Pressure acceleration of proteolysis: A general mechanism
- PMID: 27857573
- PMCID: PMC5036607
- DOI: 10.2142/biophysics.4.29
Pressure acceleration of proteolysis: A general mechanism
Abstract
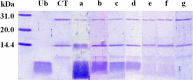
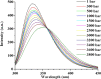
Remarkable acceleration of enzymatic proteolysis by pressure at kbar range is reported with ubiquitin as substrate and α-chymotrypsin as enzyme. The acceleration is interpreted in terms of the shift of conformational equilibrium in ubiquitin from the non-degradable folded conformer to the enzyme-degradable unfolded conformer by pressure because of the lower volume of the latter, while the enzymatic activity of α-chymotrypsin is still largely retained. This mechanism is considered generally applicable to most globular proteins and the method of pressure-accelerated proteolysis will have an enormous potential utility in systems wherever efficient removal of proteins is needed.
Keywords: pressure-enhanced proteolysis; shift of conformational equilibrium; ubiquitin; unfolded conformer; α-chymotrypsin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cold denaturation of ubiquitin at high pressure.Magn Reson Chem. 2006 Jul;44 Spec No:S108-13. doi: 10.1002/mrc.1820. Magn Reson Chem. 2006. PMID: 16826551
-
Two folded conformers of ubiquitin revealed by high-pressure NMR.Biochemistry. 2001 Nov 13;40(45):13556-63. doi: 10.1021/bi010922u. Biochemistry. 2001. PMID: 11695903
-
Basic folded and low-populated locally disordered conformers of SUMO-2 characterized by NMR spectroscopy at varying pressures.Biochemistry. 2008 Jan 8;47(1):30-9. doi: 10.1021/bi7014458. Epub 2007 Dec 15. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18081309
-
High-Pressure NMR Spectroscopy Reveals Functional Sub-states of Ubiquitin and Ubiquitin-Like Proteins.Subcell Biochem. 2015;72:199-214. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-9918-8_10. Subcell Biochem. 2015. PMID: 26174383 Review.
-
Conformational fluctuations of proteins revealed by variable pressure NMR.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Mar;1764(3):331-45. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2005.12.014. Epub 2006 Jan 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16448868 Review.
Cited by
-
Synergistic effect between polishing and high-pressure enzyme treatment for low protein rice production.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2024 Dec 18;34(2):383-390. doi: 10.1007/s10068-024-01755-1. eCollection 2025 Jan. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39944675
-
Cholinium-Based Ionic Liquids Modulate Protein Stability: A Comparative Study of Enzymes and Albumins.Molecules. 2025 Mar 31;30(7):1574. doi: 10.3390/molecules30071574. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40286162 Free PMC article.
-
Pressure-assisted dissociation and degradation of "proteinase K-resistant" fibrils prepared by seeding with scrapie-infected hamster prion protein.Prion. 2014;8(4):314-8. doi: 10.4161/pri.32081. Prion. 2014. PMID: 25482603 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taniguchi Y, Suzuki K. Pressure inactivation of alpha-chymotrypsin. J. Phys. Chem. 1983;87:5185–5193.
-
- Mozhaev VV, Lange R, Kudryashova EV, Balny C. Application of high hydrostatic pressure for increasing activity and stability of enzymes. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1996;52:320–331. - PubMed
-
- Morild E. The theory of pressure effects on enzymes. Adv. Prot. Chem. 1981;34:93–166. - PubMed
-
- Vijay-Kumar S, Bugg CE, Cook WJ. Structure of ubiquitin refined at 1.8 Å resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1987;194:531–544. - PubMed
-
- Weber PL, Brown SC, Mueller L. Sequential 1H NMR assignments and secondary structure identification of human ubiquitin. Biochemistry. 1987;26:7282–7290. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
