Sequence analysis of the gliding protein Gli349 in Mycoplasma mobile
- PMID: 27857551
- PMCID: PMC5036628
- DOI: 10.2142/biophysics.1.33
Sequence analysis of the gliding protein Gli349 in Mycoplasma mobile
Abstract
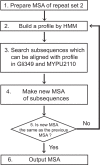
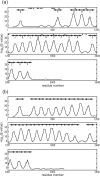
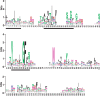
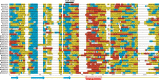
The motile mechanism of Mycoplasma mobile remains unknown but is believed to differ from any previously identified mechanism in bacteria. Gli349 of M. mobile is known to be responsible for both adhesion to glass surfaces and mobility. We therefore carried out sequence analyses of Gli349 and its homolog MYPU2110 from M. pulmonis to decipher their structures. We found that the motif "YxxxxxGF" appears 11 times in Gli349 and 16 times in MYPU2110. Further analysis of the sequences revealed that Gli349 contains 18 repeats of about 100 amino acid residues each, and MYPU2110 contains 22. No sequence homologous to any of the repeats was found in the NCBI RefSeq non-redundant sequence database, and no compatible fold structure was found among known protein structures, suggesting that the repeat found in Gli349 and MYPU2110 is novel and takes a new fold structure. Proteolysis of Gli349 using chymotrypsin revealed that cleavage positions were often located between the repeats, implying that regions connecting repeats are unstructured, flexible and exposed to the solvent. Assuming that each repeat folds into a structural domain, we constructed a model of Gli349 that fits well the shape and size of images obtained with electron microscopy.
Keywords: Gli349; Mycoplasma mobile; YGF motif; motility; repeat sequence; sequence analysis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of a 349-kilodalton protein (Gli349) responsible for cytadherence and glass binding during gliding of Mycoplasma mobile.J Bacteriol. 2004 Mar;186(5):1537-45. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.5.1537-1545.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 14973017 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a 521-kilodalton protein (Gli521) involved in force generation or force transmission for Mycoplasma mobile gliding.J Bacteriol. 2005 May;187(10):3502-10. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.10.3502-3510.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 15866938 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular shape and binding force of Mycoplasma mobile's leg protein Gli349 revealed by an AFM study.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 Jan 15;391(3):1312-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.12.023. Epub 2009 Dec 14. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. PMID: 20004642
-
Unique centipede mechanism of Mycoplasma gliding.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2010;64:519-37. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.112408.134116. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20533876 Review.
-
Prospects for the gliding mechanism of Mycoplasma mobile.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016 Feb;29:15-21. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2015.08.010. Epub 2015 Oct 21. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26500189 Review.
Cited by
-
Detailed Analyses of Stall Force Generation in Mycoplasma mobile Gliding.Biophys J. 2018 Mar 27;114(6):1411-1419. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2018.01.029. Biophys J. 2018. PMID: 29590598 Free PMC article.
-
Motility Assays of Mycoplasma mobile Under Light Microscopy.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2646:321-325. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3060-0_26. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36842126
-
Identification of a novel nucleoside triphosphatase from Mycoplasma mobile: a prime candidate motor for gliding motility.Biochem J. 2007 Apr 1;403(1):71-7. doi: 10.1042/BJ20061439. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17083328 Free PMC article.
-
Movements of Mycoplasma mobile Gliding Machinery Detected by High-Speed Atomic Force Microscopy.mBio. 2021 Jun 29;12(3):e0004021. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00040-21. Epub 2021 May 28. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34044587 Free PMC article.
-
Gliding ghosts of Mycoplasma mobile.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Sep 6;102(36):12754-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506114102. Epub 2005 Aug 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16126895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miyata M. Gliding motility of mycoplasmas — the mechanism cannot be explained by current biology. In: Blanchard A, Browning G, editors. Mycoplasmas: Pathogenesis, Molecular Biology, and Emerging Strategies for Control. Horizon Scientific Press; 2005. pp. 137–163.
-
- Fraser CM, Gocayne JD, White O, Adams MD, Clayton RA, Fleischmann RD, Bult CJ, Kerlavage AR, Sutton G, Kelley J, Fritchman RD, Weidman JF, Small KV, Sandusky M, Fuhrmann J, Nguyen D, Utterback TR, Saudek DM, Phillips CA, Merrick JM, Tomb J-F, Dougherty BA, Bott KF, Hu P-C, Lucier TS. The minimal gene complement of Mycoplasma genitalium. Science. 1995;270:397–403. - PubMed
-
- Jaffe JD, Stange-Thomann N, Smith C, DeCaprio D, Fisher S, Butler J, Calvo S, Elkins T, FitzGerald MG, Hafez N, Kodira CD, Major J, Wang S, Wilkinson J, Nicol R, Nusbaum C, Birren B, Berg HC, Church GM. The complete genome and proteome of Mycoplasma mobile. Genome Res. 2004;14:1447–1461. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
