Efficacy and Safety of High-Dose Ivermectin for Reducing Malaria Transmission (IVERMAL): Protocol for a Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Dose-Finding Trial in Western Kenya
- PMID: 27856406
- PMCID: PMC5133431
- DOI: 10.2196/resprot.6617
Efficacy and Safety of High-Dose Ivermectin for Reducing Malaria Transmission (IVERMAL): Protocol for a Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Dose-Finding Trial in Western Kenya
Abstract
Background: Innovative approaches are needed to complement existing tools for malaria elimination. Ivermectin is a broad spectrum antiparasitic endectocide clinically used for onchocerciasis and lymphatic filariasis control at single doses of 150 to 200 mcg/kg. It also shortens the lifespan of mosquitoes that feed on individuals recently treated with ivermectin. However, the effect after a 150 to 200 mcg/kg oral dose is short-lived (6 to 11 days). Modeling suggests higher doses, which prolong the mosquitocidal effects, are needed to make a significant contribution to malaria elimination. Ivermectin has a wide therapeutic index and previous studies have shown doses up to 2000 mcg/kg (ie, 10 times the US Food and Drug Administration approved dose) are well tolerated and safe; the highest dose used for onchocerciasis is a single dose of 800 mcg/kg.
Objective: The aim of this study is to determine the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of ivermectin doses of 0, 300, and 600 mcg/kg/day for 3 days, when provided with a standard 3-day course of the antimalarial dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine (DP), on mosquito survival.
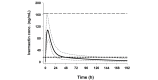
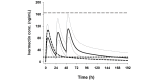
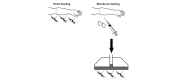
Methods: This is a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, 3-arm, dose-finding trial in adults with uncomplicated malaria. Monte Carlo simulations based on pharmacokinetic modeling were performed to determine the optimum dosing regimens to be tested. Modeling showed that a 3-day regimen of 600 mcg/kg/day achieved similar median (5 to 95 percentiles) maximum drug concentrations (Cmax) of ivermectin to a single of dose of 800 mcg/kg, while increasing the median time above the lethal concentration 50% (LC50, 16 ng/mL) from 1.9 days (1.0 to 5.7) to 6.8 (3.8 to 13.4) days. The 300 mcg/kg/day dose was chosen at 50% of the higher dose to allow evaluation of the dose response. Mosquito survival will be assessed daily up to 28 days in laboratory-reared Anopheles gambiae s.s. populations fed on patients' blood taken at days 0, 2 (Cmax), 7 (primary outcome), 10, 14, 21, and 28 after the start of treatment. Safety outcomes include QT-prolongation and mydriasis. The trial will be conducted in 6 health facilities in western Kenya and requires a sample size of 141 participants (47 per arm). Sub-studies include (1) rich pharmacokinetics and (2) direct skin versus membrane feeding assays.
Results: Recruitment started July 20, 2015. Data collection was completed July 2, 2016. Unblinding and analysis will commence once the database has been completed, cleaned, and locked.
Conclusions: High-dose ivermectin, if found to be safe and well tolerated, might offer a promising new tool for malaria elimination.
Keywords: Anopheles gambiae s.s.; Kenya; Plasmodium falciparum; clinical trial; dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine; insecticide; ivermectin; malaria; pharmacokinetics; study protocol.
©Menno R Smit, Eric Ochomo, Ghaith Aljayyoussi, Titus Kwambai, Bernard Abong'o, Nabie Bayoh, John Gimnig, Aaron Samuels, Meghna Desai, Penelope A Phillips-Howard, Simon Kariuki, Duolao Wang, Steve Ward, Feiko O ter Kuile. Originally published in JMIR Research Protocols (http://www.researchprotocols.org), 17.11.2016.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Chaccour CJ, Kobylinski KC, Bassat Q, Bousema T, Drakeley C, Alonso P, Foy BD. Ivermectin to reduce malaria transmission: a research agenda for a promising new tool for elimination. Malar J. 2013 May 07;12:153. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-12-153. http://malariajournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1475-2875-12-153 1475-2875-12-153 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- González P, González FA, Ueno K. Ivermectin in human medicine, an overview of the current status of its clinical applications. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012 May;13(6):1103–9.BSP/CPB/E-Pub/0000126 - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Onchocerciasis fact Sheet. [2016-09-06]. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs374/en/
-
- World Health Organization Lymphatic Filariasis fact Sheet. [2016-09-06]. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs102/en/
-
- World Health Organization Strongyloidiasis fact Sheet. [2016-09-06]. http://www.who.int/intestinal_worms/epidemiology/strongyloidiasis/en/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

