Increasing Role of Titin Mutations in Neuromuscular Disorders
- PMID: 27854229
- PMCID: PMC5123623
- DOI: 10.3233/JND-160158
Increasing Role of Titin Mutations in Neuromuscular Disorders
Abstract
The TTN gene with 363 coding exons encodes titin, a giant muscle protein spanning from the Z-disk to the M-band within the sarcomere. Mutations in the TTN gene have been associated with different genetic disorders, including hypertrophic and dilated cardiomyopathy and several skeletal muscle diseases.Before the introduction of next generation sequencing (NGS) methods, the molecular analysis of TTN has been laborious, expensive and not widely used, resulting in a limited number of mutations identified. Recent studies however, based on the use of NGS strategies, give evidence of an increasing number of rare and unique TTN variants. The interpretation of these rare variants of uncertain significance (VOUS) represents a challenge for clinicians and researchers.The main aim of this review is to describe the wide spectrum of muscle diseases caused by TTN mutations so far determined, summarizing the molecular findings as well as the clinical data, and to highlight the importance of joint efforts to respond to the challenges arising from the use of NGS. An international collaboration through a clinical and research consortium and the development of a single accessible database listing variants in the TTN gene, identified by high throughput approaches, may be the key to a better assessment of titinopathies and to systematic genotype- phenotype correlation studies.
Keywords: Childhood-juvenile onset Emery-Dreifuss-like phenotype without cardiomyopathy; Congenital centronuclear myopathy (CNM); Early-onset myopathy with fatal cardiomyopathy (EOMFC); Hereditary myopathy with early respiratory failure (HMERF); Late-onset autosomal dominant tibial muscular dystrophy (TMD); Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD); Multi-minicore disease with heart disease (MmDHD); TTN; neuromuscular disorders; titin.
Figures
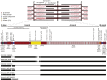

References
-
- Bang M-L, Centner T, Fornoff F, Geach AJ, Gotthardt M, McNabb M, et al. The Complete Gene Sequence of Titin, Expression of an Unusual â‰^700-kDa Titin Isoform, and Its Interaction With Obscurin Identify a Novel Z-Line to I-Band Linking System. Circulation Research. 2001;89(11):1065–72. - PubMed
-
- Linke WA, Stockmeier MR, Ivemeyer M, Hosser H, Mundel P. Characterizing titin’s I-band Ig domain region as an entropic spring. Journal of Cell Science. 1998;111(Pt 11):1567–74. - PubMed
-
- Linke WA, Kulke M, Li H, Fujita-Becker S, Neagoe C, Manstein DJ, et al. PEVK domain of titin An entropic spring with actin-binding properties. Journal of Structural Biology. 2002;137(1-2):194–205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

