N-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide (2PY)-Major Metabolite of Nicotinamide: An Update on an Old Uremic Toxin
- PMID: 27854278
- PMCID: PMC5127135
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins8110339
N-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide (2PY)-Major Metabolite of Nicotinamide: An Update on an Old Uremic Toxin
Abstract
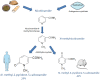
N-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide (2PY, a major metabolite of nicotinamide, NAM) was recently identified as a uremic toxin. Recent interventional trials using NAM to treat high levels of phosphorus in end-stage renal disease have highlighted new potential uremic toxicities of 2PY. In the context of uremia, the accumulation of 2PY could be harmful-perhaps by inhibiting poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 activity. Here, we review recently published data on 2PY's metabolism and toxicological profile.
Keywords: N-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide; chronic kidney disease; niacin; nicotinamide; uremic toxin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
N-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide (N-Me-2PY) has potent anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory activity in a fibrotic kidney model: is it an old uremic toxin?Clin Exp Nephrol. 2023 Nov;27(11):901-911. doi: 10.1007/s10157-023-02379-1. Epub 2023 Jul 25. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37490135
-
N-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide: a novel uremic toxin?Kidney Int Suppl. 2003 May;(84):S19-21. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.63.s84.36.x. Kidney Int Suppl. 2003. PMID: 12694300 Review.
-
Accumulation of plasma N-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide in patients with chronic renal failure.Mol Cell Biochem. 2002 Feb;231(1-2):83-8. doi: 10.1023/a:1014445329756. Mol Cell Biochem. 2002. PMID: 11952169
-
Nicotinamide metabolites accumulate in the tissues of uremic rats.J Ren Nutr. 2008 Jan;18(1):56-9. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2007.10.012. J Ren Nutr. 2008. PMID: 18089445
-
Disposition and clinical implications of protein-bound uremic toxins.Clin Sci (Lond). 2017 Jun 30;131(14):1631-1647. doi: 10.1042/CS20160191. Print 2017 Jul 15. Clin Sci (Lond). 2017. PMID: 28667064 Review.
Cited by
-
N-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide (N-Me-2PY) has potent anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory activity in a fibrotic kidney model: is it an old uremic toxin?Clin Exp Nephrol. 2023 Nov;27(11):901-911. doi: 10.1007/s10157-023-02379-1. Epub 2023 Jul 25. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37490135
-
Roles of NAD+ in Acute and Chronic Kidney Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 21;24(1):137. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010137. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex-specific hippocampal metabolic signatures at the onset of systemic inflammation with lipopolysaccharide in the APPswe/PS1dE9 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Brain Behav Immun. 2020 Jan;83:87-111. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2019.09.019. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Brain Behav Immun. 2020. PMID: 31560941 Free PMC article.
-
LC-MS-based metabolomics analysis to identify meprin-β-associated changes in kidney tissue from mice with STZ-induced type 1 diabetes and diabetic kidney injury.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019 Oct 1;317(4):F1034-F1046. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00166.2019. Epub 2019 Aug 14. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31411076 Free PMC article.
-
Defining NAD(P)(H) Catabolism.Nutrients. 2023 Jul 7;15(13):3064. doi: 10.3390/nu15133064. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37447389 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Katai K., Tanaka H., Tatsumi S., Fukunaga Y., Genjida K., Morita K., Kuboyama N., Suzuki T., Akiba T., Miyamoto K., et al. Nicotinamide inhibits sodium-dependent phosphate cotransport activity in rat small intestine. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1999;14:1195–1201. doi: 10.1093/ndt/14.5.1195. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vanholder R., De Smet R., Glorieux G., Argilés A., Baurmeister U., Brunet P., Clark W., Cohen G., De Deyn P.P., Deppisch R., et al. European Uremic Toxin Work Group (EUTox) Review on uremic toxins: Classification, concentration, and interindividual variability. Kidney Int. 2003;63:1934–1943. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00924.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

