Characterization of the flagellar motor composed of functional GFP-fusion derivatives of FliG in the Na+-driven polar flagellum of Vibrio alginolyticus
- PMID: 27857593
- PMCID: PMC5036772
- DOI: 10.2142/biophysics.7.59
Characterization of the flagellar motor composed of functional GFP-fusion derivatives of FliG in the Na+-driven polar flagellum of Vibrio alginolyticus
Abstract
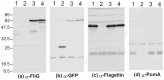
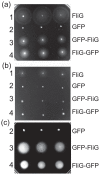
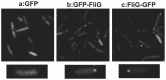
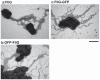
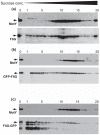
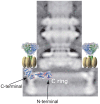
The polar flagellum of Vibrio alginolyticus is driven by sodium ion flux via a stator complex, composed of PomA and PomB, across the cell membrane. The interaction between PomA and the rotor component FliG is believed to generate torque required for flagellar rotation. Previous research reported that a GFP-fused FliG retained function in the Vibrio flagellar motor. In this study, we found that N-terminal or C-terminal fusion of GFP has different effects on both torque generation and the switching frequency of the direction of flagellar motor rotation. We could detect the GFP-fused FliG in the basal-body (rotor) fraction although its association with the basal body was less stable than that of intact FliG. Furthermore, the fusion of GFP to the C-terminus of FliG, which is believed to be directly involved in torque generation, resulted in very slow motility and prohibited the directional change of motor rotation. On the other hand, the fusion of GFP to the N-terminus of FliG conferred almost the same swimming speed as intact FliG. These results are consistent with the premise that the C-terminal domain of FliG is directly involved in torque generation and the GFP fusions are useful to analyze the functions of various domains of FliG.
Keywords: C-ring; FliG; GFP; Na+-driven; Vibrio alginolyticus; basal body; flagellar motor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mutations targeting the C-terminal domain of FliG can disrupt motor assembly in the Na(+)-driven flagella of Vibrio alginolyticus.J Mol Biol. 2011 Nov 18;414(1):62-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.09.019. Epub 2011 Oct 1. J Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21986199
-
Expression, purification and biochemical characterization of the cytoplasmic loop of PomA, a stator component of the Na(+) driven flagellar motor.Biophysics (Nagoya-shi). 2013 Feb 5;9:21-9. doi: 10.2142/biophysics.9.21. eCollection 2013. Biophysics (Nagoya-shi). 2013. PMID: 27493537 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of functional fragments of the cytoplasmic loop with the C-terminal region of PomA, a stator component of the Vibrio Na+ driven flagellar motor.J Biochem. 2014 Mar;155(3):207-16. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvt115. Epub 2014 Jan 6. J Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24398784
-
Sodium-driven motor of the polar flagellum in marine bacteria Vibrio.Genes Cells. 2011 Oct;16(10):985-99. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2011.01545.x. Epub 2011 Sep 5. Genes Cells. 2011. PMID: 21895888 Review.
-
Directional Switching Mechanism of the Bacterial Flagellar Motor.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019 Jul 31;17:1075-1081. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2019.07.020. eCollection 2019. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019. PMID: 31452860 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A novel dnaJ family gene, sflA, encodes an inhibitor of flagellation in marine Vibrio species.J Bacteriol. 2013 Feb;195(4):816-22. doi: 10.1128/JB.01850-12. Epub 2012 Dec 7. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23222726 Free PMC article.
-
The role of morphological adaptability in Vibrio cholerae's motility.mBio. 2025 Jan 8;16(1):e0246924. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02469-24. Epub 2024 Nov 29. mBio. 2025. PMID: 39611848 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kudo S, Magariyama Y, Aizawa S. Abrupt changes in flagellar rotation observed by laser dark-field microscopy. Nature. 1990;346:677–680. - PubMed
-
- Magariyama Y, Sugiyama S, Muramoto K, Maekawa Y, Kawagishi I, Imae Y, Kudo S. Very fast flagellar rotation. Nature. 1994;371:752. - PubMed
-
- Samatey FA, Matsunami H, Imada K, Nagashima S, Shaikh TR, Thomas DR, Chen JZ, Derosier DJ, Kitao A, Namba K. Structure of the bacterial flagellar hook and implication for the molecular universal joint mechanism. Nature. 2004;431:1062–1068. - PubMed
-
- Francis NR, Sosinsky GE, Thomas D, DeRosier DJ. Isolation, characterization and structure of bacterial flagellar motors containing the switch complex. J Mol Biol. 1994;235:1261–1270. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
