A conceptual framework for understanding illegal killing of large carnivores
- PMID: 27854069
- PMCID: PMC5347529
- DOI: 10.1007/s13280-016-0852-z
A conceptual framework for understanding illegal killing of large carnivores
Abstract
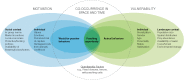
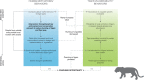
The growing complexity and global nature of wildlife poaching threaten the survival of many species worldwide and are outpacing conservation efforts. Here, we reviewed proximal and distal factors, both social and ecological, driving illegal killing or poaching of large carnivores at sites where it can potentially occur. Through this review, we developed a conceptual social-ecological system framework that ties together many of the factors influencing large carnivore poaching. Unlike most conservation action models, an important attribute of our framework is the integration of multiple factors related to both human motivations and animal vulnerability into feedbacks. We apply our framework to two case studies, tigers in Laos and wolverines in northern Sweden, to demonstrate its utility in disentangling some of the complex features of carnivore poaching that may have hindered effective responses to the current poaching crisis. Our framework offers a common platform to help guide future research on wildlife poaching feedbacks, which has hitherto been lacking, in order to effectively inform policy making and enforcement.
Keywords: Carnivores; Feedbacks; Gulo gulo; Panthera tigris; Poaching; Social–ecological systems.
Figures

References
-
- Adams L, Stephenson R. Population dynamics and harvest characteristics of wolves in the central Brooks Range, Alaska. Wildlife Monographs. 2008;170:1–25.
-
- Arias A. Understanding and managing compliance in the nature conservation context. Journal of Environmental Management. 2015;153:134–143. - PubMed
-
- Becker M, McRobb R, Watson F, Droge E, Kanyembo B, Murdoch J, Kakumbi C. Evaluating wire-snare poaching trends and the impacts of by-catch on elephants and large carnivores. Biological Conservation. 2013;158:26–36.
-
- Beirne P. For a nonspeciesist criminology: Animal abuse as an object of study. Criminology. 1999;37:117–148.
-
- Bekoff M. Ignoring nature no more: The case for compassionate conservation. Chicago: Chicago University Press; 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

