Two-dimensional periodic texture of actin filaments formed upon drying
- PMID: 27857588
- PMCID: PMC5036779
- DOI: 10.2142/biophysics.7.11
Two-dimensional periodic texture of actin filaments formed upon drying
Abstract
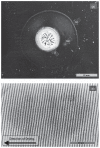
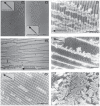
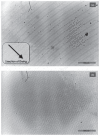
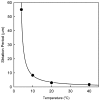
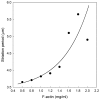
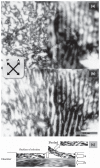
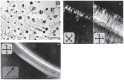
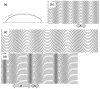
We found that a solution of actin filaments can form a periodic texture in the process of drying on a flat glass surface in the air; the periodic texture was composed of smooth meandering bundles of actin filaments. We also found that a branched salt crystal grows in the space between the meandering bundles of actin filaments. The distance between the adjacent striae (striation period) in the resulting dried two-dimensional pattern of striation decreased from about 50 to 2 μm, as the ambient temperature was increased from 4 to 40°C at 1 mg/ml actin, and showed an increasing tendency from a few to several tens μm with the increase in the initial concentration of actin filaments from 0.6 to 2.0mg/ml at room temperature. As the speed of drying is increased at a certain temperature, the striation period was also found to decrease. We propose that the formation of the two-dimensional striation pattern of bundles of actin filaments is the result of condensation of proteins due to dehydration, and suggest that the solvent flow from the center to the periphery of the sample causes the meandering of actin filaments.
Keywords: Drying of actin solution; liquid crystal; striation pattern; texturing.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Millimeter-sized belt-like pattern formation of actin filaments in solution by interacting with surface myosin in vitro.Biophys Physicobiol. 2019 Jan 9;16:1-8. doi: 10.2142/biophysico.16.0_1. eCollection 2019. Biophys Physicobiol. 2019. PMID: 30775198 Free PMC article.
-
The architecture of actin filaments and the ultrastructural location of actin-binding protein in the periphery of lung macrophages.J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):1007-20. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.1007. J Cell Biol. 1986. PMID: 3745263 Free PMC article.
-
F-actin bundles in Drosophila bristles are assembled from modules composed of short filaments.J Cell Biol. 1996 Dec;135(5):1291-308. doi: 10.1083/jcb.135.5.1291. J Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8947552 Free PMC article.
-
The filamins: properties and functions.Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;63(6):397-413. doi: 10.1139/o85-059. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1985. PMID: 3899327 Review.
-
Unravelling the structure of the lamellipodium.J Microsc. 2008 Sep;231(3):479-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.2008.02060.x. J Microsc. 2008. PMID: 18755003 Review.
Cited by
-
Millimeter-sized belt-like pattern formation of actin filaments in solution by interacting with surface myosin in vitro.Biophys Physicobiol. 2019 Jan 9;16:1-8. doi: 10.2142/biophysico.16.0_1. eCollection 2019. Biophys Physicobiol. 2019. PMID: 30775198 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oosawa F, Asakura S. Thermodynamics of the Polymerization of Protein. Academic Press; London: 1975.
-
- Newman J, Mroczka N, Schick KL. The spontaneous formation of long-range order in actin polymer networks. Macromolecules. 1989;22:1006–1008.
-
- Fujime S, Maeda T, Ishiwata S. In: Biomedical Application of Laser Light Scattering. Sattelle DB, Lee WI, Ware BR, editors. Elsevier Biomed. Press; Amsterdam: 1983. p. 251.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
