Modeling of the gap junction of pancreatic β-cells and the robustness of insulin secretion
- PMID: 27857584
- PMCID: PMC5036665
- DOI: 10.2142/biophysics.6.37
Modeling of the gap junction of pancreatic β-cells and the robustness of insulin secretion
Abstract
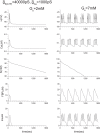
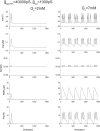
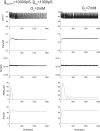
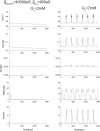
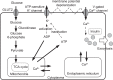
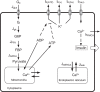
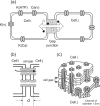
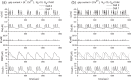
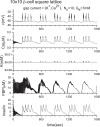
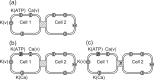
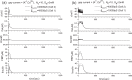
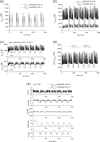
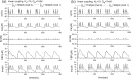
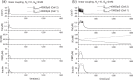
Pancreatic β-cells are interconnected by gap junctions, which allow small molecules to pass from cell to cell. In spite of the importance of the gap junctions in cellular communication, modeling studies have been limited by the complexity of the system. Here, we propose a mathematical gap junction model that properly takes into account biological functions, and apply this model to the study of the β-cell cluster. We consider both electrical and metabolic features of the system. Then, we find that when a fraction of the ATP-sensitive K+ channels are damaged, robust insulin secretion can only be achieved by gap junctions. Our finding is consistent with recent experiments conducted by Rocheleau et al. Our study also suggests that the free passage of potassium ions through gap junctions plays an important role in achieving metabolic synchronization between β-cells.
Keywords: gap junctions; pancreatic β-cells; robustness; synchronization.
Figures



References
-
- Nagano S. Modeling the model organism Dictyostelium discoideum. Develop. Growth Differ. 2000;42:541–550. - PubMed
-
- Nagano S. Diffusion-assisted aggregation and synchronization in Dictyostelium discoideum. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998;80:4826–4829.
-
- Nagano S. Biological receptor scheme for the robust synchronization of limit cycle oscillators. Prog. Theor. Phys. 2002;107:861–877.
-
- Nagano S. Receptors as a master key for synchronization of rhythms. Phys. Rev. E. 2003;67:0562151–0562154. - PubMed
-
- Yokoyama A, Nagano S. Biological receptor scheme for the external synchronization of mutually coupled oscillator systems. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2008;77:0240021–0240029.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
