Decreased plasma miR-335 expression in patients with acute ischemic stroke and its association with calmodulin expression
- PMID: 27856935
- PMCID: PMC5536753
- DOI: 10.1177/0300060516665707
Decreased plasma miR-335 expression in patients with acute ischemic stroke and its association with calmodulin expression
Abstract
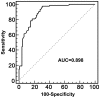
Objective To determine the expression and clinical significance of plasma miR-335 in patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) and investigate its association with calmodulin (CaM) expression. Methods Plasma miR-335 and CaM expression levels in patients with AIS and healthy controls were examined. Correlations between miR-335, CaM, and National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale scores were also analysed. Furthermore, the potential regulatory function of miR-335 on CaM expression was investigated. Results Plasma miR-335 levels were significantly lower in AIS and negatively correlated with NIHSS scores. The converse was observed for plasma CaM levels. Plasma miR-335 and CaM levels were negatively correlated. Plasma miR-335 was confirmed as a novel biomarker for AIS diagnosis and an independent predictor of AIS. Up-regulation of miR-335 suppressed CaM protein expression, and CaM was confirmed as a direct target of miR-335. Conclusions Plasma miR-335 was down-regulated in AIS patients and represents a potential noninvasive circulating biomarker.
Keywords: MicroRNA-335; acute ischemic stroke; calmodulin; diagnosis.
Figures


References
-
- Alonso de Leciñana M, Gutiérrez-Fernández M, Romano M, et al. Strategies to improve recovery in acute ischemic stroke patients: Iberoamerican stroke group consensus. Int J Stroke 2014; 9: 503–513. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin KA, McCoy SL. Making a case for acute ischemic stroke. J Pharm Pract 2010; 23: 387–397. - PubMed
-
- Adams HP, Jr., del Zoppo G, Alberts MJ, et al. Guidelines for the early management of adults with ischemic stroke: a guideline from the American heart association/American stroke association stroke council, clinical cardiology council, cardiovascular radiology and intervention council, and the atherosclerotic peripheral vascular disease and quality of care outcomes in research interdisciplinary working groups: the American academy of neurology affirms the value of this guideline as an educational tool for neurologists. Circulation 2007; 115: e478–e534. - PubMed
-
- Wang DZ, Rose JA, Honings DS, et al. Treating acute stroke patients with intravenous tPA. The OSF stroke network experience. Stroke 2000; 31: 77–81. - PubMed
-
- Katzan IL, Hammer MD, Hixson ED, et al. Utilization of intravenous tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. Arch Neurol 2004; 61: 346–350. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

