Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADES) as a Tool for Bioavailability Improvement: Pharmacokinetics of Rutin Dissolved in Proline/Glycine after Oral Administration in Rats: Possible Application in Nutraceuticals
- PMID: 27854256
- PMCID: PMC6272970
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules21111531
Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADES) as a Tool for Bioavailability Improvement: Pharmacokinetics of Rutin Dissolved in Proline/Glycine after Oral Administration in Rats: Possible Application in Nutraceuticals
Abstract
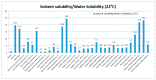
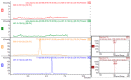
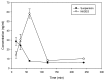
There is a need for innovation in plant-derived pharmaceuticals, food supplements and nutraceutical products regarding the use of more eco-sustainable solvents for their extraction. Furthermore, the poor oral bioavailability of several phytochemicals with health promoting effects stimulates the research in the field of pharmaceutical formulations. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADES) are formed by natural compounds, and can be considered as future solvents being especially useful for the preparation of nutraceuticals and food-grade extracts. In this paper various NADES were prepared using sugars, aminoacids and organic acids. Rutin (quercetin-3-O-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→6))-β-d-glucopyranose) was used as a model compound to study NADES. Moreover, the effect of various eutectic mixtures on rutin's water solubility was studied. Proline/glutamic acid (2:1) and proline/choline chloride (1:1) mixtures have a solubility comparable to ethanol. The proline/glutamic acid (2:1) eutectic containing rutin was used in a pharmacokinetic study in Balb/c mice while bioavailability was compared to oral dosing of water suspension. Plasmatic levels of rutin were measured by HPLC-MS/MS showing increased levels and longer period of rutin permanence in plasma of NADES treated animals. This paper reports the possible use of non-toxic NADES for pharmaceutical and nutraceutical preparations.
Keywords: HPLC-MS; NADES; pharmacokinetics; rutin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Joana Gil-Chávez G., Villa J.A., Fernando Ayala-Zavala J., Basilio Heredia J., Sepulveda D., Yahia E.M., González-Aguilar G.A. Technologies for Extraction and Production of Bioactive Compounds to be used as Nutraceuticals and Food Ingredients: An Overview. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2013;12:5–23. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12005. - DOI
-
- Paiva A., Craveiro R., Aroso I., Martins M., Reis R.L., Duarte A.R.C. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents—Solvents for the 21st Century. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014;2:1063–1071. doi: 10.1021/sc500096j. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

