategy. Most factors we found to affect individual teachers' strategies and their use of medical teaching policy lie at the departmental level. If an individual teacher's strategy is focused on medical teaching and a medical teaching career, and the departmental context offers support and opportunity for his/her development, this promotes faculty's use of teaching policy incentives.
Keywords: Faculty development; Grounded theory; Medical teaching policy; Organizational development; Policy implementation.
Figures
References
-
- AERA. Retrieved 11–16, 2015 from http://www.aera.net/grantsprogram/.
-
- Ajzen I. The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes. 1991;50(2):179–211. doi: 10.1016/0749-5978(91)90020-T. - DOI
-
- AMEE. Retrieved 11–16, 2015 from https://www.amee.org/awards-prizes/research-grant-award-programme.
-
- Bandura A. Social foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory. Prentice-Hall series in social learning theory. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall, Inc; 1986.
-
- Billett S. Learning through work: Workplace affordances and individual engagement. Journal of Workplace Learning. 2001
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources