Comprehensive renal function evaluation in patients treated for synchronous bilateral Wilms tumor
- PMID: 27856008
- PMCID: PMC5218869
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2016.10.027
Comprehensive renal function evaluation in patients treated for synchronous bilateral Wilms tumor
Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to perform a comprehensive assessment of long-term renal function in patients treated at our institution for synchronous bilateral Wilms tumor (BWT) and to determine the optimal method for estimating glomerular filtration rate (eGFR).
Methods: Surgical approach, adjuvant therapy, and pathology reports were reviewed for patients with at least six months follow-up from definitive surgery. eGFRs, as assessed by the Schwartz and Chronic Kidney Disease in Children (CKiD) formulas, were compared to measured GFR (mGFR) determined by 99mTc-DTPA scanning. Urine studies, including microalbumin, β-microglobulin, and FENa were also reviewed.
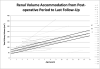
Results: Forty-two patients were identified. Of 36 living patients, 28 (77.8%) had greater than 6months follow-up, with a median overall follow-up of 5.2years (range: 1.4-13.4). The median mGFR was 97mL/min/1.73m2, while the median eGFRSchwartz and eGFRCKiD were 103.3mL/min/1.73m2 and 79.7mL/min/1.73m2, respectively, (p=0.13 and p=0.75, compared to mGFR). Eleven (39.3%) patients had at least one abnormal urine study (microalbumin >30μg/g creatinine, n=3; β-2 microglobulin >133μg/g creatinine, n=9; FENa>1%, n=4).
Conclusions: In our series, few patients had an abnormally low GFR. Neither method for estimating GFR gave a significantly different result from measured GFR, suggesting that the Schwartz equation is adequate, although specific urine tests may be more sensitive for detecting subtle renal dysfunction.
Level of evidence: Level IV - retrospective case series with no comparison group.
Keywords: Bilateral Wilms tumor; Nephron-sparing surgery; Renal function.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Dome JS, Huff V. In: Wilms Tumor Overview. Pagon RA, Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Bird TD, et al., editors. University of Washington, Seattle; GeneReviews. Seattle (WA): Dec 19, 2003. pp. 1993–2014.
-
- Breslow N, Olshan A, Beckwith JB, Green DM. Epidemiology of Wilms tumor. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1993;21(3):172–81. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz GJ, Furth S, Cole SR, Warady B, Munoz A. Glomerular filtration rate via plasma iohexol disappearance: pilot study for chronic kidney disease in children. Kidney Int. 2006 Jun;69(11):2070–7. - PubMed
-
- Work DF, Schwartz GJ. Estimating and measuring glomerular filtration rate in children. Curr Opin Nephol Hypertens. 2008 May;17(3):320–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

