Parenchymal and Stromal Cells Contribute to Pro-Inflammatory Myocardial Environment at Early Stages of Diabetes: Protective Role of Resveratrol
- PMID: 27854328
- PMCID: PMC5133113
- DOI: 10.3390/nu8110729
Parenchymal and Stromal Cells Contribute to Pro-Inflammatory Myocardial Environment at Early Stages of Diabetes: Protective Role of Resveratrol
Abstract
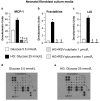
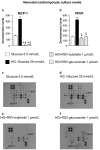
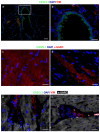
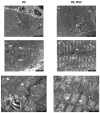
Background: Little information is currently available concerning the relative contribution of cardiac parenchymal and stromal cells in the activation of the pro-inflammatory signal cascade, at the initial stages of diabetes. Similarly, the effects of early resveratrol (RSV) treatment on the negative impact of diabetes on the different myocardial cell compartments remain to be defined. Methods: In vitro challenge of neonatal cardiomyocytes and fibroblasts to high glucose and in vivo/ex vivo experiments on a rat model of Streptozotocin-induced diabetes were used to specifically address these issues. Results: In vitro data indicated that, besides cardiomyocytes, neonatal fibroblasts contribute to generating initial changes in the myocardial environment, in terms of pro-inflammatory cytokine expression. These findings were mostly confirmed at the myocardial tissue level in diabetic rats, after three weeks of hyperglycemia. Specifically, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and Fractalkine were up-regulated and initial abnormalities in cardiomyocyte contractility occurred. At later stages of diabetes, a selective enhancement of pro-inflammatory macrophage M1 phenotype and a parallel reduction of anti-inflammatory macrophage M2 phenotype were associated with a marked disorganization of cardiomyocyte ultrastructural properties. RSV treatment inhibited pro-inflammatory cytokine production, leading to a recovery of cardiomyocyte contractile efficiency and a reduced inflammatory cell recruitment. Conclusion: Early RSV administration could inhibit the pro-inflammatory diabetic milieu sustained by different cardiac cell types.
Keywords: cardiac cell compartments; cardiomyocyte mechanics; cytokines; diabetes; intracellular calcium dynamics; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
In vivo administration of urolithin A and B prevents the occurrence of cardiac dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017 Jul 6;16(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12933-017-0561-3. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017. PMID: 28683791 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol treatment reduces cardiac progenitor cell dysfunction and prevents morpho-functional ventricular remodeling in type-1 diabetic rats.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39836. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039836. Epub 2012 Jun 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22768138 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol induces nuclear factor-κB activity in human cardiac cells.Int J Cardiol. 2013 Sep 10;167(6):2507-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2012.06.006. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Int J Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 22748497
-
Diabetes during pregnancy influences Hofbauer cells, a subtype of placental macrophages, to acquire a pro-inflammatory phenotype.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1832(12):1959-68. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.07.009. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23872577
-
Targeting the stromal microenvironment in chronic inflammation.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2006 Aug;6(4):393-400. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2006.03.007. Epub 2006 May 8. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16682252 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of histone deacetylase inhibitors in diabetic cardiomyopathy in experimental models (Review).Med Int (Lond). 2022 Aug 2;2(4):26. doi: 10.3892/mi.2022.51. eCollection 2022 Jul-Aug. Med Int (Lond). 2022. PMID: 36699507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the heart-brain axis response in COVID-19 patients: A suggestive perspective for therapeutic development.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Jun;168:105581. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105581. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 33781873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol Inhibits ROS-Promoted Activation and Glycolysis of Pancreatic Stellate Cells via Suppression of miR-21.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Apr 26;2018:1346958. doi: 10.1155/2018/1346958. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 29854071 Free PMC article.
-
Urolithin A attenuates severity of chronic pancreatitis associated with continued alcohol intake by inhibiting PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2022 Oct 1;323(4):G375-G386. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00159.2022. Epub 2022 Sep 13. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36098401 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol-Induced Downregulation of NAF-1 Enhances the Sensitivity of Pancreatic Cancer Cells to Gemcitabine via the ROS/Nrf2 Signaling Pathways.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Mar 22;2018:9482018. doi: 10.1155/2018/9482018. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 29765509 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Becher P.M., Lindner D., Fröhlich M., Savvatis K., Westermann D., Tschöpe C. Assessment of cardiac inflammation and remodeling during the development of streptozotocin-induced diabetic cardiomyopathy in vivo: A time course analysis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013;32:158–164. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

