Parental rheumatoid arthritis and childhood epilepsy: A nationwide cohort study
- PMID: 27856781
- PMCID: PMC5206999
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003424
Parental rheumatoid arthritis and childhood epilepsy: A nationwide cohort study
Abstract
Objective: To assess the influence of parental rheumatoid arthritis (RA) on risk of epilepsy.
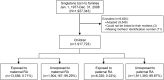
Methods: We performed a nationwide cohort study including all singletons born in Denmark from 1977 to 2008 (n = 1,917,723) through individual linkage to nationwide Danish registries. The children were followed for an average of 16 years. Main outcome measures were adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) for epilepsy with onset in early childhood (29 days-4 years), late childhood (5-15 years), adolescence/adulthood (≥15 years), and at any age until the end of follow-up (December 31, 2010).
Results: Compared to unexposed children, children exposed to maternal RA had an increased risk of early and late childhood epilepsy (adjusted HRs 1.34 [95% confidence interval (CI) 1.13-1.60] and 1.26 [95% CI 1.13-1.41]), while children exposed to maternal RA had no increased risk of epilepsy in adolescence/adulthood (HR 1.15 [95% CI 0.92-1.45]). Paternal RA was not associated with an overall risk of epilepsy in the offspring (HR 0.96 [95% CI 0.81-1.15]) or at any age. Children exposed to maternal RA in utero had a more pronounced increased risk of early childhood epilepsy than children exposed to mothers who were diagnosed with RA after childbirth (HR 1.90 [95% CI 1.26-2.86] vs HR 1.26 [95% CI 1.03-1.52], respectively [p = 0.16]).
Conclusions: Exposure to maternal RA was associated with an increased risk of childhood epilepsy, while exposure to paternal RA was not, which indicates that changes in the intrauterine environment may play a role.
© 2016 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures

Comment in
-
Maternal autoimmunity is a risk factor for common neurologic diseases of childhood.Neurology. 2016 Dec 13;87(24):2502-2503. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003440. Epub 2016 Nov 16. Neurology. 2016. PMID: 27856778 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Children Born by Women With Rheumatoid Arthritis and Increased Susceptibility for Chronic Diseases: A Nationwide Cohort Study.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2018 Aug;70(8):1192-1197. doi: 10.1002/acr.23461. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2018. PMID: 29226569
-
Parental rheumatoid arthritis and long-term child morbidity: a nationwide cohort study.Ann Rheum Dis. 2016 Oct;75(10):1831-7. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208072. Epub 2015 Dec 23. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016. PMID: 26698849 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Maternal Autoimmune Diseases With Risk of Mental Disorders in Offspring in Denmark.JAMA Netw Open. 2022 Apr 1;5(4):e227503. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.7503. JAMA Netw Open. 2022. PMID: 35426923 Free PMC article.
-
Parental Rheumatoid Arthritis and Autism Spectrum Disorders in Offspring: A Danish Nationwide Cohort Study.J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2018 Jan;57(1):28-32.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2017.10.002. Epub 2017 Oct 9. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29301665
-
School performance and psychiatric comorbidity in childhood absence epilepsy: A Danish cohort study.Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2023 Jan;42:75-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpn.2022.12.008. Epub 2022 Dec 24. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36584475 Review.
Cited by
-
Causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and epilepsy in a European population: a univariate and multivariate Mendelian randomization study.Front Immunol. 2024 May 16;15:1389549. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1389549. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38817604 Free PMC article.
-
Association between disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis and maternal and fetal outcomes in pregnant women: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023 Oct 11;23(1):724. doi: 10.1186/s12884-023-06033-2. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023. PMID: 37821885 Free PMC article.
-
The genetic link between systemic autoimmune disorders and temporal lobe epilepsy: A bioinformatics study.Epilepsia Open. 2023 Jun;8(2):509-516. doi: 10.1002/epi4.12727. Epub 2023 Mar 22. Epilepsia Open. 2023. PMID: 36929812 Free PMC article.
-
The role of inflammation in the development of epilepsy.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 May 15;15(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1192-7. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 29764485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk factors for adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with rheumatoid arthritis and follow-up of their offspring.Clin Rheumatol. 2022 Oct;41(10):3135-3141. doi: 10.1007/s10067-022-06233-9. Epub 2022 Jun 13. Clin Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35698010
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
