A synthetic pathway for the fixation of carbon dioxide in vitro
- PMID: 27856910
- PMCID: PMC5892708
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aah5237
A synthetic pathway for the fixation of carbon dioxide in vitro
Abstract
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is an important carbon feedstock for a future green economy. This requires the development of efficient strategies for its conversion into multicarbon compounds. We describe a synthetic cycle for the continuous fixation of CO2 in vitro. The crotonyl-coenzyme A (CoA)/ethylmalonyl-CoA/hydroxybutyryl-CoA (CETCH) cycle is a reaction network of 17 enzymes that converts CO2 into organic molecules at a rate of 5 nanomoles of CO2 per minute per milligram of protein. The CETCH cycle was drafted by metabolic retrosynthesis, established with enzymes originating from nine different organisms of all three domains of life, and optimized in several rounds by enzyme engineering and metabolic proofreading. The CETCH cycle adds a seventh, synthetic alternative to the six naturally evolved CO2 fixation pathways, thereby opening the way for in vitro and in vivo applications.
Copyright © 2016, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures
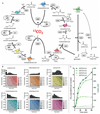
Comment in
-
Fixing carbon, unnaturally.Science. 2016 Nov 18;354(6314):830-831. doi: 10.1126/science.aal1559. Science. 2016. PMID: 27856865 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fuchs G. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2011;65:631–658. - PubMed
-
- Aresta M. In: Buncel E, editor. Greenhouse gases: Mitigation and utilization, CHEMRAWN-XVII and ICCDU-IX Conference; July 8 to 12, 2007; Kingston, ON, Canada: Queen's University; 2009. pp. 123–149.
-
- Glueck SM, Gumus S, Fabian WMF, Faber K. Chem Soc Rev. 2010;39:313–328. - PubMed
-
- Rosgaard L, de Porcellinis AJ, Jacobsen JH, Frigaard NU, Sakuragi Y. J Biotechnol. 2012;162:134–147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

